Current Affairs December 21, 2023: PM- AJAY, RAMP Scheme, 7th Economic Census, Rupay Kisan Credit Card (KCC), MSCS (Amendment) Act and Rules, 2023, Operation Prosperity Guardian, Sahitya Akademi Awards, Yemen’s Houthi Movement
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – WH} Yemen’s Houthi Movement
- Context (TH): Attacks on commercial ships were carried out by Houthi militants from Yemen in the Red Sea as the spillover of the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict.
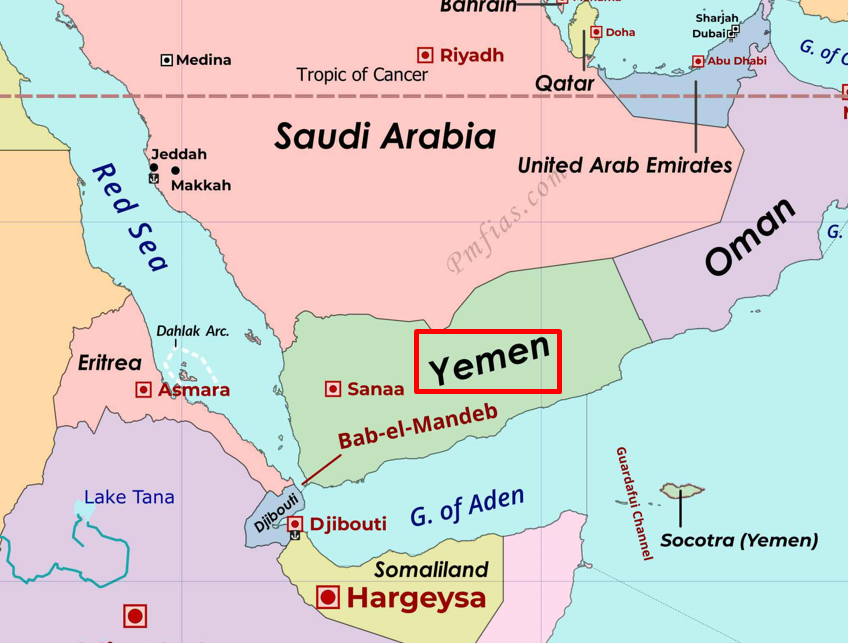
Background
- Its origin is traced to “Believing Youth”, a Zaydi revivalist group — a part of the Shia sect of Islam, involving them in the Shia-Sunni conflict.
- It was a powerful sect within Yemen, establishing an imamate in the 16th century and resisting Ottoman influence in the 17th century.
- The dominance of Zaydis declined in the 19th century due to the fall of the monarchy in Egypt and the rise of Wahhabism.
- The Houthi movement was founded to reassert the Zaydi influence in the early 1990s.
- It was inspired by the Iranian Revolution of 1979 and the rise of Hezbollah in southern Lebanon.
Growth of the Houthi Rebellion
- From religious and social concerns, the movement turned political against the Saleh government’s perceived corruption and Western influence.
- After the Iraq war, Houthis adopted a new slogan, “Death to America, death to Israel, curse upon the Jews, victory to Islam”.
- A government crackdown in 2004 backfired, strengthening the Houthi movement.
- By January 2015, the Houthis captured the capital, Sana’a and much of northern Yemen, triggering Saudi military intervention.
- Accusations of Iranian support persist, with both the U.S. and Saudi Arabia pointing fingers at Iran.
| Operation Rahat: India launched a massive air and sea operation to evacuate over 4000 Indian nationals from Yemen in April 2015. |
Impact on Yemen
- It is undergoing a humanitarian crisis, with 80% of its population dependent on aid and protection.
- Since 2015, over three million people have been displaced.
Current Status
- There is a ceasefire in Yemen, with Saudi Arabia in talks with Houthis and Iran to de-escalate the issue.
- Houthis declared war against Israel during the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict, targeting vessels passing through the Red Sea.
