Current Affairs August 30, 2023: El Nino, La Nina, Indian Ocean Dipole, OBC Reservation, Adani Vs Hindenburg, Sickle Cell Anaemia, PRIP Scheme, PMJDY, Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary, Self Respect Marriage, GREAT Scheme, Chat GPT
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Climatology – 2023/08/30} Driest-ever August
- Context (IE | IE): August 2023 is set to go down as the driest August since 1901.
- August is normally the second rainiest month in India, after July.

Reasons Behind the Driest August
El Nino Effect

- El Nino is a climatic phenomenon of unusual warming of the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It is a part of the larger climatic phenomenon called El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- El Nino and Indian monsoon are inversely related.
- The location of low-pressure over the Western Pacific is conducive for Indian monsoon. But El Nino shifts this low pressure eastward from its normal position which reduces monsoon rainfall in India.
- The most prominent droughts in India have been El Nino droughts.
- However, not all El Nino/ENSO years led to a drought in India.
- El Nino last for 9 to 12 months, occurs every 3 to 5 years.
- 2023 is El Nino year and now its effect is becoming prominent.
|
Failure of Positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)
- IOD is defined by the difference in sea surface temperature between the Arabian Sea (western Indian Ocean) and the eastern Indian Ocean south of Indonesia.
- It has two phases: positive IOD and negative IOD.
- During positive IOD, winds over the Indian Ocean blow from east to west (from the Bay of Bengal towards the Arabian Sea). This results in the Arabian Sea becoming much warmer and the eastern Indian Ocean becoming colder and dry.
- In the negative IOD, the reverse happens.
- Positive IOD is advantageous for Indian Monsoon and results in more rainfall.
- Currently, positive IOD is going on but it is failing to compensate for El Nino.
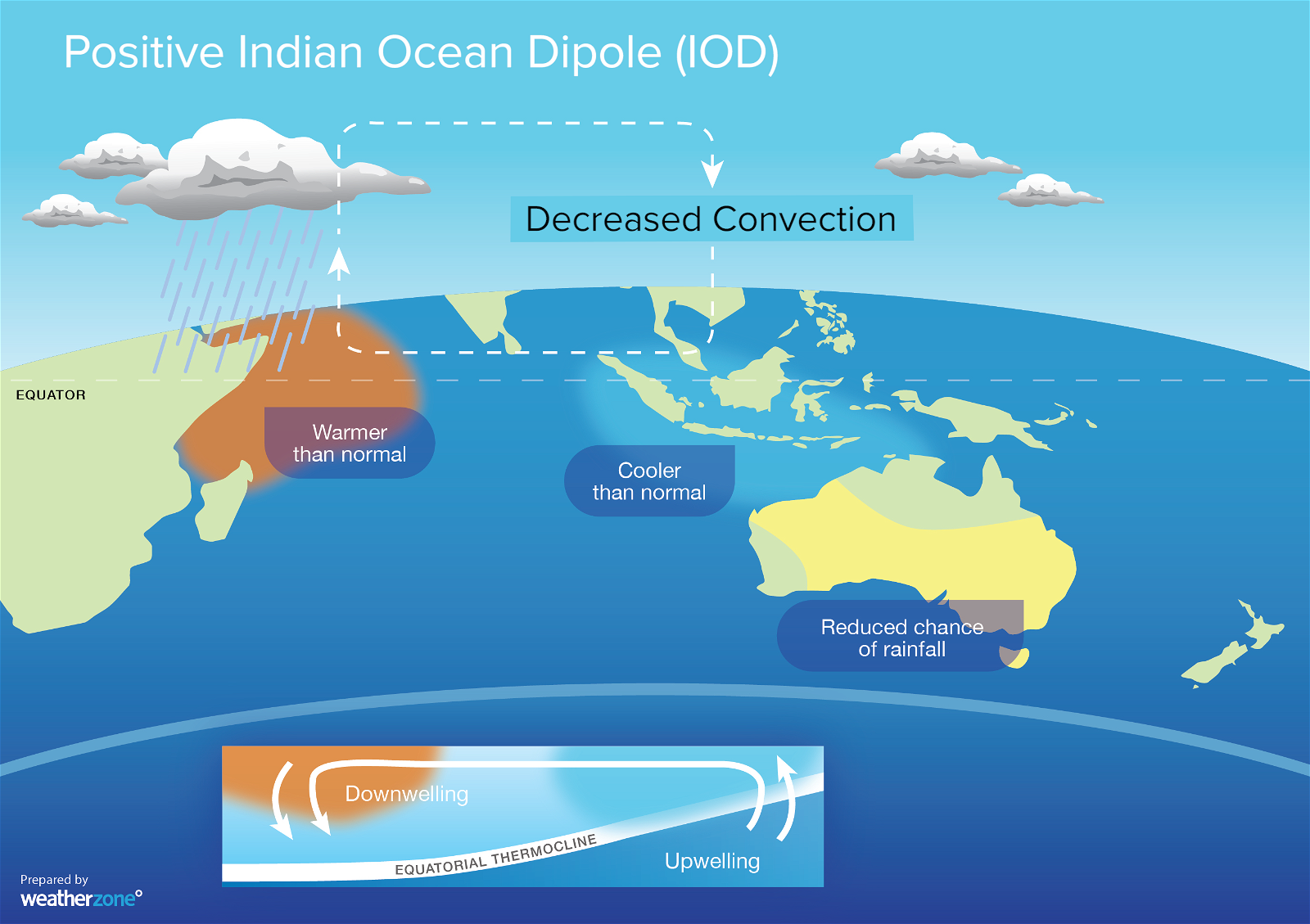
