Current Affairs January 20, 2024: Iran-Pakistan Relations, Secularism in India, Somnath Temple, Great Indian Bustard, Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar, Pulikulam Cattle, Mahayogi Vemana
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – IR – Iran-Pakistan} Evolution of Iran-Pakistan Relations
- Context (IE): Iran and Pakistan have attacked militant bases in each other’s territory.
- The Iran-Pakistan border, known as the Goldsmith Line, stretches from a tripoint with Afghanistan to the northern Arabian Sea.

Evolution of Iran-Pakistan relations
- Iran was the first country to recognise Pakistan with diplomatic relations on 14 August 1947.
Cold War Era
- Western inclination: Both countries joined the Central Treaty Organization (CENTO) in 1955.
|
- War Cooperations: Iran provided material and weapons support to Pakistan during the 1965 and 1971 wars. Pakistan supported Iran in the Iran- Iraq war (1980s).
- Common Baloch animosity: Cooperated against Baloch separatists in Balochistan operations.
- Islamic Republic of Iran: Established after the Iranian Revolution of 1979 overthrew the Pahlavi dynasty; Pakistan was the first to recognise it.
Divergence and Divide
- Shia – Sunni divide: Ayatollah Khomeini’s ultra-conservative Shiite regime in Iran and Sunni majority Pakistan’s Islamisation under dictator Gen Zia-ul-Haq led to the divergence.
- US-Pakistan closeness: The Iranian revolution distanced the US and Iran, while the US drew Pakistan closer, generating distrust.
- Arab Nations: The export of republican ideas of the Iranian revolution irked family-governed Arab nations, while Pakistan continued close relations with Arab nations.
- Afghanistan: Iran supported the Northern Alliance against the Taliban, especially after attacks on Persian-speaking Shia Hazaras and Iranian diplomats in Mazar-i-Sharif in 1998.
Ups and downs of Reconciliation efforts
- Benazir Bhutto Government: Visit in 1995, Import of Iranian Gas, Called Pakistan ” Brother in Islam”.
- Musharraf Period: Military coup (1999) and soured relations.
- 2008-2013: Signing of Iran-Pakistan pipeline project under the Zardari government indicated improvement, but Pakistan’s Sunni Arab allies feared the Iran-led “Shi’ite triangle”.
- Post-2013, the Pakistani Sharif government came closer to Arab allies to undo the Iranian tilt.
- Strategic convergence: China has become most important strategic partner of both Iran and Pakistan.
- Occasional border issues and minority rights continue to raise concerns between both nations.
{GS2 – IR – Iran-Pakistan} Iran strikes in Iraq, Syria and Pakistan

Recent attacks on Iran
- December 2023: Police station in Iran’s Sistan Baluchestan province was attacked by the Jaish al-Adl.
- Senior adviser to Iran’s elite Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) was killed in an alleged Israeli air strike in a southern suburb of Damascus (Syria) in December 2023.
- The Islamic State-Khorasan (the Afghanistan-based branch of the Islamic State terrorist group) claimed Kerman blasts in January 2024.
Retaliatory Iranian air strikes
- It launched missiles and kamikaze drones into Erbil, the capital of Iraq’s Kurdistan.
- The IRGC claimed to have destroyed “an espionage centre” of Mossad, Israel’s external security agency.
- Iran launched missiles into Syria’s Idlib, the northwestern region controlled by jihadists and rebels.
- Iran carried out a surprise attack in Panjgur, a border town in Pakistan’s Balochistan, claiming to target the training camps of Jaish al-Adl.
Pakistan’s response
- Pakistan denounced the attack as a “blatant violation” of its airspace and UN charter.
- It has recalled the country’s Ambassador to Iran.
- Pakistan has launched retaliatory strikes, claiming to target “terrorist hideouts” in Iran’s Sistan-Baluchestan province.
{GS2 – IR – Iran-Pakistan} Jaish al-Adl
- Context (IE): Iran claimed to target the training camps of Jaish al-Adl in Pakistan’s Balochistan.