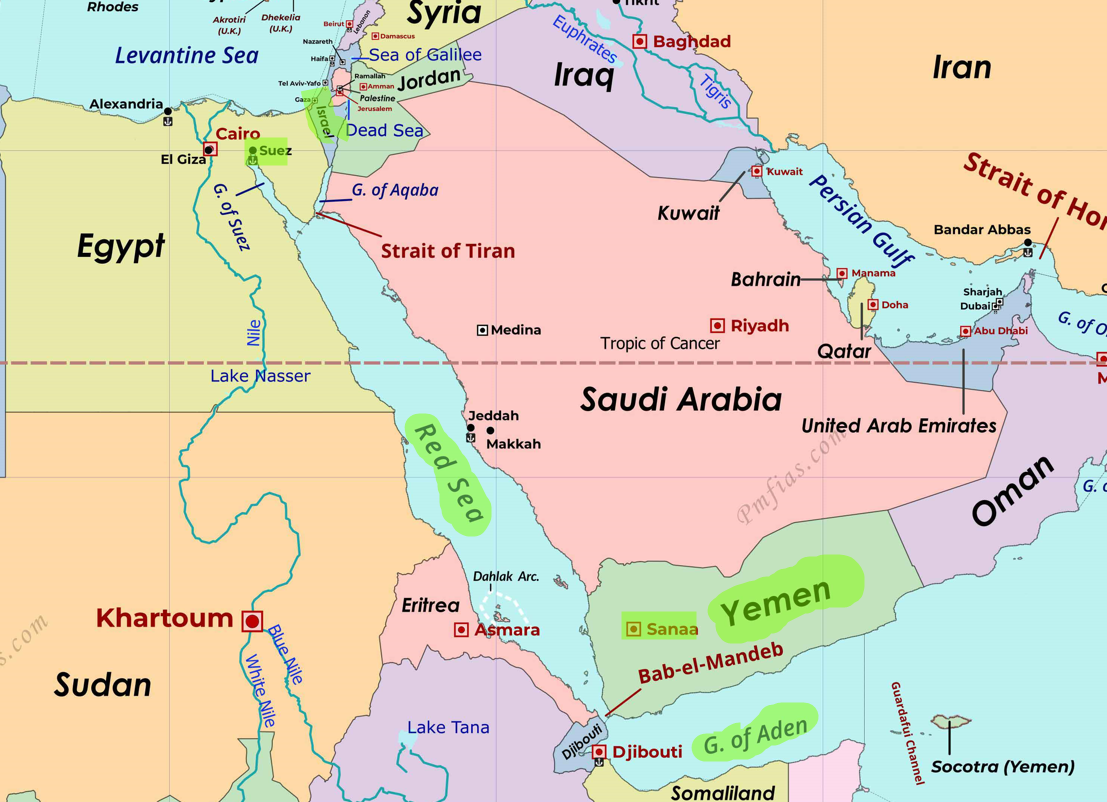
{GS2 – IR – Red Sea} Houthi Attacks | Operation Prosperity Guardian
- Context (IE | TH): Attacks on commercial ships were carried out by Houthi militants from Yemen in the Red Sea as the spillover of the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict.
- The US has launched Operation Prosperity Guardian to ensure the safety of commercial ships.
Houthis and Isareal-Palestine War Connection
- During the Second intifada of 2000, Houthis staged protests in solidarity with the Palestinian cause.
- Houthis declared war against Israel after the Israel-Palestine conflict and launched attacks towards Israel and Israel-related vessels in the Red Sea.
Global economy and Red Sea attacks
- The Red Sea provides a shorter route to the Mediterranean Sea with the Indian Ocean via the Suez Canal.
- Houthi attacks forced the ship to take a two-week longer route via Africa.
- Attacks near the Red Sea and Suez Canal (12% of global shipments) may lead to rising global inflation.
Impact on Oil prices
- With the Suez Canal accounting for 9.2 million barrels per day of total oil flows in the first half of 2023.
- Instability in the Red Sea causes increased fuel costs and war risk surcharge.
- Oil prices rose more than a dollar a barrel after the Houthi attacks.
Operation Prosperity Guardian
- The US initiated a new multinational security joint patrol initiative in the Red Sea.
- It is being carried out under the Combined Maritime Forces and the leadership of its Task Force 153.
- The Combined Maritime Forces is a multi-naval taskforce with 39 members, including India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, the United States and Yemen.
- Combined Task Force 153 was set up in April 2022 to improve maritime security in the Red Sea, Bab el–Mandeb and the Gulf of Aden.
{GS2 – IR – UN} 2023 Article IV Consultation with India
- Context (IE): The Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded the Article IV consultation with India.
IMF Article IV Consultation
- Under Article IV of the IMF’s Articles of Agreement, the IMF usually holds bilateral discussions with members annually.
- An IMF staff team collects economic data, visits the country, and engages with authorities (RBI in India) to discuss economic developments and policies.
Observations of Report
- IMF has reclassified India’s “de facto” exchange rate regime to “stabilised arrangement” from “floating” for December 2022 to October 2023.
- Exchange rate stability reflects improvements in India’s external position.
