Current Affairs August 07, 2023: Coup in Niger, PMAY-G, Creation of New Districts, Cauvery River Water Dispute, Bhu-Vision, Devika River Rejuvenation, Theaterisation Of Armed Forces, Manhattan Project
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – IR – West Africa – 2023/08/07} Coup in Niger
- Context (TH): Niger army announced that the President had been removed.
- The head of Niger’s presidential guard proclaimed himself as the head of the state.
- It is the 9th coup or attempted power grab in just over three years in West and Central Africa.
- Countries in Africa where recent coups have occurred include Mali, Chad, Guinea and Burkina Faso.

Players
Against the coup
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is against the coup.
- The U.S. and French troops are already present in the Niger to fight against the insurgency.
For the coup
- Most citizens of Niger support the military coup.
- Mali and Burkina Faso have announced solidarity with the coup makers.
External interests
- Anti-French sentiments in Niger have been going on since mid-2022 when the government approved the re-deployment of France’s Barkhane force to Niger.
- The pro-Russian slogans indicate Niger is seeking a similar trajectory to Mali and Burkina Faso.
- Unlike the West, which stresses democratic norms, China and Russia’s security partnership without conditions is preferable for the West African military governments.
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
Operation Barkhane
Niger
Uranium
|
{GS2 – MoRD – Schemes – 2023/08/07} PMAY-G
- Context (TH): Under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G), the J&K administration has approved allotment of five marlas (a marla is ~270 square feet) of land each to the landless and those occupying state, forest or any other land, where construction is not permitted.
- In the first phase, 2,711 beneficiaries have been identified. The MoRD has stipulated the target of extending the scheme to 1.99 lakh beneficiaries in J&K by 2024.
Issues with the J&K PMAY-G
- Locals demand that those who arrived in J&K after 2019 should not be included in these lists.
- The figure of 1.99 lakh beneficiaries is dubious, as there are approximately 19,000 homeless individuals in J&K, according to records shared in Parliament.
- Locals are worried that it could be an attempt to alter the UT’s demographic composition.
- Unless the beneficiaries are clearly defined and identified, it might facilitate the settling of outsiders, and further deteriorate the law and order situation and social strife in J&K.
Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)
- In 2016, GoI launched the PMAY-G to achieve the target of “Housing for All” in rural areas.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- It aims to provide assistance to construct 2.95 crore pucca houses with basic amenities by Mar’24.
- State Government is responsible for providing land to landless PMAY-G beneficiaries.
Beneficiaries
- The beneficiaries under PMAY-G have been identified based on the housing deprivation parameters prescribed under Socio Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011.
- In 2018, the MoRD conducted an Awaas+ survey to identify beneficiaries left out under the 2011 SECC and thus prepared an additional list of potential beneficiaries.
Assistance
- The unit assistance of Rs. 1.20 lakh in plain and Rs 1.30 lakh in hilly/difficult areas is provided.
- The minimum unit (house) size is 25 sq meters, including a dedicated area for hygienic cooking.
- The beneficiaries are free to construct their houses more than the minimum unit area prescribed.
- The assistance for the construction of the toilet shall be leveraged through convergence with SBM-G, MGNREGS or any other dedicated funding source.
- Convergence for piped drinking water, electricity connection, LPG gas connection etc., different Government programmers are also to be attempted.
Sharing between Centre and State
- The cost of unit assistance is to be shared between the Central and State Governments in the ratio of 60:40 in plain areas and 90:10 for North Eastern and the Himalayan States.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Devolution of Powers – 2023/08/07} Creation of New Districts
- Context (TH): The formation of 19 new districts approved in Rajasthan.