Why the Deficit Rainfall is a Cause of Concern?
- It is cause of concern because situation the El Nino effect is further going to worsen.
- Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) which measures the average SST deviation from the normal in the east-central equatorial Pacific region, has touched 1°C.
- This was twice the El Nino threshold of 0.5°C.
- This will lead to further drop in reservoir levels which is already in precarcious level in many states.
- As a result the crop cultivations (esp. upcoming rabi crops) will take a hit.
- Reduction in crop produce will lead to food inflation.

{GS1 – Geo – PG – Climatology – 2023/08/30} Pacific Decadal Oscillation
- Context (TH): Global warming and the negative phase of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) may increase the frequency of near-equatorial tropical cyclones over the North Indian Ocean.
|
- Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is a long-term ocean fluctuation of the Pacific Ocean.
- PDO waxes and wanes approximately every 20 to 30 years.
- Causes of PDO are not fully identified, but it may be due to a combination of factors including:
- Long-lasting fingerprints of El Nino and La Nina events in the tropical Pacific Ocean
- Changes in atmospheric pressure in the northern Pacific
- Impact of industrial pollution
- Natural variability
Phases of PDO
- PDO has two phases: Positive Phase and Negative Phase.
Positive Phase of PDO
- During a positive PDO phase, the eastern Pacific Ocean is warmer than average and the western Pacific Ocean is cooler than average.
- Impacts of positive phase of PDO:
- Increased storm activity in the North Pacific
- Droughts in the SW United States
- Increased precipitation in the NW United States and Canada
- El Nino-like conditions in the tropical Pacific
- Less tropical cyclones in the post-monsoon months that originate near the equator
Negative Phase of PDO
- During a negative PDO phase, the eastern Pacific Ocean is cooler than average and the western Pacific Ocean is warmer than average.
