Current Affairs February 23, 2024: Misuse of Interpol’s Notice System, Issues in Financial Devolution, Open Book Exam Plan, Pigeon Pea, Outcomes Budgeting, FDI in Space Sector, Human Rating of LVM3 Launch Vehicle, Paruveta Festival, Guinea Worm Disease
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – IR – International Organisations} Misuse of Interpol’s Notice System
- Context (TH): Concerns have been raised about the misuse of Interpol’s notice system, especially the issuance of blue corner notices, which are less scrutinised than their red corner notices.
- Critics argue that countries often exploit existing protocols to target political refugees and dissidents.
- Much of this outrage is directed at Russia, which has repeatedly issued notices and diffusions for the arrest of Kremlin opponents.
Major Interpol Notices

Blue Corner Notice
- A blue corner notice, also known as an enquiry notice, allows police forces in member states to share critical crime-related information, such as obtaining a person’s criminal record and location and having his or her identity verified, among others.
- For instance, in January 2020, Interpol issued a blue corner notice to help locate fugitive selfstyled godman Nithyananda.
Red Corner Notice
- A red corner notice is issued by a member state to arrest a wanted criminal through extradition or any other similar lawful action.
- Such notices are issued against persons wanted by national jurisdictions for prosecution or to serve a sentence based on an arrest warrant or a court decision.
- The country issuing the request need not be the home country of the fugitive. Interpol acts even on the request of a country where the alleged crime has been committed.
- While blue corner notices are issued prior to the filing of criminal charges, red corner notices generally follow criminal convictions.
- The concerned individual can be stopped and arrested while traveling through a member state.
- There will also be other detrimental consequences, such as the closure of bank accounts.
- However, Interpol cannot compel law enforcement authorities in any country to arrest the subject of a red corner notice as the exercise of such powers is entirely discretionary.
- In 2018, a red corner notice was issued against fugitive billionaire Nirav Modi in relation to the Punjab National Bank scam.
- However, in October 2022, Interpol rejected a second request by India to issue such a notice against Gurpatwant Singh Pannun, whom the Union Ministry of Home Affairs has listed as a terrorist.
- The agency said that India has failed to provide sufficient information to support its case and that his activities have a clear political dimension.
To learn more on Interpol, visit Interpol.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Federal Structure} Issues in Financial Devolution
- Context (TH): Recently, various States, especially from south India, have claimed that they have not been receiving their fair share compared to their contribution in tax collection as per the present scheme of financial devolution.
What is divisible pool of taxes?
- It refers to the distribution of net tax proceeds between the Union government and the States as outlined in Article 270 of the Constitution.
- Shared taxes include corporation tax, personal income tax, Central GST, and the Centre’s share of IGST.
- Apart from the share of taxes, States are also provided grants-in-aid as per the recommendation of the FC.
- Notably, cess and surcharge imposed by the Centre are not part of the divisible pool.
FC composition & Qualification
- The President of India constitutes the Finance Commission every fifth year or earlier under Article 280 of the Constitution.
- It consists of a chairman and four other members who are appointed by the President.
- The Finance Commission (Miscellaneous Provisions) Act, 1951 specifies the qualifications for the chairman and other members of the commission.
- It makes recommendations on the distribution of financial resources between the Union and the states.
- The Union government has notified the constitution of the 16th Finance Commission under the chairmanship of Dr Arvind Panagariya for making its recommendations for the period of 2026-31.