Procedure for creation of new districts in India
- The power to create new districts or alter or abolish districts rests with the State governments.
- This can be done through an executive order or by passing a law in the State Assembly.
- Many States prefer the executive route by simply issuing a notification in the official gazette.
Central Government Role
- The central government does not play a role in creating or altering districts.
- However, the central government’s Home Ministry does come into the picture when a state government wants to change the name of a district or a railway station.
- The central government’s role is limited to providing clearance for names from different ministries.
Advantages of creating new districts
- Better administration and governance
- Service to the increased population
- Bring administration closer to the people
- District-specific government initiatives
- Increase employment
Challenges with creating new districts
- The government has to find office space and land acquisition for different departments and fill many new positions. All this will require a considerable government exchequer.
- Zilla Parishad and Panchayat Samiti do not enjoy power in many states. Grievances go to the collector. Creating smaller districts without empowering these bodies is against decentralisation.
- The growth centres built in the new district headquarters will also increase land rates and other service costs in the long run.
- Due to political motives, many states reorganise the existing districts and form new ones. For example, new districts containing a support base of the ruling party will be advantageous for it.
- If the district is too small, the administration and associated machinery will be underutilised, making the districts’ management harder for states.
Conclusion
- State governments should focus on ensuring that new districts are created consistent with the principles of decentralisation and good governance.
{GS2 – Polity – Inter-State Disputes – 2023/08/07} Cauvery River Water Dispute
- Context (TH): CM of TN urged the PM to instruct Karnataka to release Cauvery water.
- Cauvery Delta receives very little rainfall during the southwest monsoon.
- The cultivation of kuruvai and the sowing of samba paddy crops fully depend on water release from the Mettur dam, which, in turn, depends solely on the flows from Karnataka.
Kuruvai cultivation
Samba Cultivation
Other paddy seasons in Tamil Nadu
|
Origins and Initial Dispute
- The river Cauvery originates in Karnataka’s Talakaveri in Kodagu (Coorg) district and flows into Tamil Nadu, eventually reaching the Bay of Bengal.
- In 1892, a dispute arose between the Madras Presidency and the Princely state of Mysore.
- Madras opposed Mysore’s proposal to build irrigation systems.
- In 1924, Mysore and Madras reached an agreement that permitted Mysore to construct a dam at Kannambadi village.
- The agreement had a duration of 50 years and was subject to review, ultimately leading to the construction of the Krishnaraja Sagar dam in Karnataka.
- The 1924 water-sharing agreement ended in 1974.
Establishment of the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (1990)
- Central Government, in 1990, in the exercise of the powers conferred by section 4 of the Inter-State River Water Disputes Act, 1956 had constituted the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal to resolve the water dispute among Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Puducherry.
- The tribunal issued its final award in 2007, stating that Tamil Nadu should receive 419 tmcft of water, 270 TMC to Karnataka, 30 TMC to Kerala and 7 TMC to Puducherry.

Supreme Court Intervention and the Final Verdict
- In 2016, TN experienced a water deficit of 50.0052 tmcft due to insufficient rainfall in Karnataka.
- Seeking resolution, Tamil Nadu approached SC, resulting in court orders to release water.
- SC initially ordered Karnataka to release 15,000 cusecs of water per day to Tamil Nadu for ten days, which led to protests in Karnataka. Later, SC modified the order, specifying 2,000 cusecs per day.
- In 2018, SC delivered its final verdict, granting Karnataka an additional 14.75 TMC of river water.
- The final allocation for a total of 740 TMC is
- Karnataka: 284.75 (270 + 14.75) TMC
- Tamil Nadu: 404.25 (419 – 14.75) TMC
- 30 TMC to Kerala and
- 7 TMC to Puducherry
- The water allocation arrangement will stand unchanged for the next 15 years.
Cauvery Water Management Authority
- In exercising the powers conferred by section 6A of the said Act, the Central Government notified the Cauvery Water Management Scheme in 2018, inter alia, constituting the ‘Cauvery Water Management Authority’ and the ‘Cauvery Water Regulation Committee’.
- The Authority ensures for securing compliance and implementation of the Award of the Tribunal as modified by the Hon’ble Supreme Court:
- storage, apportionment, regulation and control of Cauvery waters;
- supervision of the operation of reservoirs and regulation of water releases therefrom with the assistance of the Regulation Committee;
- regulated release by Karnataka at the inter-State contact point presently identified as Billigundulu gauge and discharge station, located on the common border of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Mekedatu Reservoir Project
- The Mekedatu Reservoir Project aims to provide water for drinking purposes to Bengaluru city and generate approximately 400 megawatts (MW) of power.
- In 2018, Tamil Nadu raised objections against the project and approached the Supreme Court.
- Tamil Nadu opposes any projects in the upper riparian region unless they receive approval from the Supreme Court, ensuring water flow protection to Tamil Nadu.