- Average moderation in headline inflation persists despite ongoing volatility from food price shocks.
- Employment has surpassed the pre-pandemic level.
- Though formalisation has progressed, the informal sector continues to dominate.
- The financial sector has been resilient and largely unaffected by global financial stress in early 2023.
- The Current account deficit (CAD) in FY2022-23 widened due to the post-pandemic recovery aided by transitory external shocks.
- Robust services exports and proactive diversification of critical oil imports tried to balance the CAD.
- Public debt remains elevated, and fiscal buffers need to be rebuilt.
|
India-IMF debate on intervention by RBI
- IMF Staff’s Assessment: Forex intervention by the RBI likely exceeded levels necessary to address disorderly market conditions.
- It led to the classification of the exchange rate system as a “stabilised“ arrangement.
India’s Stand
- India has strongly disagreed with the IMF’s staff assessment, saying that such a view is “incorrect”.
- IMF staff’s assessment is short-term without any rationale.
- RBI has consistently maintained that it doesn’t target a level for the rupee but intervenes in the market to smoothen the volatility.
{GS2 – MoC – Laws} MSCS (Amendment) Act and Rules, 2023
- Context (PIB): Recently, the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (MSCS) (Amendment) Act & Rules, 2023 were notified.
Provisions introduced
- Reservation of two seats for women and one for SC or ST on the board of MSCS has been introduced.
- Provision of a Cooperative Election Authority for timely and regular elections has been included.
- Allows inclusion of directors having experience in banking, management, cooperative management, finance or relevant fields.
- A quorum of 1/3rd of elected members has been prescribed for board meetings.
- Meeting must be called on requisition from at least 50 % of board members.
- New disqualification criteria for directors aim to enhance governance and expedite dues recovery.
- Compulsory absence of the directors of MSCS from the voting on their personal interest matters.
{GS2 – MoMSME – Schemes} PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman Yojana
- Context (PIB): The Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra is an initiative to inform citizens about the Centre’s flagship schemes, including the PM Vishwakarma Scheme/ “PM VIKAS Yojana.”
- It is a Central Sector Scheme fully funded by the GOI.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MoMSME).
- The Scheme will be jointly implemented by
- MoMSME
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
- Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, GOI.
- It is designed to uplift traditional artisans and craftspeople engaged in various occupations like blacksmithing, goldsmithing, pottery, carpentry, and sculpting
Objective
- Preserving and integrating cultural heritage into the formal economy and global value chains.
- Provide skill upgradation and make relevant and suitable training opportunities.
- Provide support for better and modern tools.
- Provide for brand promotion and market linkages.
Features
- Recognition: Artisans and craftspeople enrolled in the scheme will receive a PM Vishwakarma certificate and an ID card.
- Financial assistance: They will also be eligible for collateral-free credit support at a concessional interest rate.
- Skill Development and Empowerment: It offers a daily stipend for skill training and a grant to purchase modern tools.
- Scope and Coverage: The scheme encompasses 18 traditional trades across rural and urban areas.
Initiatives for the Upliftment of Artisans
- Ambedkar Hastshilp Vikas Yojana
- Mega Cluster Scheme
- National Handicraft Development Programme
- Comprehensive Handicrafts Cluster Development Scheme
- Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts
- One District One Product
- Atmanirbhar Hastshilpkar Scheme.
{GS2 – MoMSME – Schemes} RAMP Scheme
- Context (PIB): MoMSME launches three sub-schemes under Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) Programme.
- RAMP scheme is a World Bank-assisted program that aims to improve the performance of MSMEs.
- Nodal ministry: Ministry of MSME.
- An important component of the Scheme is the preparation of Strategic Investment Plans (SIPs) which would include outreach plans for the identification and mobilization of MSMEs, identify the constraints in the sector, and project the budget requirement for interventions.
Objectives of the Scheme
- Improving access to the market and credit for MSMEs.
- Improving centre-state linkages and partnerships.
- Greening of MSMEs, technology upgradation.
Sub-Schemes under RAMP Scheme
MSME Green Investment and Financing for Transformation Scheme (MSME GIFT Scheme)
- It would help MSMEs adopt green technology with interest subvention and credit guarantee support.
MSE Scheme for Promotion and Investment in Circular Economy (MSE SPICE Scheme)
- It is the 1st ever scheme to support circular economy projects to be done through credit subsidy thereby realizing the goal of Net Zero Emissions by 2070.
MSME Scheme on Online Dispute Resolution for Delayed Payments (MSME ODR Scheme)
- 1st-of-its-kind scheme to synergize legal support with modern IT tools and AI to address the incidences of delayed payments for SMEs.