- Jaish al-Adl, the “Army of Justice”, is a Sunni Salafist militant group.
- It operates in the Baloch areas of Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.
- It is an offshoot of Jundallah – a designated Foreign Terrorist Organisation by the US.
- It aims for independence of the Sistan and Baluchestan provinces (known as Asli Balouchestan).
|
Balochs in Iran
- Ethnic groups of the Pakistani province of Balochistan and Iran’s Sistan and Baluchestan provinces.
- They speak the Balochi language with a unique cultural identity, different from ethnic Persians.
- The Sunni Baloch minority in Iran has faced religious persecution by the Shia state, especially after the Revolution of 1979.
- Moreover, Sistan and Baluchestan remain among the country’s poorest regions.
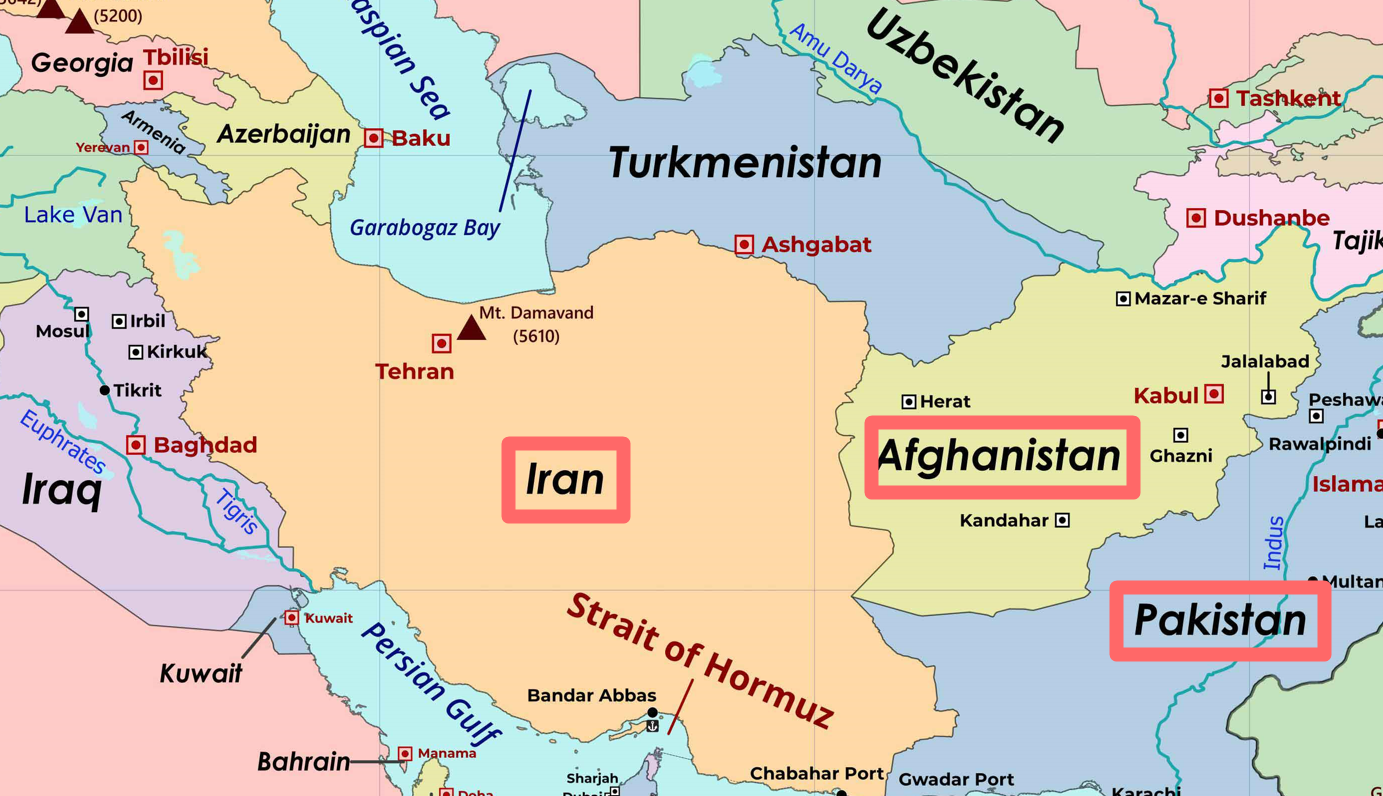
Neighbouring Countries of Iran, Pakistan and Afghanistan
- Iran: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, Turkey.