{GS3 – Agri – Tech – 2023/08/07} Bhu-Vision
- Context (TT): Bhu-Vision is an advisory platform that was launched by the ICAR-IIRR.
- The system can perform 12 key soil parameter tests in just 30 minutes, delivering accurate results via mobile soil health cards to farmers and stakeholders.
- The system can also be used to generate agronomy advisory reports, which help farmers improve the productivity of their land.
- The system is based on Internet of Things (IoT) technology, which allows it to collect and transmit data in real time.
Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
|
{GS3 – Envi – Conservation – 2023/08/07} Devika River Rejuvenation Project
- Context (PIB): North India’s first River Rejuvenation Project, named Devika, is almost finished.
- This project modeled on ‘Namami Ganga‘ initiative, for restoring Devika River (in Udhampur, J&K).
- The project was launched in 2019 by the Udhampur Development Authority (UDA).
- The project is expected to cost around Rs. 190 crore and to be completed by the end of 2023.
- The project involves a number of measures:
- Construction of sewage treatment plants
- Creation of a network of pipes and manholes to collect and treat wastewater
- Removal of encroachments from the riverbed
- Afforestation along the riverbanks
{GS3 – IS – Security Forces – 2023/08/07} Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control and Discipline) Bill, 2023
- Context (TOI I TH): Lok Sabha passed the Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control and Discipline) Bill, 2023, amid a push for theaterisation.
- It seeks to empower the Commander-in-Chief and Officer-in-Command of Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs) with all disciplinary and administrative power w.r.t personnel servings.
Theaterisation Of Armed Forces
- Theaterisation is a concept that integrates the capabilities of the three services — army, air force and navy — and utilises their resources for wars and operations.
- At present, the three divisions of the Indian Armed Forces have a total of 17 commands.

Key Features of the Bill
Inter-Services Organisation (ISO)
- The bill will recognise existing ISOs, such as Andaman and Nicobar Command, Defence Space Agency, and National Defence Academy.
- Government will constitute an ISO with personnel belonging to at least two of the three services placed under Officer-in-Command.
- Joint Services Command will be placed under Commander-in-Chief.
Control of Inter-Services Organisations
- Presently, the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command are not empowered to exercise disciplinary or administrative powers over the personnel belonging to other services. The Bill empowers both of them to do so.
- The superintendence of an ISO will be vested in the central government.
Other forces under the central government
- The Government can notify any force raised and maintained in India that may be included in ISO’s.
Commander-in-Chief
- The officers eligible to be appointed as the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command are:
- General Officer of the Army (above the rank of Brigadier)
- Flag Officer of the Navy (rank of Admiral of the Fleet, Admiral, Vice-Admiral, or Rear-Admiral).
- Air Officer of the Air Force (above the rank of group captain)
Commanding Officer
- Commanding Officer will command a unit, ship, or establishment.
Chief of Defence Staff (CDS)
Appointment of CDS
|
{GS3 – S&T – Tech – 2023/08/07} Nuclear Bomb
- Context (IE | IE | IE | TH): The science and history behind nuclear bombs have been reignited by Christopher Nolan’s Oppenheimer, Russia’s nuclear threat to Ukraine, and Japan’s push for a nuclear-weapon-free world at the G7 summit.
- Nuclear bombs derive their destructive force from nuclear reactions, which involve changes in the structure of atomic nuclei, leading to the release or absorption of energy.
- Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion are two types of nuclear reactions used in nuclear bombs.
Atomic Nuclei: The Basis of Nuclear Reactions
- Atoms are the basic building blocks of all matter.
- They cannot be broken down further by simple chemical processes.
- Most of an atom is empty space. The rest comprises three basic types of subatomic particles:
- positively charged protons
- negatively charged electrons
- neutral neutrons
- The protons and neutrons combine to form the atom’s nucleus.
- The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of electrons in orbit.
|

Isotopes and Nuclear Reactions
- Isotopes are members of a family of an element that all have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
- Different isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties, but very different nuclear properties. So, the outcome of nuclear reactions is determined by the isotopes involved.
|

Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear fission is the process of splitting a heavy atomic nucleus into two smaller nuclei, releasing energy in the form of heat, light, and radiation.