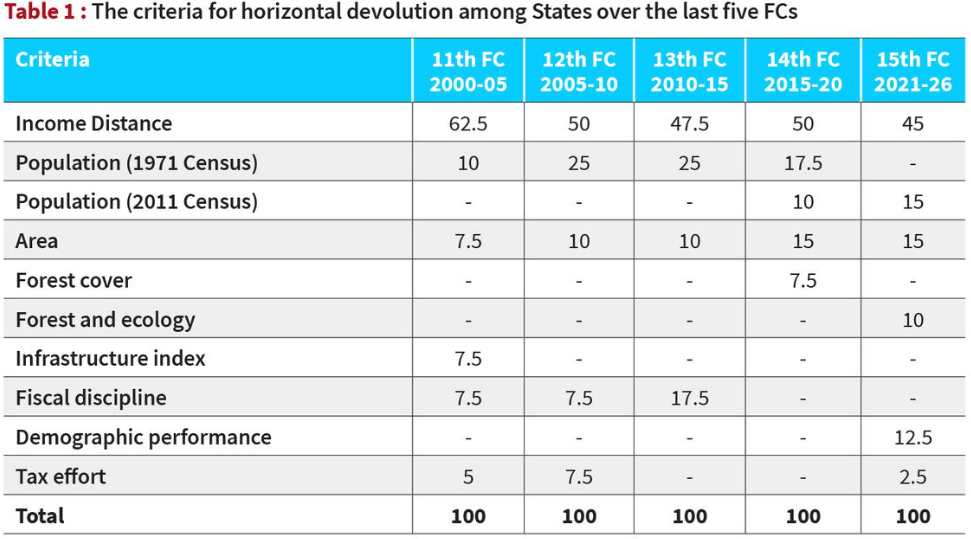
What is the basis for allocation?
- The share of States from the divisible pool (vertical devolution) stands at 41% as per the recommendation of the 15th FC.
- The distribution among the States (horizontal devolution) is based on various criteria. (See the figure below)
What are the issues?
- Firstly, cess and surcharge, estimated at around 23% of its gross tax receipts, are not shared with the States.
- The total tax revenue for the years 2022-23 (actual), 2023-24 (revised estimates) and 2024-25 (Budget estimates) of the Union government is (₹30.5, ₹34.4, and ₹38.8 lakh crore), respectively.
- The State’s share was (₹9.5, ₹11.0, and ₹12.2 lakh crore), respectively, which constitutes around 32% of the total tax receipts of the Centre. This is way less than the 41% recommended by the 15th FC.
- Cess, like the GST compensation cess, is also used for centrally sponsored schemes that benefit the States. However, the States have no control over these components.
- Secondly, the amount each State gets back for every rupee they contribute to Central taxes shows steep variation.
- Industrially developed states received much less than a rupee for every rupee they contributed against states like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- This is because many corporations are headquartered in these state capitals, where they would remit their direct taxes, and there is a difference in GST collection among various states.

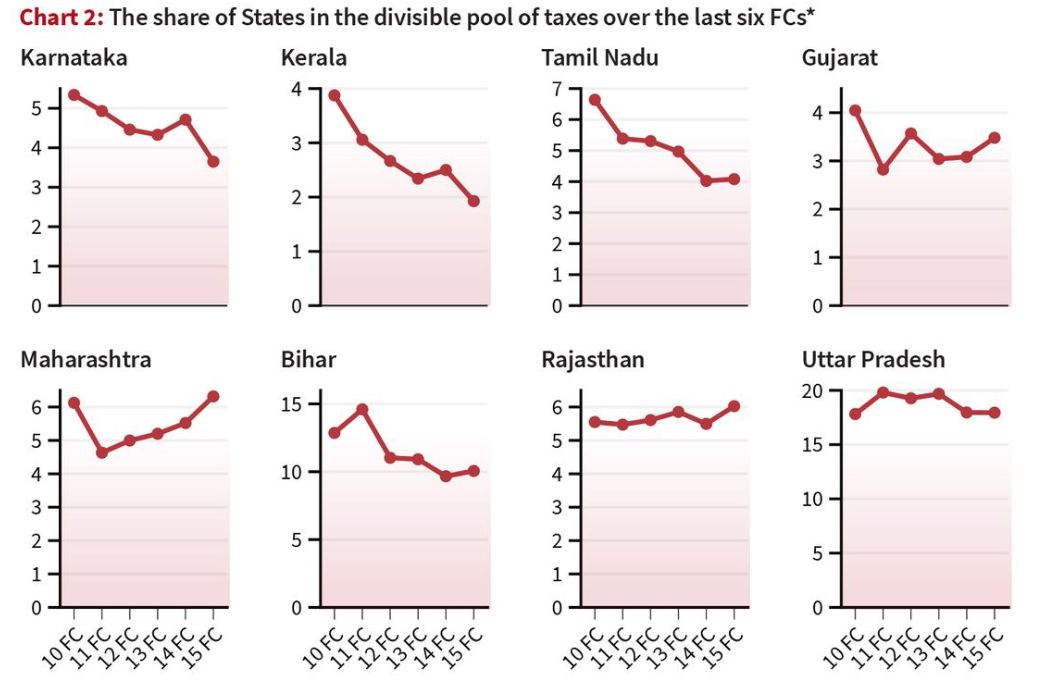
- Thirdly, the percentage share in the divisible pool of taxes has been reducing for southern States over the last six FCs.