- Pakistan: Afghanistan, Iran, India. Pakistan does not border China (India’s Official Map).
- Afghanistan: China, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, India.
{GS2 – IR – Iran-Pakistan} Pakistan’s attack on Iran
- Context (IE): Pakistan targeted Iran-based hideouts of the Baloch Liberation Front (BLF) and the Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA) — both deemed as “terrorist organisations” by Pakistan.

Baloch Liberation Front (BLF)
- It was founded by Jumma Khan Marri in Damascus, Syria, in 1964.
- Carried out Baloch insurgency in Iran in 1968-73, then in Pakistan in 1973-78.
- It moved to Afghanistan in the 1980s, with a resurgence in 2004 led by Allah Nazar Baloch.
Balochistan Liberation Army (BLA)
- Founded around 2000 and began a violent struggle for Baloch self-determination in Pakistan in 2004.
- Currently led by Basheer Zeb.
Militant activities by BLF & BLA
- Attacks on Pakistan: On civilians, journalists, government officials and military in Pakistan, Balochistan and beyond.
- Attacks on Chinese personals: Both these Baloch militant groups target Chinese gas and infrastructure projects in Pakistan.
- Alleged India connection: Pakistan has alleged that India provides arms, training, and financial aid to these groups.
- Rejection by India: India and the militant groups reject such baseless claims.
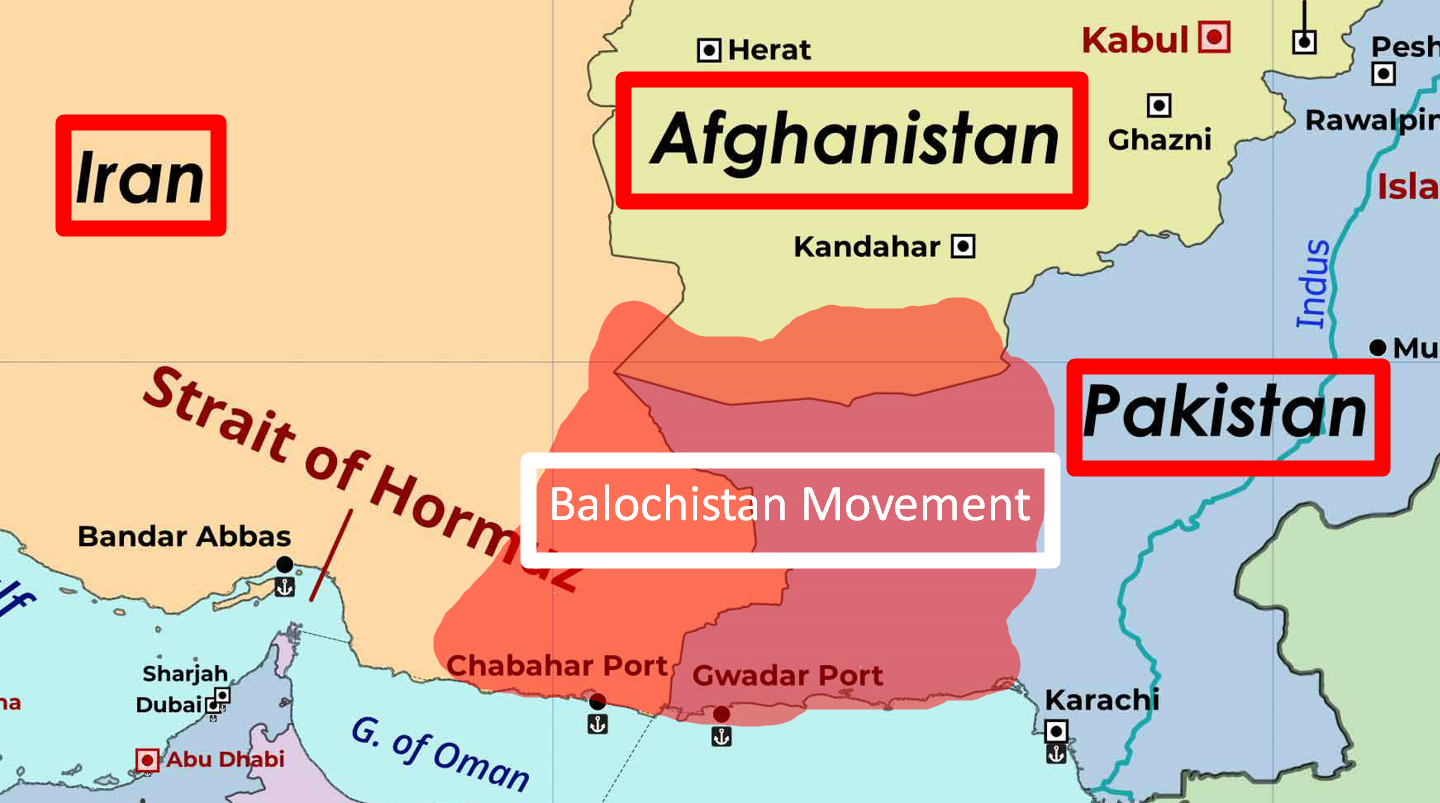
{GS2 – IR – Pakistan} Balochistan Region
- Context (IE): Pakistan-Iran air strikes highlighted the importance of the Balochistan region.
Geographical features
- Sulaiman Range lies in the East and South-East.
- Central Makran Range and the Makran Coast Range to the south divide the coastal plain from the rest of the plateau.
- Mountain Pass: Bolan pass, Khojak pass, Lak pass, Harnai pass, Gonshero pass etc.
- Rivers: Bolan, Zhob, Hingol, Nari, Porali, Kud, Dasht etc.