{GS2 – MoPPP – Schemes} D-Remit QR code for NPS
- Context (PIB): The Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) has now allowed the use of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) QR code to the National Pension System (NPS).
- It will take place through a D-Remit virtual account.
- The D-Remit virtual account is distinct from the Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN).
- PRAN is a unique 12-digit number for users registered in NPS.
|
Benefits of D-Remit QR code
- Same-Day Investment: Contributions received will be invested on the same day, optimising returns.
- Auto Debit: Subscribers can set up periodic auto-debit payments without frequent payments.
- Flexible: One-time or Regular Contributions based on individual preferences and financial goals.
- Long-term retirement wealth creation via leveraging standing instructions and rupee cost averaging.
- D-remit can be used to set up a Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) in NPS.
|
PFRDA
- The PFRDA Act, 2013, provided its statutory status. It comes under the Ministry of Finance.
- It was first constituted through a government resolution in 2003 to run NPS. PFRDA also runs Atal Pension Yojana (APY).
New Pension Scheme (NPS)
|
{GS2 – MoSJE – Schemes} PM- AJAY
- Context (PIB): A total of 1398 villages of all 30 districts of Odisha have been covered under the Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY) component of PM-AJAY for the upliftment of the SC community.
- PM- AJAY is a 100% centrally sponsored scheme.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment
- It has been framed after merging the three schemes, namely:
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY)
- Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Caste Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP)
- Babu Jagjivan Ram Chatrawas Yojana (BJRCY)
Components of PM-AJAY
- The scheme has three components, which are as under-
- Development of SC-dominated villages into an ‘Adarsh Gram’ component.
- Grants-in-aid for District/State-level Projects for SCs.
- Construction of Hostels in Higher Educational Institutions’component.
Development of SC-dominated villages into an “Adarsh Gram”:
- To ensure the integrated development of SC-majority villages to have adequate infrastructure.
Grants-in-aid for District/State-level Projects:
- Financial support intending to improve the socio-economic conditions of SC communities.
- Comprehensive Livelihood Projects such as Skill development, financial assistance towards loans taken by beneficiaries for acquisition/creation of assets required for livelihood generation, etc.
Construction of Hostels
- In higher educational institutions (Top-ranked as per the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) of the GOI) and schools, funded by the Centre/State/UT Governments either fully or partially.
{GS2 – MoSPI – Initiatives} 7th Economic Census
- Context (PIB): Fieldwork of 7th economic census was completed.
- Pending results and approval from some states/UTs led to the non-finalisation of the results.
- IT-based digital platform is being used for Economic census for the first time.
- West Bengal is the only state not participating in the 7th Economic Census.
Economic Census
- It is being carried out by the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI).
- Technical support will be provided by the Common Service Centre (CSC).
- Starting from 1978, it is conducted every five years.
- Geographical spread, ownership pattern, persons engaged, etc., of economic activities are recorded.
|
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Comparison} 14th Amendment of the US Constitution
- Context (IE I TH): The SC of the U.S. State of Colorado disqualified Trump from holding the office of President under Section Three of the 14th Amendment to the USA.
- This has barred former Trump from running for office again in the 2024 presidential election.
- The 14th Amendment of the US Constitution was ratified on July 9th,1868.
- The primary purpose (14th Amendment) was to address civil rights issues following the Civil War, particularly regarding formerly enslaved people.
- This was in response to post-Civil War issues, including the Black Codes in Southern states.
American Civil War (1861-1865)
Economic Disparity between Northern and Southern States
Election of President Abraham Lincoln
Black Codes
|
Key Clauses of the 14th Amendment
- Citizenship Clause: Citizenship for all persons born or naturalised in the U.S.
- Due Process Clause: Fair legal process is required for all citizens.
- Equal Protection Clause: Equal legal protection for all citizens.
Significance of the amendment
- Extended Bill of Rights protections to state actions.
- Foundation for numerous civil rights advancements and Supreme Court decisions.
Impact on Federalism
- Altered the balance of power between the federal government and states, especially in civil rights and liberties.
Section 3 of the amendment
- It disqualifies anyone who has taken an oath to support the Constitution but engages in insurrection or rebellion against it, or aids its enemies, from holding any civil or military office in the US.
Similar provisions in the Indian Constitution
Equal Protection Clause
- Article 14: IC guarantees “equality before the law” and “equal protection of the laws” within India.