- This is due to the higher weightage being given to equity (income gap) and needs (population, area, and forest) than efficiency (demographic performance and tax effort).
- Finally, grants-in-aid varies among various States.
- As per the 15th FC, there are revenue deficits, sector-specific and State-specific grants given to various States, and grants to local bodies. It is based on population and area of States.
Way forward
- It is the responsibility of all States to contribute towards the more equitable development of our country.
- However, the reforms suggested below may be considered for maintaining the balance between equity and federalism while sharing revenue.
- Suggested reforms
- The divisible pool can be enlarged by including some portion of cess and surcharge in it.
- The Centre should also gradually discontinue various cesses and surcharges it imposes by suitably rationalising the tax slabs.
- The weightage for efficiency criteria in horizontal devolution should be increased.
- Relative GST contribution from States can be included as a criterion by providing suitable weightage in future FCs.
- Like the GST council, a more formal arrangement for the participation of States in the constitution and the working of the FC should be considered.
- States generate around 40% of the revenue and bear around 60% of the expenditure. The FC and its recommendations should assess this imbalance and propose a fair sharing mechanism.
- It is also imperative that the States uphold principles of fiscal federalism by devolving adequate resources to local bodies.
{GS2 – Social Sector – Education} CBSE’s Open Book Exam Plan
- Context (IE | TH): Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has proposed a pilot study to check the feasibility of open book exams for Classes 9 to 12.
- The pilot will be held in select schools in November-December for subjects like English, Mathematics and Science for Classes 9-10, and English, Mathematics & Biology for Classes 11-12.
- CBSE has proposed this form of assessment based on the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) released last year.
What is an Open Book Exam (OBE)?
- In an open book exam (OBE), students are allowed to refer to their books and notes to answer questions.
- OBEs can be either of a restricted type or a free type.
- In a restricted open book assessment, only the study material approved by the exam-conducting authority is allowed during the exam.
- In a free type, students can bring any material they find relevant.
- Unlike a closed book exam, the test questions in OBEs are structured in a way that students have to apply concepts, instead of just copying information from the available material.
- They aim to test whether a student understands the big picture and can apply analytical skills on the concepts learnt.
Is OBE a new concept for Indian students?
- Open-book exams are not a new idea in India.
- In 2014, CBSE had introduced an Open Text Based Assessment (OBTA) to relieve the students from the burden of mugging up, and acquire skills of information processing.
- The Board, however, discontinued the practice in the 2017-18 academic year, because of its inability to cultivate “critical abilities” among students.
- In 2019, the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) allowed open book exams in engineering colleges based on the recommendation of an advisory body.
- During the pandemic, several Central universities like Delhi University, Jamia Millia Islamia, Jawaharlal Nehru University and Aligarh Muslim University conducted an open book test to assess students.
Are these exams easier?
- Contrary to popular opinion, open book assessments are not easier than the traditional form of examination.
- They are designed to test learning beyond facts and definitions.
- For teachers too, setting up questions for an open book exam can be a challenge, as, unlike a traditional exam, the questions cannot be direct.
Why has CBSE proposed the OBE now?
- The CBSE’s proposal falls in line with the larger reforms planned in the school education system.
- While there is no mention of the open book examination per se in the NEP 2020, one of the primary reforms it suggests is transition from rote memorisation to competency-based learning.
- The National Curriculum Framework for School Education highlights the need to reform the current assessment process “focused on measuring rote learning” and at its worst “creates fear.”