Balochistan Independence Movement in Pakistan
- It is spread across Pakistan’s Balochistan province, the Iranian province of Sistan-Baluchestan and the Balochistan region of southern Afghanistan.
- After the formation of Pakistan in 1947, the rulers of the Khanate of Kalat, a princely state under the British and part of today’s Balochistan, refused to join the new nation.
- Pakistan sent troops in March 1948 to annex the territory.
- The then-ruler of Kalat later signed a treaty of accession.
- Some groups continued to fight, triggering the first conflict between Balochis and the Pakistani Army.
- Unique Ethnic Identity, underdevelopment and exploitation by governments with appropriation of the region’s natural resources have led to the continued insurgency in the region.
- Political vacuum due to the ban on Baloch nationalist parties and human rights violations have led to aggravated dissent.
- Balochistan Liberation Army, Lashkar-e-Balochistan and the Balochistan Liberation United Front (BLUF) are some of the major insurgent groups.
{GS2 – Polity – IC} Secularism in India | Somnath Temple
- Context (IE): The inauguration of Ram Temple by PM Modi brought into focus the Somnath Temple, inaugurated by the President seventy three years ago and the relation between state and religion.
Secularism
- It refers to the principle of separating religion from other aspects of society, such as politics, law, education, and culture.
Constitutional Provisions Pertaining to Secularism in India
- Article 14 provides equality before the law and equal protection of laws to all citizens.
- Article 16 (1) guarantees equality of opportunity in matters of public employment and prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, and residence.
- Article 25 ensures freedom of conscience and the right to freely profess, practice, and propagate religion for all individuals.