- Impacts of negative phase of PDO:
- Decreased storm activity in the North Pacific
- Wetter winters in the SW United States
- Drier summers in the NW United States and Canada
- La Nina-like conditions in the tropical Pacific
- More tropical cyclones in the post-monsoon months that originate near the equator

Comparison Between PDO and El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
|
PDO |
ENSO |
| PDO cycles last for 20 to 30 years | ENSO cycles last for 6 to 18 months |
| Two phases: Positive (Warm) and Negative (Cool) | Two phases: El Nino (Warm) and La Nina (Cool) |
| Eastern Pacific Ocean is warmer than average during Positive phase. | Eastern Pacific Ocean is warmer than average during El Nino. |
| Effects of PDO are most visible in the North Pacific/North America | Effects of ENSO are most visible in the Tropics |
| PDO can intensify or diminish the impacts of ENSO | ENSO can intensify or diminish the impacts of PDO |
| In India, El Nino with a positive PDO brings less rain, but with a negative PDO, brings more rain. | |
{GS2 – Health – Diseases – 2023/08/30} Sickle Cell Anaemia
- Context (TH): Union Minister of Tribal Affairs launched the ‘Awareness Campaign and Training of Trainers’ as a part of the Mission for Elimination of Sickle Cell Anaemia.
- In sickle cell anaemia (SCA), some red blood cells are shaped like sickles or crescent moons.
- These sickle cells also become rigid and sticky, slowing or blocking blood flow.
|
- Because of the rigid nature, the sickle cells break apart easily and die (In 10 to 20 days).
- This leads to a shortage of red blood cells (anaemia).
- Without enough red blood cells, the body can’t get enough oxygen, and this causes fatigue.
|
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
- It is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in chromosome 11 that leads to faulty haemoglobin (Haemoglobin S).
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal dominant
|
Causes
- SCA is an autosomal recessive disease.
- For a child to be affected, both mother and father must carry at least one copy of the sickle cell gene and pass both copies of the altered form to the child.
- If only one parent passes the sickle cell gene to the child, that child will have the sickle cell trait.
|
Treatment
- There’s no cure for most people with sickle cell anaemia. Treatments can relieve pain and help prevent complications associated with the disease.
Sickle Cell Elimination Programme
- It aims to eliminate sickle cell disease as a public health problem in India before 2047.
- It will cover the screening, prevention, and management of sickle cell anaemia.
- Sickle cell disease is one of the ten special problems in tribal health.
|
Objectives
- Provision of affordable and accessible care to all SCD patients
- To ensure quality of care for SCD patients
- To reduce the prevalence of SCD
Three pillars strategy
- Health promotion: Awareness generation and pre-marital genetic counselling
- Prevention: Universal screening and early detection
- Holistic Management and Care
Beneficiaries
- In its initial stage, the mission covers all tribal and other high prevalent areas States/UTs of India.
- It would subsequently expand to include the entire population from zero to 18 years of age and shall incrementally include the entire population up to 40 years in all states/UTs.
{GS2 – MoC&F – Schemes – 2023/08/30} Promotion of Research & Innovation in Pharma MedTech Sector (PRIP Scheme)
- Context (TH): The Union Cabinet approved the Promotion of Research & Innovation in Pharma-MedTech sector (PRIP) scheme with an outlay of ₹5,000 crore for five years.
- The scheme aims to shift the sector from cost-based competitiveness to innovation-based growth.
- The scheme also focuses on two components:
- Strengthening research infrastructure through Centres of Excellence (CoE) in seven existing National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs).
- Supporting R&D projects of pharmaceutical companies, startups and researchers.
- It will be implemented by the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers, under the guidance of an Empowered Committee under the chairmanship of CEO, NITI Aayog.
{GS2 – MoE – Initiatives – 2023/08/30} Let’s Move Forward
- Context (TH): NCERT, in collaboration with UNESCO, released a comic book titled “Let’s Move Forward”. It focuses on good health and wellness through stories.
- It covers diverse subjects, including emotional well-being, interpersonal relationships, gender equality, nutrition and health, substance abuse prevention, reproductive health, internet safety, etc.
{GS2 – MoF – Schemes – 2023/08/30} PMJDY
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is the National Mission for Financial Inclusion.
- It was launched in 2014 under the Ministry of Finance.