- Nuclear bombs using fission are commonly referred to as atomic bombs.
- Radioactive atoms (or isotopes) are used in nuclear fission.
- Uranium-235 (U-235) and plutonium-239 (Pu-239) are commonly used isotopes for fission.
- U-235, an extremely rare isotope of uranium, is the most commonly used nuclear fuel.
Radioactive Atoms (or Isotopes)
|
Chain Reaction
- The nuclear fission is initiated by subjecting a U-235 or Pu-239 nucleus to neutrons.
- The nucleus immediately absorbs an extra neutron, becomes unstable, and breaks into two lighter atoms and a few extra neutrons. This process releases what is known as atomic energy.
- The fission of a U-235 or Pu-239 atom produces about 2 to 3 new neutrons. If other U-235 or Pu-239 atoms absorb these new neutrons, it creates an exponentially growing chain reaction.
- Such chain reaction releases large amounts of energy. A controlled chain reaction is used to run a nuclear reactor. An uncontrolled (runaway) chain reaction explodes an atomic bomb.

Need to Enrich Uranium
- ~99.3% of naturally occurring uranium is of the isotope U-238, which is not fissionable.
- Naturally occurring uranium, therefore, cannot be used as a weapon, or in nuclear power plants.
- Thus, uranium ore is enriched in order to increase the concentration of U-235.
- Fission bombs need 90% U-235 enrichment to sustain a (runaway) chain reaction.
- Nuclear power plants require an enrichment of 3-4% U-235 to sustain a chain reaction.
- This is done in specific enrichment facilities using some highly complex equipment.

Critical Mass and Nuclear Explosion
- A critical mass is the least fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction.
- At critical mass, there is a perfect balance between the production rate and loss rate of neutrons.
- The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties, density, shape, enrichment, purity, temperature, and surroundings.
Subcritical Mass
- A subcritical mass refers to a quantity of fissile material that is smaller than the critical mass.
- During this state, the loss rate of neutrons is greater than the production rate of neutrons.
Supercritical Mass
- A supercritical mass refers to a quantity of fissile material that is larger than the critical mass.
- During this state, the production rate of neutrons is greater than the loss rate of neutrons.
- Achieving a supercritical state is the basis for nuclear explosions.
How is Nuclear Fission Used in Nuclear Explosions?
- In a fission bomb, the fuel is kept in separate subcritical masses and brought together when the explosion is intended. There are two trigger mechanisms to achieve this:
- Conventional Explosives Method
- Implosion Method
Conventional Explosives Method
- In this method, the fission is triggered by making a “gun” fire one subcritical mass into another.
- This method is used for U-235 bombs in which one subcritical mass of U-235, shaped like a “bullet”, is placed on one end of a barrel. The other is placed on the other end as the “target”.
- A conventional explosive shoot the bullet down the gun barrel. When the bullet hits the target, it forms a supercritical mass, resulting in a chain reaction and an atomic explosion.
- This was the kind of bomb (Little Boy) used over Hiroshima in WWII.

Implosion Method
- In this method, the subcritical masses are compressed together by means of an implosion to create a supercritical mass. This method is used for Pu-239 bombs.
- Plutonium implosion bombs are more complex to make. But Pu-239 is easier and cheaper to obtain in critical mass quantities. These bombs can be more efficient than their U-235 counterparts.
- Pu-239 bomb was used in the Trinity Test at Los Alamos, New Mexico, USA, as a part of the Manhattan Project (produced the first nuclear weapons) and Nagasaki (Fat Man) in WWII.

Nuclear Fusion
- Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two light atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a tremendous amount of energy. This process is what powers the sun and other stars.
- Nuclear bomb using fusion are referred to as thermonuclear bombs or hydrogen bombs.
- For fusion bombs, two extremely rare isotopes of hydrogen, deuterium and tritium, are used.
- The hydrogen isotopes are fused together under extremely high temperatures (millions of degrees Celsius) and pressure for the nuclear explosion to occur. (A fission trigger might be required)