What does research say on OBEs?
- According to a 2021 study conducted among medical students of All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Bhubaneswar, open book exams have the benefit of being less stressful.
- As per pilot study, published in Cambridge University Press, the best advantage of open book assessment was that it was stress-free.
- A 2021 study conducted by Dhananjay Ashri for DU students stated that even though mean marks scored by the students in an OBE is higher than in a closed book exam, the university did not focus on developing the skills required for a student to crack an OBE.
{GS3 – Agri – Crops} Hike in Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)
- Context (IE): The Centre recently hiked the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane to Rs 340 per quintal (earlier Rs 315 per quintal) for Sugar Season 2024-25 (Oct-Sept).
- FRP was set at 107% higher than the A2+FL cost of sugarcane.
- The announcement is essential, particularly for Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra, the two largest sugarcane-growing states.
Sugarcane
|
{GS3 – Agri – Crops} Pigeon Pea
- Context (DTE): A new fast-breeding protocol is likely to make it easier for scientists to develop better quality varieties of Pigeon Pea at a faster rate, according to the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT).
- New protocol shortens the breeding & control over factors like photoperiod, temperature, humidity, & breeding cycle to 2–4 years while traditional Pigeon Pea breeding takes upto 13 years.

- Pigeon Pea (Arhar) is commonly known as red gram or tur.
- It is predominantly a crop of tropical areas mainly cultivated in semi-arid regions of India.
- It is a shrubby, drought-tolerant, fast-growing legume with a long tap root and a mass of fibrous roots.
- It can grow up to 4 m (13 ft) in height but is not tolerant to low temperatures or frost.
- Temperature: It can be grown with a temperature ranging from 26˚C to 30˚C in the rainy season (June to October) and 17˚C to 22˚C in the post rainy (November to March) season.
- Soil: It is successfully grown in black cotton soils, well drained with a pH ranging from 7.0-8.5.
- It is very sensitive to low radiation at pod development, therefore flowering during the monsoon and cloudy weather, leads to poor pod formation.
- It has low glycaemic index and is rich in thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B-6, folate, vitamin A, calcium, zinc, iron, magnesium and phosphorus.
- Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, MP, Maharashtra and UP are major Pigeon pea producing states in India.
{GS3 – IE – Budget} Outcome Budgeting
- Context (DTE): Need for Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) linked outcome budgeting in India.
- Prioritising SDG goals will help India tackle several emerging challenges, like the impacts of climate change, increasing inequities, and lagging human development indices.
- Timely access to sufficient financial resources is important for achieving SDG. So, it is important to have outcome-oriented budgeting in the country.
- Assam’s utilisation of Outcome-Based Strategies (OBS) aligned with SDG outcomes serves as a noteworthy example.
What is outcome-oriented budgeting?
- It is a way of planning and managing money where the focus is on achieving specific results or outcomes rather than just spending money on various activities.
- It helps ensure that resources are used efficiently to achieve the intended goals and bring about positive changes in society.
- Fundamental to understanding this type of budgeting is the difference between outputs and outcomes:
- Outputs are the goods and services that governments produce or provide.
- Outcomes are the impact or consequences of the outputs for the community. E.g, Swachh Bharat Abhiyan.
- Outputs: Construction of a specific number of toilets.
- Outcomes: Improved public health due to reduced open defecation.
- Outcomes of programmes are measured not just in terms of rupees but also in terms of physical units like kilowatts of energy or tonnes.
- Also, outcomes are expressed in terms of qualitative targets and achievements to make the technique more comprehensive.