- Under it, a basic savings bank deposit (BSBD) account can be opened in any bank branch or Business Correspondent (Bank Mitra) outlet, by persons not having any other account.
Objectives
- Ensure affordable access to financial products and services. Such as:
- Availability of basic savings bank account
- Access to need-based credit
- Remittances facility
- Insurance and pension facility
- Use of technology to lower cost and widen reach.
Six pillars of PMJDY
- Universal access to banking services
- Overdraft (OD) Facility
- Financial Literacy Programme
- Creation of Credit Guarantee Fund: To provide banks with some guarantee against defaults.
- Insurance
- Pension Scheme for the Unorganised Sector
Benefits
- One basic savings account can be opened online as well as offline.
- A RuPay debit card is provided to the account holder.
- No requirement to maintain any minimum balance in these accounts.
- Interest is earned on the deposit.
- Accident Insurance Cover of Rs. One lakh (enhanced to Rs. two lakhs for new PMJDY accounts opened after 28.8.2018) is available with a RuPay card issued to the PMJDY account holders.
- PMJDY accounts are eligible for:
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY)
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY)
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
- Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency Bank (MUDRA) scheme.
- An overdraft (OD) facility up to Rs. 10,000 to eligible account holders is available.
- The account holder can get an OD of Rs. 10,000/- after six months from the opening of an account.
- There will not be any conditions attached for OD up to Rs 2,000.
- The age limit for availing OD facility is revised to 18-65 years.
- Simplified KYC / e-KYC in place of complicated KYC formalities.
Achievements
- More than 50 crore beneficiaries banked under PMJDY since inception.
- 56% of Jan-Dhan account holders are women, and 67% of Jan-Dhan accounts are in rural and semi-urban areas.
- 33.98 crore RuPay cards are issued to PMJDY account holders.
Jan Dhan Darshak (JDD) App
|
{GS2 – MoT – Schemes – 2023/08/30} GREAT scheme
- Context (BS): The GREAT scheme is an initiative by the Ministry of Textiles to support the development and commercialisation of innovative products and technologies in the field of Technical Textiles.

- Technical textiles are used for their functional properties rather than aesthetic or decorative characteristics.
- They have applications in various sectors: agriculture, health, defence, infrastructure, sports, etc.
- The GREAT scheme aims to provide a grant-in-aid of up to Rs 50 lakh for up to 18 months to individuals and companies for technical textiles products.
- The scheme also aims to provide 10 per cent of the total grant-in-aid to incubators, that will mentor and support the innovators.
National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM)
|
{GS2 – MoYAS – Initiatives – 2023/08/30} NSF Portal
- Context (PIB): The Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports launched the National Sports Federations portal, a unified online portal for the National Sports Federations (NSFs).
- It will ensure better coordination among the Department of Sports and the NSFs.
- It will be a single window system for processing the annual renewal of recognition of NSFs by the Union Sports Ministry, elections of National Sports Federations, etc.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Local Bodies – 2023/08/30} OBC Reservation in Local Bodies
- Context (TH): The Gujarat government increased reservation for the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) from 10% to 27% for elections to the panchayats and urban local bodies.
- In areas notified under the Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) (PESA) Act, the reservation for OBCs in local bodies will continue to be 10%.
- The decision is based on the recommendation of the Justice Jhaveri Commission report.
Reservation in Local bodies
Article 243D of IC: Reservation of seats (Panchayat)
- Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST): It says that seats shall be reserved for SCs and STs in every Panchayat in proportion to their population.
- Women: At least one-third of the total seats in Panchayats at all levels must be reserved for women.
- OBCs: The reservation for OBC candidates in Panchayati Raj institutions is not mandatory by law. However, some states have implemented reservations for OBCs based on their discretion.
Article 243T of IC: Reservation of seats (Municipality)
- Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST): It says that seats shall be reserved for SCs and STs in every Municipality in proportion to their population.
- Women: At least one-third of the total seats in every Municipality must be reserved for women.