Advantages of Nuclear Fusion Bombs
- Fusion bombs are more destructive and efficient than fission bombs.
- They also have no limit to the yield produced.
- The largest fusion bomb ever tested is the Soviet Tsar Bomba.
Challenges for Nuclear Fusion Bombs
- Obtaining adequate fusionable material is not easy.
- The energy required to create conditions of a fusion reaction is immense.
Nuclear Fission vs Nuclear Fusion
|
Nuclear Fission |
Nuclear Fusion |
| Splitting of a large atom into two or more smaller ones. | Fusing two or more lighter atoms into a larger one. |
| It involves a chain reaction, which can lead to dangerous meltdowns. | There is no chain reaction involved. |
| Does not usually occur in nature. | Fusion occurs in stars, such as the sun. |
| Produces many highly radioactive particles (nuclear waste). | The fusion reaction produces few radioactive particles, but radioactive particles will result if a fission “trigger” is used. |
| A critical mass of the substance and high-speed neutrons are required. | High density, high-temperature environment is required. |
| Takes little energy to split two atoms. | Extremely high energy is required to bring two or more protons close enough that nuclear forces overcome their electrostatic repulsion. |
| The energy released by fission is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions. | The energy released by fusion is three to four times greater than that in fission. |
| Used in an atomic bomb. | Used in a hydrogen bomb, which uses a fission reaction to “trigger” a fusion reaction. |
| Fission is used in nuclear power plants. | Fusion is an experimental power-producing technology. |
| Uranium and Plutonium isotopes are the primary fuel. | Hydrogen isotopes (Deuterium and Tritium) are the primary fuel in experimental fusion power plants. |
| Nuclear waste, a by-product of fission, is an environmental challenge. | There is no nuclear waste produced in a thermonuclear reactor. |
What Happens When a Nuclear Device Explodes?
- Nuclear weapons are thousand to million times more powerful than conventional explosives.
- A Blast (or Shock Wave): The initial blast wave from the explosion creates a shockwave that travels outward at high speeds. It flattens and obliterates any physical structures in the blast radius.
- Bright Light: can cause permanent blindness even many kilometres away.
- Intense Heat: The intense heat produced can instantly turn human bodies into ashes.
- Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP): High-energy gamma radiation released during the explosion can interact with the Earth’s atmosphere, producing an electromagnetic pulse (EMP). This pulse disrupts or damages communication devices and infrastructure
- Radiation: A nuclear explosion releases two types of radiation that cause harm to all living beings:
- Initial radiation (produced within a minute of detonation)
- Residual (or delayed) radiation (emitted over a period of time).

Nuclear Fallout
- A nuclear explosion near the ground sucks up debris, dirt, and other materials, making them highly radioactive. This radioactive debris falls back to the ground as fallout.
- Fallout can contaminate the area, water sources, and crops, posing long-term risks to health risks and the environment.
Mushroom Clouds
- A mushroom cloud is a distinctive formation resulting from a nuclear explosion.