- Article 26 grants the right to religious groups or individuals to establish and maintain institutions for religious and charitable purposes and manage their affairs in matters of religion.
- Article 27 states that the state shall not compel any citizen to pay taxes for the promotion or maintenance of any particular religion or religious institution.
- Article 28 allows educational institutions maintained by different religious groups to impart religious instruction.
- Articles 29 and 30 provide cultural and educational rights to minorities.
- Article 51A (Fundamental Duties) obliges all citizens to promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood and to value and preserve the rich heritage of India’s composite culture.
- 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976: The word ‘secular’ was inserted into the Preamble, defining it as a republic where there is equal respect for all religions.
Relationship of Religion and State: West vs. India
| Basis | West | India |
| Secular Traditions | Evolved secularism without deep historical roots. | Deeply rooted since the Indus Valley Civilization. |
| State-Religion Separation | Rigid separation with minimal state influence on religion. | “Principled distance” maintains neutrality. |
| Status of Religions | Focus on individual rights; less emphasis on communal aspects. | Equal status for all religions. |
| Freedom | Emphasis on individual freedom of religion. | Equal protection, respect, and treatment to all religions, balancing personal and community rights. |
| State Aid to Religious Institutions | No state aid | State aid to religious institutions (Article 30). |
| Public Display of Religious Symbols: | Opposition to public display of religious symbols for maintaining a secular public sphere. | Freedom to practice religion with symbols (e.g., Sikh kirpans) and recognition of religious symbols in public life. |
| Intra and Inter-Community Domination | Addresses intra-community domination. | Mitigates both intra and inter-community domination, encouraging balanced representation. |
| Religious Reform | Internal reforms within religious communities. | Secular traditions with a history of religious diversity and coexistence. |
| Plurality of Religions | Emphasizes religious diversity. | Acceptance of the plurality of religions, promoting coexistence and mutual respect. |
| Government Interaction with Religious Groups | Limited | interacts regularly |
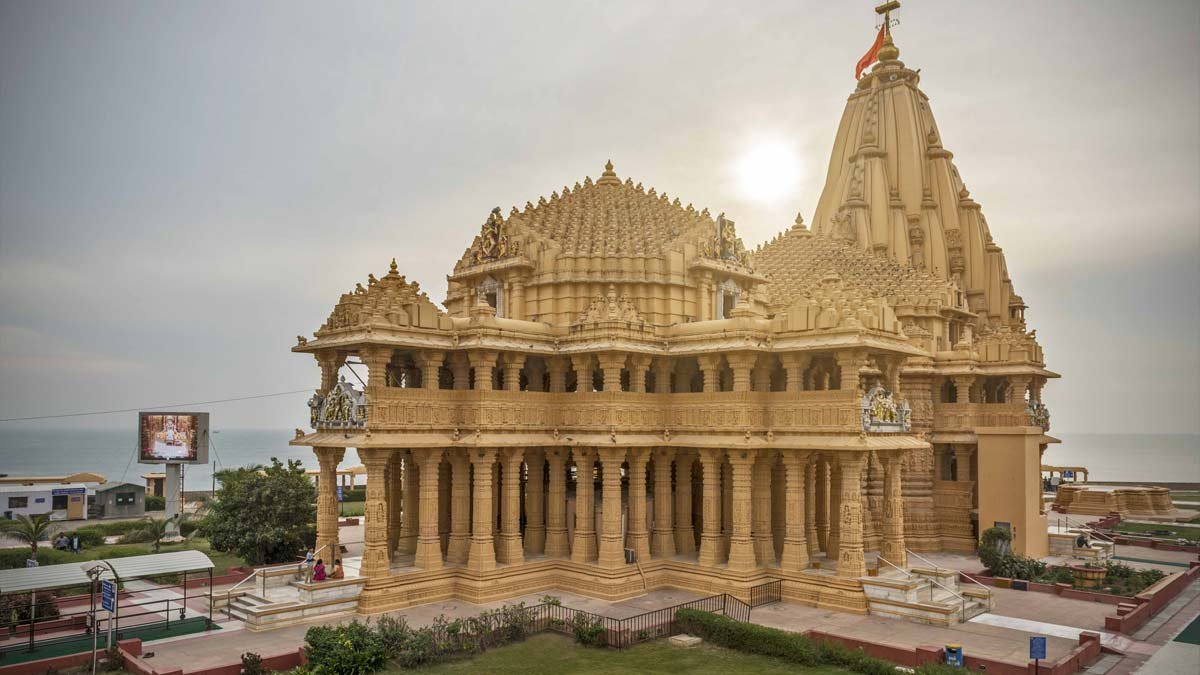
Somnath Temple
- Located in Prabhas Patan, Veraval, Gujarat, Somnath Temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva and is the first among the Twelve Jyotirlinga shrines of Lord Shiva.