- OBCs: The reservation for OBC candidates in Municipality is not mandatory by law. However, some states have implemented reservations for OBCs based on their discretion.
SC’s Triple test for OBC quota
- SC stated that caste population surveys conducted by the States are insufficient. It prescribed the triple test for providing reservations for OBCs in local bodies:
- Set up a dedicated commission to “conduct empirical inquiry into the nature and implications of the backwardness specifically concerning local bodies, within the state”.
- Specify the proportion of reservation required in the local body based on the commission’s recommendations.
- Total reservation must not exceed the aggregate of 50% of the seats.
Related Constitutional Provisions
States Where Panchayati Raj Don’t ExistArticle 243M of the IC
|
{GS2 – UCC – 2023/08/30} SC order on the validity of ‘Self-Respect’ marriages
- Context (IE I HT): SC upheld the validity of ‘Self-Respect’ marriages, a form of secular and simple weddings that do not require any priest or ritual, as per the Tamil Nadu law.
- The court said that not every valid marriage requires a public declaration and that couples may refrain for various reasons, such as familial opposition or fear for their safety.
- The court emphasised autonomy in choosing life partners and said that any interference by the state or society in this matter would violate the fundamental rights of individuals.

- SC set aside a 2014 ruling of the Madras HC, which had held that marriages performed by advocates are not valid and that ‘self-respect’ marriages cannot be solemnised in secrecy.
- The court noted that the Tamil Nadu law, which was amended in 1968 to introduce Section 7-A in the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955, was aimed at radically simplifying weddings by shunning the need for mandatory Brahmin priests, holy fire and saptapadi (seven steps).
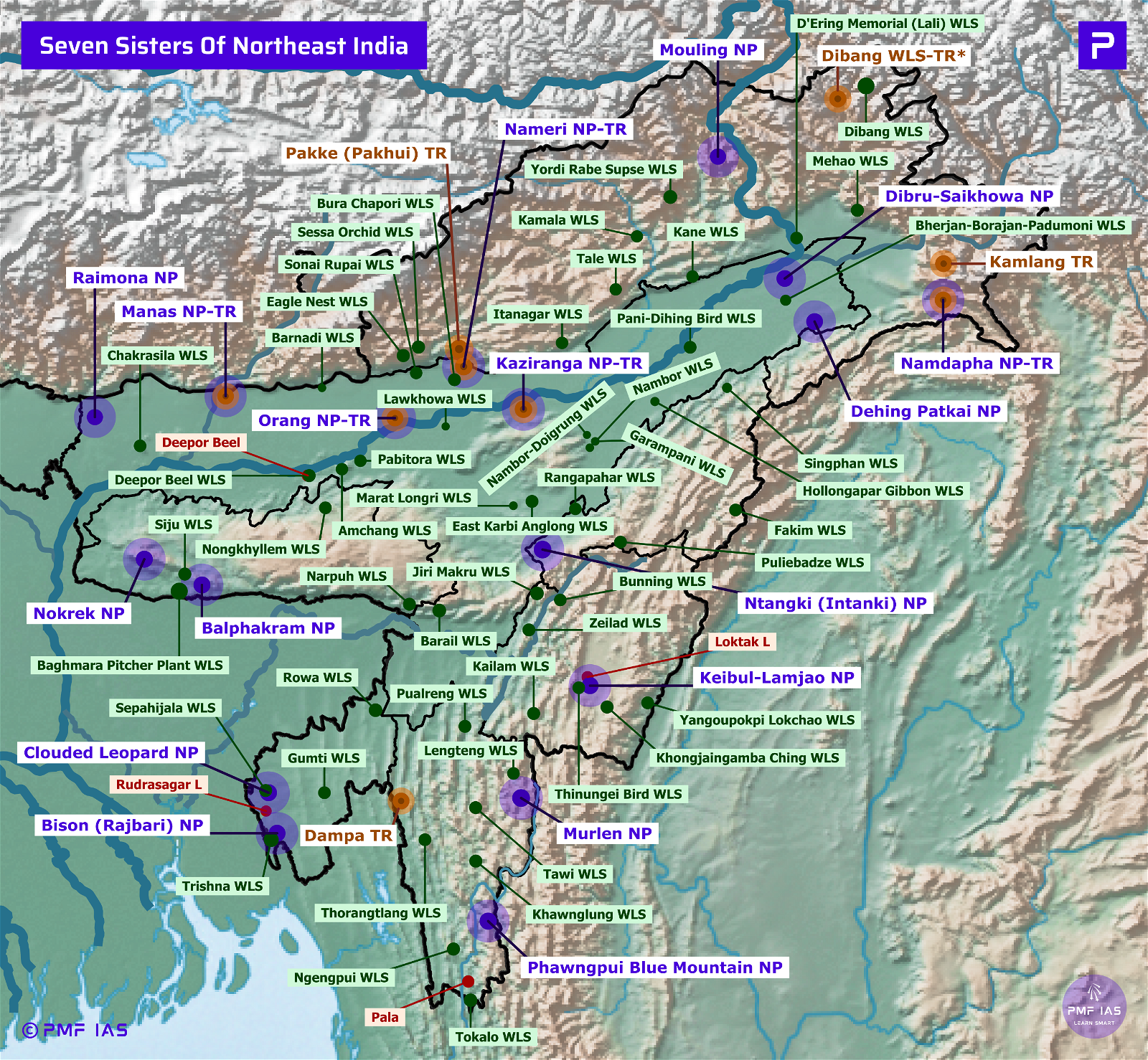
{GS3 – Envi – Conservation – 2023/08/30} Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary
- Context (TH): Rerouting of the railway track that runs through Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary is suggested in a Wildlife Institute of India (WII) Report.
- Hoollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary is an evergreen forest area located in the Jorhat district, Assam.
- It is home to the only apes in India, the western hoolock gibbon, and the North-eastern India’s only nocturnal primate, the Bengal slow loris.
- Other primate species it shelters are the Assamese macaque, the capped langur, the northern pig-tailed macaque, the rhesus macaque, and the stump-tailed macaque.
- Concern: It has become a forest island due to lost connectivity with surrounding forest patches.

Western Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock hoolock)
- Western hoolock gibbon (or white-browed gibbon) is one of the three species of hoolock gibbon (a primate). Gibbons are a family of apes and are called Lesser apes.
- Distribution: Bangladesh, India (Northeast India), and Myanmar (west of the Chindwin River).
- Habitat: This arboreal and diurnal ape resides in tropical evergreen rainforests, tropical evergreen, semi-evergreen, and mixed deciduous forests, and subtropical broadleaf hill forests.
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, and hunting.
- IUCN: EN | CITES: Appendix I | WPA: Schedule I

What is the Issue of the Railway Track?
- Gibbons are exclusively arboreal animals inhabiting the forest’s upper canopy, so, they are particularly sensitive to canopy gaps.
- The railway line has created canopy gap, resulting isolation of gibbon families on both sides.
- Concern: Isolation is compromising the gibbon population’s genetic variability.
|
Failure of Artificial Canopy Bridge
- An artificial canopy bridge is a conservation initiative for facilitating the movement of arboreal animals across life-threatening man-made structures or projects.
- An iron canopy bridge was built but it was not suitable for the gibbons to swing across the track.
- A natural canopy bridge was also grown but regular pruning by the railways during track maintenance affected the movement of the apes.
Suggestions in the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) Report
- The major suggestion of the WII Report is that since it is a small sanctuary, the railway track should be rerouted to areas outside the sanctuary.