Manhattan Project
- The Manhattan Project was a research and development project undertaken during World War II to produce the first atomic bombs.
- It began in 1939, when the US government was alarmed by the possibility of Nazi Germany developing atomic weapons.
- The Manhattan Project involved the contributions of prominent scientists like J. Robert Oppenheimer, Enrico Fermi, Richard Feynman, and Niels Bohr.
Result of the Manhatten Project
- The project successfully developed two types of atomic bombs:
- Little Boy: It used U-235 and was dropped on Hiroshima, Japan, on August 6, 1945.
- Fat Man: It used Pu-239 and was dropped on Nagasaki, Japan, on August 9, 1945.
Impact of the Manhatten Project
- The bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki led to Japan’s surrender and the end of World War II.
- It ushered in the nuclear age, which profoundly affected international relations.
Trinity Test
- Trinity was the code name of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon.
- It was conducted by the US Army on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project.
- It was tested on White Sands Missile Range in the Jornada del Muerto desert, New Mexico.
- It tested an implosion-design plutonium device, nicknamed the “Gadget”.
- Fat Man bomb detonated over Nagasaki, Japan, was of the same design.
- The name “Trinity” was assigned by J. Robert Oppenheimer, inspired by the poetry of John Donne.
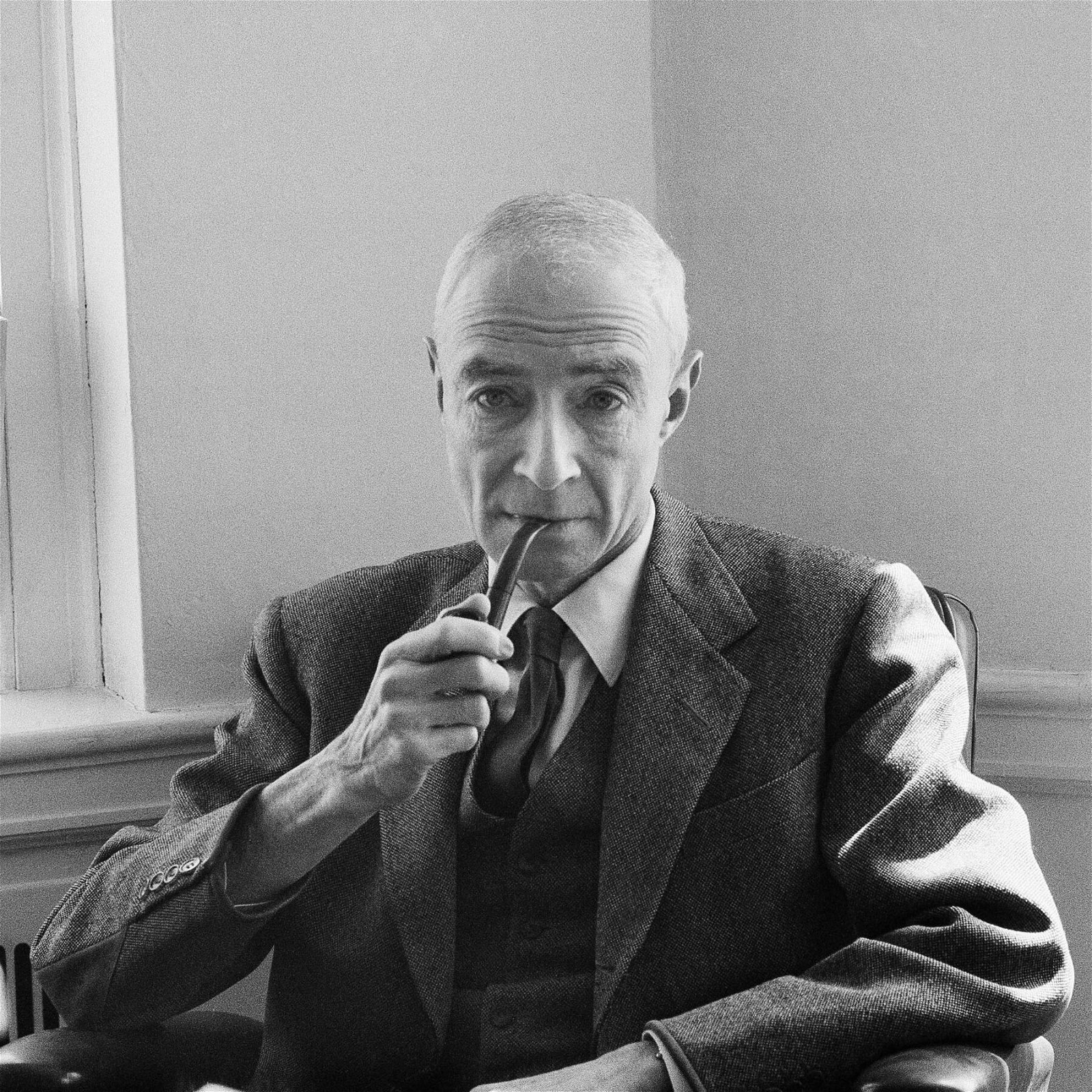
Robert J. Oppenheimer: Father of the Atomic Bomb
- Oppenheimer was a theoretical physicist. He was a Jewish immigrant from Germany.
- He is best known for having led the Manhattan Project.
- He was proud of the making of the atomic bomb and was supportive of its use in Hiroshima.
- But he fervently hoped that that would be the last time it would ever be used.
- Later, he was suspected of being a communist and a Soviet spy.
- More than 50 years after his death, the United States cleared him of the allegations.
- He learned Sanskrit, and the Bhagwat Gita was among his favourites.
- After witnessing the Trinity Test, he quoted a verse from the Bhagavad Gita: “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds.”






![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)