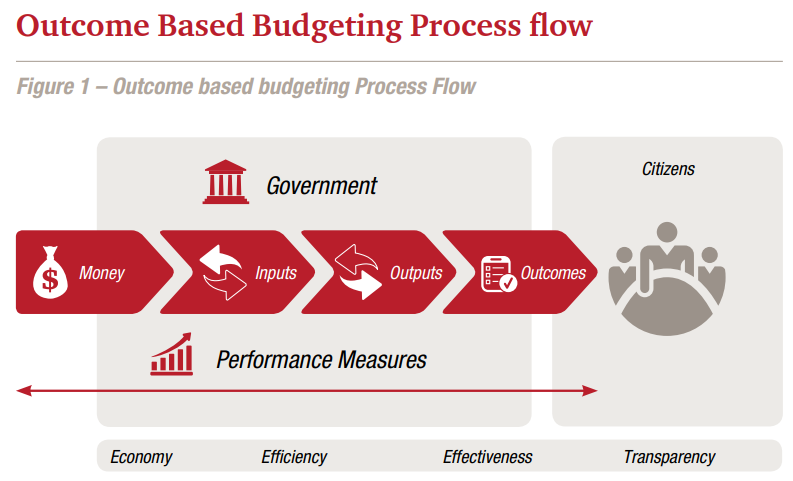
Procedure of outcome-based budgeting
- The concept of outcome budgeting was introduced in India in 2005.
- Under outcome budgeting, each Ministry presents a preliminary Outcome Budget to the Finance Ministry, which is responsible for compiling them.
- The Outcome Budget becomes a progress card on what various Ministries and Departments have done with the outlays in the previous annual budget.
- From 2007-08 onwards, the previous Performance Budget was merged with the Outcome Budget.
- Around 11 Indian states have started following the practice of formulating their OBSs in the past few years.
Significance
- Better service delivery.
- Effective Decision-making.
- Evaluation of programme performance and results.
- Communicating programme goals.
- Improving programme effectiveness.
- Make budgets cost-effective.
- Fix accountability.
- Aid better scheme management.
Challenges
- Lack of political ownership.
- Linking funds with performance may result in additional costs.
- Cultural change is required in central agencies to move from compliance-based management to outcome-based management.
- The process of identifying outcomes may become problematic.
- Unpreparedness for the enhanced accountability in government agencies.
- Poor accounting and IT systems that don’t support the reform.
{GS3 – IE – Institutions} Financial Stability and Development Council
- Context (LM | TH | IT): The 28th Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) meeting chaired by finance minister was held recently.
- The FSDC discussed various issues related to formulation of strategy for implementing the decisions of the FSDC and the Union Budget announcements.
- The FSDC has decided to implement a standardised Know Your Customer (KYC) process.
- The FSDC also deliberated on measures to counter the negative impacts of illegal lending apps that engage in charging exorbitant interest rates and employing predatory recovery practices.
- They also discussed fundraising by social enterprises through social stock exchanges.
Standardised KYC Process
- This uniform KYC approach aims to verify customers consistently across the entire financial sector.
- At present, KYC verification processes vary across most banks and financial institutions.
- The decision came shortly after the RBI took regulatory action against Paytm Payments Bank for non-compliance issues related to KYC.
- Finance Minister in her Budget speech for FY 2023-24 had proposed that the KYC process will be simplified adopting a ‘risk-based’ instead of ‘one size fits all’ approach.
Measures to counter illegal lending apps
- Over the years, fraudulent firms have mushroomed on the back of rapid growth in digital lending.
- As per the information received from MeitY, during April 2021 – July 2022, Google had reviewed approximately 3,500 to 4,000 loan apps and suspended/removed over 2,500 loan apps from its Play Store.
- RBI has shared a list of 442 unique digital lending apps used by the regulated entities with MeitY for the purpose of whitelisting and the same was shared with Google.
|
Social stock exchanges
- In the Budget speech of 2019-20, Finance Minister had proposed creation of a social stock exchange (SSE) to facilitate raising money by social enterprises and voluntary organizations.
- Following this, SEBI Board approved a framework for SSE.
- Then the Finance Ministry declared zero coupon zero principal instruments (ZCZP) as securities.
- This decision aims to assist organizations, including corporates, in utilizing funds designated for social responsibility.
- It also helps non-profit organizations access funds more transparently.
{GS3 – Infra – Initiatives} Kiru Hydel Power Project
- Context (IE): CBI conducted raids at locations linked to the former Jammu and Kashmir Governor. The investigation focuses on alleged corruption in awarding a contract for the Kiru Hydel Project in J&K’s Kishtwar district.