- The first version of the Somnath temple was built around the 9th century CE.
- It is believed that first this holy temple was built by the Moon God with gold, by Ravana in silver, by Krishna in wood, and by Bhimdev in stone.
- Reconstructed several times in the past after repeated destruction by several Muslim invaders and Portuguese the present temple was reconstructed in Chaulukya style of Hindu temple architecture and completed in May 1951.
- The present temple is in Māru-Gurjara style (Chaulukya or Solanki style) of architecture.

{GS3 – Envi – Species} Great Indian Bustard (Ardeotis nigriceps)
- Context (TH | HT): Supreme Court seeks centre’s views on balancing the preservation of Great Indian Bustard with India’s solar energy needs.
- The Great Indian bustard is a large bird with a horizontal body and long bare legs, giving it an ostrich-like appearance.
- Endemic to the Indian subcontinent, they are one of the heaviest-flying birds in the world.
- It is considered the flagship grassland species, representing the health of the grassland ecology.
- They are the largest among the four bustard species (Houbara bustard, Lesser florican, Bengal florican & Great Indian Bustard) found in India.
- They are primarily terrestrial birds. They spend most of their time on the ground with occasional flights to travel from one place to another.
- They are diurnal birds, usually active in the early morning and evening hours.
- It is the state bird of Rajasthan.

Distribution
- They were formerly found across the Indian Subcontinent, but they are now locally extinct in 90% of its original range.
- In India, they are found scattered throughout the Indian states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka.
- They inhabit dry and semi-dry grasslands with dispersed bushes and patches of scrub.

Diet
- They are omnivores, feeding on insects, grass seeds, berries, rodents and reptiles.
- In cultivated areas, they feed on crops such as exposed groundnut, millets, & pods of legumes.
Physical features
- They can easily be distinguished by their black crown on the forehead, contrasting with the pale neck and head.
- Males have larger crowns as compared to the females.
- Males and females are distinguished by the colour of their feathers.
Threats
- Slow reproductive rate: It lays one egg every 1-2 years, and the success rate of these eggs under ideal situations is around 60-70%.
- Collision with particularly high-voltage transmission lines.
- Habitat loss/degradation due to development activities like mining, industries, wind turbines, and associated infrastructure growth.
- Noise pollution interfering with the GIB’s mating call.
- Hunting and poaching.
Conservation Status
- IUCN: Critically Endangered.
- CITES: Appendix I.
- WPA 1972: Schedule I.
Conservation Measures
- Project Great Indian Bustard announced by Rajasthan Government in 2018.
- Centres for breeding and hatching established in Jaisalmer and Kota.
- Constitution of the Bustard Task Force and the development of the National Guidelines for Recovery of Resident Bustards.
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII) launched the project “Habitat Improvement and Conservation Breeding of Great Indian Bustard: An Integrated Approach” in collaboration with MoEFCC, State Forest Departments and NGO partners.
- Objective: To build up captive population of Great Indian bustard and to release the chicks in the wild to increase the population.