- Other suggestions include:
- Reforestation on both sides of the existing track
- Enforcing train speed limits within the sanctuary and adjacent wildlife corridors
- Connecting the isolated sanctuary with neighbouring forests
- Setting up sustainable eco-tourism accommodations
Wildlife Institute of India (WII)
|
{GS3 – IE – Securities – 2023/08/30} Hindenburg Report And ED Investigation
- Context (IE I MINT I HT): The ED has concluded its preliminary investigation into the Hindenburg Research report that accused the Adani Group of inflating its share prices and evading taxes.
|
- In January 2023, Hindenburg Research published a report on the Adani Group, claiming they were pulling the “largest con in corporate history”.
- They also revealed that they were holding a short position on the Adani stocks, signalling their belief that the shares are overpriced and will dip in value soon.
- The report made several allegations against the Adani Group, such as overvalued shares, debt-fuelled business, promoters pledging their stocks, etc.

ED’s investigation into Hindenburg Research report
- The ED has cleared the Adani Group of any wrongdoing and said that their share prices, debt levels, management team, and business transactions are all legitimate and transparent.
- The ED has also questioned the credibility and motive of Hindenburg Research, which is a short-seller that profits from bringing down the share prices of the companies it targets.
ED’s investigation into short selling in Adani Group shares
- The ED has found that 12 FPIs and FIIs based in tax havens made huge profits from short-selling Adani Group shares before and after the Hindenburg Research report was published.
- The ED suspects that these FPIs and FIIs were acting as brokers for bigger players overseas who may have had prior knowledge of the Hindenburg report.
- The ED has summoned these FPIs and FIIs to explain their transactions and sources of funds.
Tax Haven
|
{GS3 – S&T – AI – 2023/08/30} News media vs OpenAI’s ChatGPT
- Context (TH): Group of news media organisations, including The New York Times, Reuters, CNN, and the Australian Broadcasting Corporation, shut off OpenAI’s ability to access their content.
Why OpenAI’s ChatGPT Requires Access News Media Content?
- OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an AI chatbot. AI chatbots are trained to have human-like conversations based on large language models (LLMs).
- LLMs are AI systems that use deep learning algorithms to generate human-like text.
- These models consume massive volumes of digital text from internet sources such as articles, news reports, and social media posts.
- These digital texts are used to train AI chatbots that predicts and produces content from scratch based on prompts and queries.
|
Why the Faceoff has Started?
- Tech companies that work on LLMs like Google, Meta, or Open AI use software called ‘web crawlers’ to scan web pages and collect the dataset required for training their LLMs.
- Now, OpenAI is simply collecting publicly available data and use it for the company’s own purposes.
- It is providing no benefit, monetary or otherwise, to news companies.
- Due to this reason media groups have blocked GPTbot.
- In the future there will be more legal battles for tech companies working on LLMs on grouns of copyright infringement and intellectual property rights (IPR).
Web Crawler Software
|
Search Engines and New Media
|
{Prelims – Mapping – PAN – NP – 2023/08/30} First Women Director of Kaziranga NP & TR
- Context (TH): IFS officer Sonali Ghosh would become the first woman field director of the Kaziranga National Park.
- Kaziranga NP is located in the Golaghat, Nagaon, and Karbi Anglong districts of Assam.
- It lies in the Eastern Himalayan biodiversity hotspot and the Brahmaputra flows through the park.
- This park which hosts 2/3rd of the world’s one-horned rhinoceroses, is a World Heritage Site.
- It is recognized as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International.
- Vegetation: Alluvial inundated grasslands and savanna woodlands, tropical moist mixed deciduous forests, and tropical semi-evergreen forests.
- Major Flora: Spear grass, elephant grass, common reed, cotton tree, and elephant apple.
- Major Fauna: One-Horned rhinoceros (VU), Royal Bengal Tiger, Asian elephant, wild water buffalo (EN) and swamp deer are collectively known as the ‘Big Five’ of Kaziranga.
- Other important fauna: Fishing cat, small Indian civets, Chinese pangolin, Indian pangolins.
- Non-human Primate: Assamese macaque, capped langur, golden langur, and hoolock gibbon.
- Threats: Floods and encroachment by people along the periphery.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)