Kiru Hydel Power Project
- Kiru hydroelectric power project is a run-of-the-river scheme being developed over the Chenab River in the Doha district in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), India.
- The project is being developed by Chenab Valley Power Projects (CVPP) (a joint venture between National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC, 49%), Jammu & Kashmir State Power Development Corporation (JKSPDC, 49%) and Power Trading Corporation (PTC, 2%)).
- Beneficiary States: J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Rajasthan, Union territories of Chandigarh & Delhi.
|
{GS3 – S&T – Space} FDI in Space Sector
- Context (TH | LM | TOI): The Union Cabinet recently approved changes in the FDI policy for the Indian space sector.
- Under the amended FDI policy, 100% FDI is allowed in space sector to attract international players.
- Under the existing policy (before amendment), FDI in satellite establishment and operation requires government approval.
Revised Policy
-
The satellite sub-sector has been divided into three different activities.
-
FDI in Satellite manufacturing, operation, satellite data products, ground, and user segments
- The revised policy allows up to 74% FDI through the automatic route.
- Government approval is needed for FDI beyond this limit (74%) in these areas.
-
FDI in launch vehicles and associated systems or subsystems, creation of spaceports
- FDI up to 49% is permitted through the automatic route.
- Government approval is necessary for FDI beyond 49% in these activities.
- FDI in manufacturing of components and systems/sub-systems for satellites, ground and user segments
- 100% overseas investments are permitted under the automatic route.
-
Significance
- Increased private sector involvement results in job creation, adoption of modern technology, and will enhance self-reliance in the sector.
- Integration of Indian companies into global value chains.
- Supports the Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives of the Government.
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Human Rating of LVM3 Launch Vehicle
- Context (TH | IE): ISRO completed human rating of its CE20 cryogenic engine that powers the cryogenic stage of the human-rated LVM3 launch vehicle for Gaganyaan mission.
|
- The final test was carried out at the High Altitude Test Facility at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri, to simulate the flight conditions.
- The ground qualification tests involved life demonstration tests, endurance tests, and performance assessment under nominal operating conditions as well as off-nominal conditions w.r.t thrust, mixture ratio, and propellant tank pressure.
CE20 Cryogenic Engine
- The CE-20 is a cryogenic rocket engine developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), a subsidiary of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It has been developed to power the upper stage of the LVM3.
- It is the first Indian cryogenic engine to feature a gas-generator cycle.
LVM3 Launch Vehicle

- It is a three-stage vehicle with a 110 ton core liquid propellant stage (L-110) and a strap-on stage with two solid propellant motors, each with 200 tons propellant (S-200).
- The upper stage will be cryogenic fueled with a propellant loading of 25 tons (C-25).
- The LVM-3 has a lift-off mass of 640 tonnes, and it can carry a payload of up to 4,000 kilograms into geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) at 35,000km.
Gaganyaan Mission
- Gaganyaan is the 1st human space flight programme of ISRO.
- Objective: To demonstrate indigenous capability of human space flight to low earth orbit.
- Launch vehicle: GSLV-Mk III, also called the LVM-3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3).
- Payloads:
- Crew Module: It is the spacecraft carrying human beings.
- Service Module: It will support the crew module and is powered by liquid propellant engines.
- This mission consists of:
- Two unmanned missions (G1 & G2): 2nd uncrewed mission (G2) will carry “Vyommitra” (a female-looking humanoid robot developed by ISRO to function on-board the Gaganyaan).
- One manned mission (G3): The Orbital Module of the crewed mission will carry three Indian astronauts, including a woman into space for 7 days. It will orbit the Earth at a low-earth-orbit at an altitude of 300-400 km.
- Russia and France are cooperating with India for Gaganyaan mission.
{GS3 – S&T – Tech} Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy
- Context (IE): An international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
- The research could open prospects to produce a gamma-ray laser that would eventually allow researchers to look inside the atomic nucleus and have applications beyond physics.
Antimatter/Anti particle
- It is a subatomic particle identical to another subatomic particle in mass but opposite to it in electric and magnetic properties.