- MOEFCC provides financial assistance to the States/ UTs under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme: Development of Wildlife Habitats for conservation of wildlife, including for Great Indian Bustard.
{Prelims – Awards} Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar
- Context (PIB): The President of India will confer the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar to 19 exceptional children in an award ceremony at Vigyan Bhawan.
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar (PMRBP)
- PMRBP is awarded annually by the Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD).
- The award is given for outstanding achievements in 7 categories: Bravery, Art & Culture, Environment, Innovation, Science & Technology, Social Service, and Sports.
- The age group of awardees is 5 – 18 years.
- Each awardee receives a Medal, a Certificate, and a Citation Booklet.
History
|
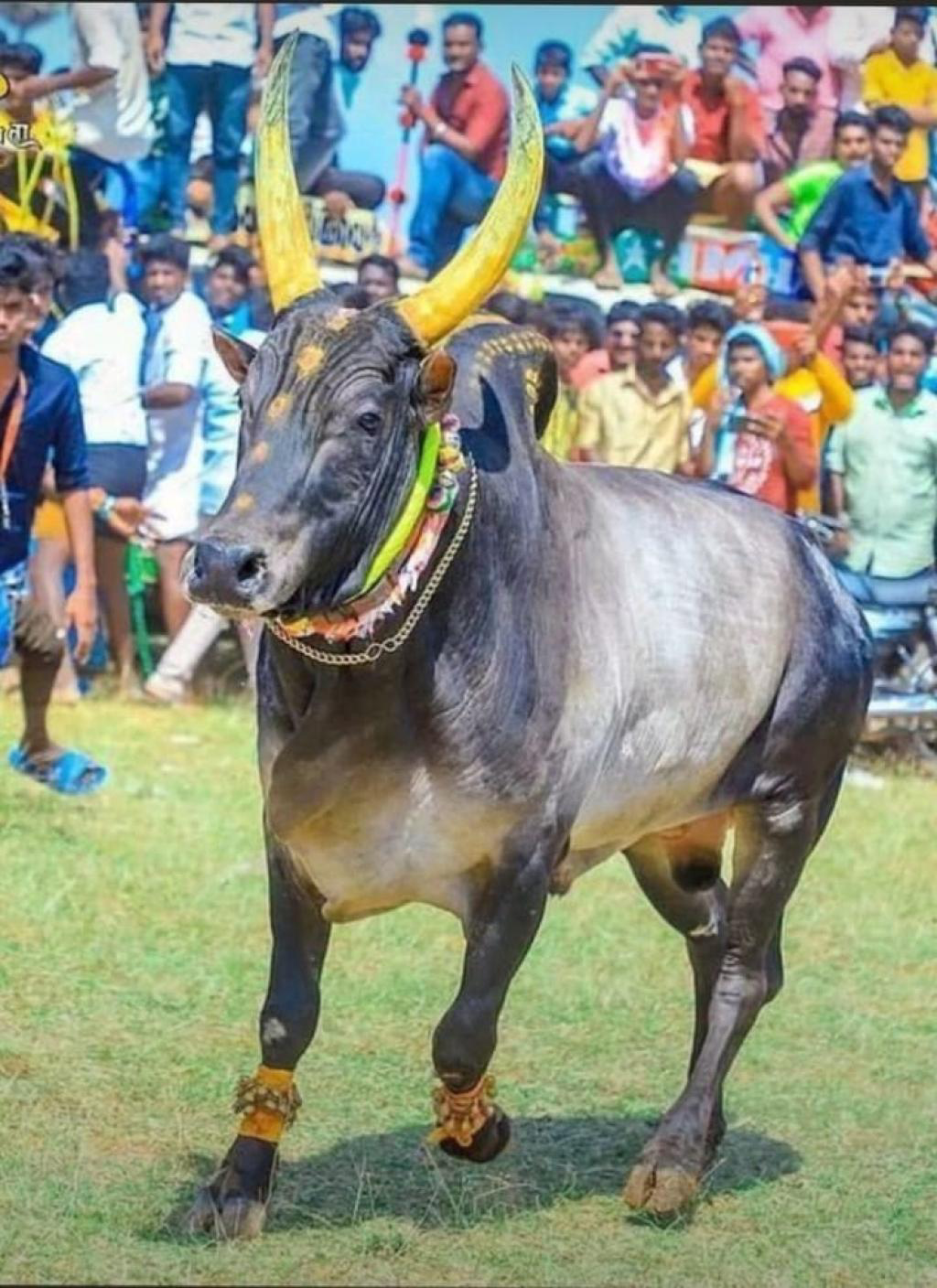
{Prelims – Envi – Species} Pulikulam Cattle
- Context (DTE): Interest in indigenous cattle breeds like the Pulikulam is reviving.