- All particles have a corresponding antiparticle.
- The antimatter particles corresponding to electrons, protons, and neutrons are called positrons, antiprotons, and antineutrons.
- Matter and antimatter cannot coexist at close range for more than a small fraction of a second because they collide with and annihilate each other.
- Humans have created antimatter particles using ultra-high-speed collisions at huge particle accelerators such as the Large Hadron Collider.
- Large Hadron Collider: It is located outside Geneva and operated by CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- There are also naturally produced antiparticles made sporadically throughout the universe.
Positronium
- It is a short-lived hydrogen-like atom composed of an electron and a positron (rather than an electron and a proton). Positrons are the antimatter of electrons.
- Due to its concise life, it annihilates with a half-life of 142 nanoseconds.
- Positronium can generate huge amounts of energy. It can shed light on antimatter which existed at the beginning of the Universe.
Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS)
- AEgIS is a collaboration of physicists from a number of countries in Europe and from India.
- It is an experiment approved by CERN with the goal of studying antihydrogen physics.
- The primary scientific goal of the AEgIS is the direct measurement of the Earth’s gravitational acceleration on antihydrogen.
- In 2018, AEgIS became the first in the world to demonstrate the pulsed production of antihydrogen atoms.
{Prelims – Festivals} ‘Paruveta’ Festival
- Context (TH | TOI): Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH) is making efforts to secure UNESCO ‘intangible cultural heritage’ recognition for the annual ‘Paruveta‘ festival.
- The ‘Paruveta‘ (mock hunting) festival is celebrated annually at the Sri Narasimha Swamy temple in Ahobilam, Andhra Pradesh.
- As far as the origin of the festival is concerned, it dates back to the incarnation of Lord Vishnu as Narasimha, the man-lion, in Ahobilam.
- It is a 40-day spiritual odyssey that not only showcases the depth of India’s intangible cultural heritage but also embodies the principles of a casteless society.
- During this time, the deity from the inner sanctum of the temple is carried to the 32 Chenchu tribal settlements surrounding Ahobilam.
Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage
- INTACH was founded in 1984 in New Delhi with the vision to spearhead heritage awareness and conservation in India.
- It is a non-profit charitable organisation registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- INTACH’s motto is “Dedicated to Conservation” and its mission is to protect India’s cultural and artistic legacy.
{Prelims – Sci – Bio – Diseases} Alaskapox Virus
- Context (DTE): The newly identified Alaskapox virus has recently caused its first reported death.
About Alaskapox Virus
- Alaskapox virus is a species of the Orthopoxvirus genus.
- The double-stranded-DNA virus comes from the same genus as smallpox, monkeypox & cowpox.
- It was 1st identified in an adult in Fairbanks, Alaska in 2015, and is most common in small mammals.
- Transmission: Through direct contact with skin lesions
- To date, no human-to-human transmission of the virus has been documented.
- Symptoms: Skin lesions (bumps or pustules), swollen lymph nodes and joint and/or muscle pain.
- Poxviruses infect various hosts, including insects, birds, reptiles, and mammals.
- In addition to the Alaskapox virus, some other orthopoxviruses have recently been recognised, such as the Akhmeta virus and the Abatino virus.
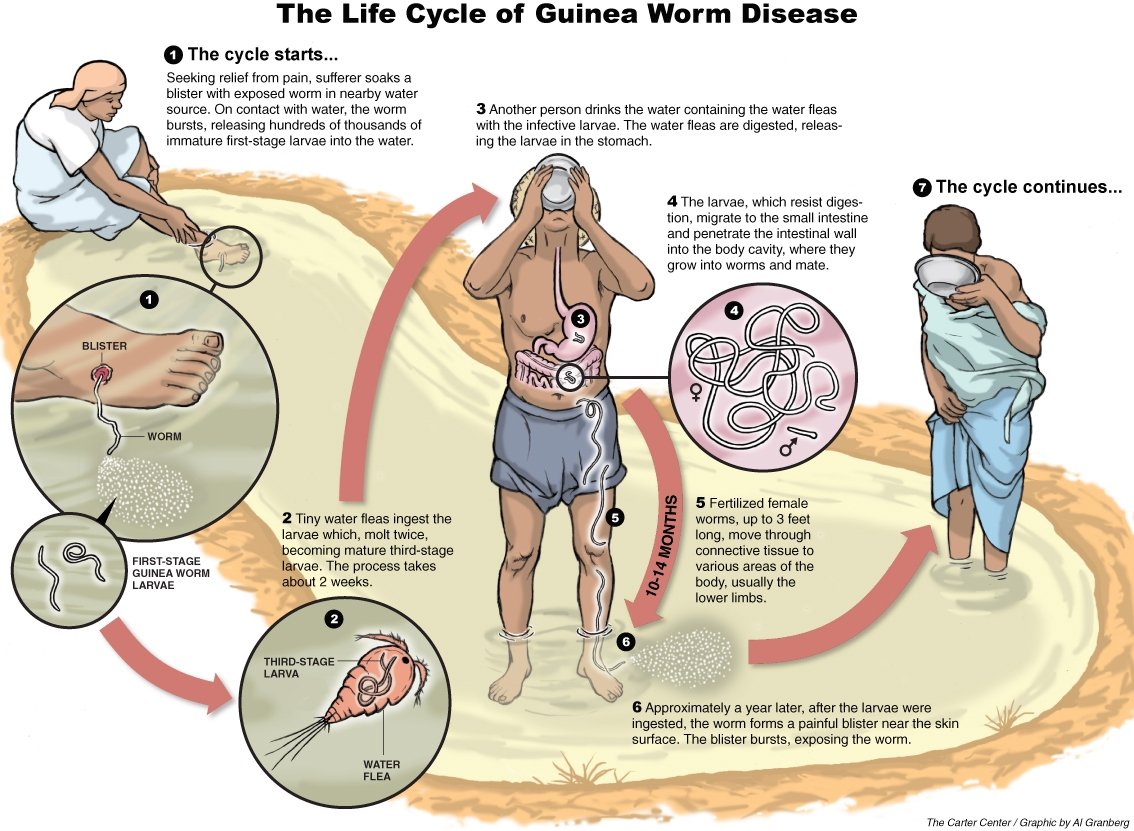
{Prelims – Sci – Bio – Diseases} Guinea Worm Disease
- Context (TH): The world is on the brink of a public health triumph as it closes in on eradicating Guinea worm disease.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of cases dwindled to 14 in 2021, 13 in 2022, and just 6 in 2023.
Guinea worm disease
- It is a neglected tropical disease (NTD) caused by the parasite Dracunculus medinensis.
- Mode of Transmission: It is contracted when people consume water contaminated with larvae of the Guinea worm.
- Symptoms: Painful blisters, usually on lower limbs.
- There is neither a drug treatment for Guinea worm disease nor a vaccine to prevent it.
{Prelims – Sci – Bio – Diseases} Progress in eliminating Kala Azar
- Context (IE): India successfully hit its target towards eliminating Kala Azar for the first time.
- India has previously missed four deadlines for Kala Azar elimination, with initial targets set for 2010, later extended to 2015, 2017, and 2020.
- In 2023, India reported 595 cases of Kala Azar nationwide, resulting in four deaths, according to the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme.
Kala-Azar or Visceral leishmaniasis
- Kala Azar is commonly referred to as “black sickness” due to the greyish or blackish discolouration of the skin during infection.
- This disease is the second-largest parasitic killer in the world (after malaria).
- It is a slow progressing indigenous disease caused by a protozoan parasite of genus Leishmania.
- In India, Leishmania donovani is the only parasite causing this disease.
- The parasite primarily infects reticuloendothelial system and may be found in abundance in bone marrow, spleen and liver.
- It is transmitted through the bites of infected female phlebotomine sandflies.
- The parasite migrates to the internal organs such as the liver, spleen (hence “visceral”), and bone marrow, and, if left untreated, will almost always result in the death of the host.
- Symptoms: Fever, weight loss, fatigue, anaemia, and substantial swelling of the liver and spleen.
- It is endemic in 75 countries across Asia, Africa and the Americas.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)