- The cattle originated from Pulikulam, a village located in Sivaganga district of Tamil Nadu.
- The Pulikulam is a popular draught and game breed of Tamil Nadu.
- Cows are poor milkers, and milk yield ranges from 0.5 to 3 kg per day with an average yield of about 1.25 kg per day.
- They are reared for draught and organic agricultural production, especially of spices.
- Pulikulam bulls faced the risk of slaughter after the jallikattu ban. With the ban lifted, there is now growing interest in indigenous breeds like the Pulikulam.

Indigenous cattle breeds
National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (NBAGR)
|
{Prelims – In News} Soil-based Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs)
- Context (IE): A team led by Northwestern University developed a new fuel cell that can harvest energy from microbes living in the soil.
- Instead of using chemicals to generate electricity, they harvest electricity from bacteria that naturally give out electrons to nearby conductors.
- These electrons flow from anode to cathode to create an electric circuit.
- It can last forever as long as there is organic carbon in the soil for the microbes to break down.
- It can potentially be used in green infrastructure and precision agriculture applications.
Fuel Cells
- A fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- It uses hydrogen and oxygen gas as fuel to generate electricity. However, there is no combustion involved.
- Fuel cells can vary from tiny devices producing only a few watts of electricity, right up to large power plants producing megawatts.
Fuel Cell Mechanism

- A fuel cell consists of a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte.
- The electrolyte enables the movement of the ions between the electrodes.
- At the anode, catalyst causes the fuel to undergo oxidation & generates +ve charged ions & electrons.
- The ions move from the anode to the cathode and the same time, the electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit, producing direct current electricity.
- At the cathode, another catalyst causes ions, electrons, & oxygen to react, forming water as by-product.
- The reaction rate of this electrochemical reaction is quite low.
- Catalysts such as platinum or palladium or gold are used to speed up the reaction.
{Prelims – PIN} Mahayogi Vemana
- Context (PIB): PM paid tributes to Mahayogi Vemana on the occasion of Vemana Jayanti.
- He lived in 17th century CE.
- Vemana was born in Gandikota, Kadapa district of Rayalaseema region in Andhra Pradesh.
- Yogi Vemana was an Achala yogi, Philosopher, social reformer and poet of the Telugu language.

Poems of Yogi Vimana
- Vemana’s poems are categorised into social, moral, satirical and mystic nature.
- His poems are treated as the best morals by the Telugu ancestors.
- His poems were preserved by people on palm leaves or orally (vocal).
- His poems were published as a book (shatakam) by Charles Philip Brown, ICS, two times in 1829 and 1839.
- He had a friend called Abhirama. Abhirama’s guru taught Vemana moksha.
- Most of his poems end with the signature line of “Vishwadaabhi Rama vinura Vema” (Hey! Abhirama listen Vemana)
Social Work
- He travelled extensively to spread his message of social change, moral values, and eradication of social evils.
- He was a radical reformer who resisted all social and religious blind beliefs and harmful traditions and practices through his poems.
- He condemned idol worship, social inequality, irrespective of caste, creed or religion.
- He had to face the wrath of orthodox people who disliked his teachings and reforms.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)