Citizenship Clause
- Articles 5 to 11: Deal with aspects of citizenship in India, including citizenship by birth, descent, registration, naturalisation, and incorporation of territory.
Due Process Clause
- Article 21: Protects life and personal liberty, stating, “No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to a procedure established by law.”
Protection of Civil Liberties
- Article 19: Ensures the protection of certain rights regarding freedom of speech, assembly, etc.
Prohibition of Discrimination
- Article 15: Prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
Disqualification for Public Office
- Representation of the People Act, 1951 (Sections 8, 9, 10, 11): Lays out disqualifications for membership of Parliament and State Legislatures due to criminal convictions, corrupt practices, and certain office-of-profit positions.
{GS2 – Polity – Laws} NCT of Delhi Laws (Special Provisions) Second (Amendment) Bill, 2023
- Context (IE): The Parliament passed the National Capital Territory of Delhi Laws (Special Provisions) Second (Amendment) Act, 2023.
Important Provisions of Act
- The act aims to shield Delhi’s unauthorised constructions (up to June 1, 2014) from official actions.
- The amendment replaces 2023 with 2026, extending the protections for another three years.
- It is justified based on the time-consuming process of conferring ownership rights and development control norms for unauthorised colonies.
Background and Need of the Act
- It will protect the settlements from the sealing drive in 2006 directed by Delhi HC and the SC.
- Earlier, The Delhi Laws (Special Provisions) Act, 2006, was passed to shield unauthorised constructions for one year, subsequently renewed yearly.
- The National Capital Territory of Delhi Laws (Special Provisions) Second Act,2011, increased protection for three years until December 31, 2014.
- Since then, the government has amended the Act three times to extend the protections for three years every time.
- Ownership rights: The NCT of Delhi (Recognition of Property Rights of Residents in Unauthorised Colonies) Act, 2019 conferred ownership rights to residents of unauthorised colonies.
Way Forward
- Timely completion and implementation of Master Plan Delhi-2041 can address the issue permanently.
{GS3 – Agri – Finance} Rupay Kisan Credit Card (KCC)
- Context (PIB): A Pilot project has been started to implement the Rupay Kisan Credit Card.
- Under this project, all the cooperative societies’ members will have accounts in the concerned District Central Cooperative Banks.
- Rupay-Kisan Credit Cards (KCCs) are being distributed to the account holders.
Kisan Credit Cards
- The scheme was introduced in 1998 to provide farmers with adequate and timely credit support.
- It was extended for Allied and non-farm activities in 2004.
- Electronic Kisan Credit Cards have been issued on the Working Group report under T. M. Bhasin.
- The age group of 18-75 years is eligible for KCC. Senior citizens must have a legal heir as a co-borrower.
- Implementing Agencies: Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks, and Cooperatives.
Objectives
- To meet the short-term credit requirements for the cultivation of crops.
- Post-harvest expenses.
- Produce marketing loan.
- Consumption requirements of farmer households.
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets and activities allied to agriculture.
- Investment credit requirement for agriculture and allied activities.
Features
- It comes with an ATM-enabled RuPay debit card.
- Aadhaar linkage is compulsory for interest subvention.
- It has a validity period of 5 years.
- It attracts no processing fee for loans under KCC.
- The limit of collateral-free agriculture loans has been revised from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs.1.6 lakh.
- It is issued at a reasonable interest rate of 7% per annum with interest subvention of 2% and 3% subvention on prompt payment for short-term crop loans up to Rs. 3 lakh.
{GS3 – Envi – Air Pollution} Aviation Industry Emissions
- Context (IE): The UK banned Air France, Lufthansa, and Etihad ads over ‘greenwashing’ claims.
Greenwashing
|
- Currently, the aviation industry contributes around 2.5% of total human-produced CO2 emissions.
- This may seem like a modest contribution, but it is set to grow quickly.
- If non-CO2 emissions like water vapour are considered, the airline industry would contribute to nearly 5% of historical global warming.
Issue of Non-Accountability of Emissions
- Emissions from domestic flights are attributed to a country’s emission accounts.
- However, emissions from international flights are not attributable to any country.
- They are classified as “bunker fuels,” and no country is obligated to limit these emissions.
{GS3 – IE – Exports} Initiatives for Export Promotion
- Context (PIB): GoI has taken various initiatives for the promotion of exports.
PM GATI Shakti
- PM Gati Shakti (National Master Plan for Multi-modal Connectivity) is a digital platform that brings 16 Ministries together for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- It will incorporate the infrastructure schemes of various Ministries and State Governments like Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, dry/land ports, UDAN, etc.
- Economic clusters will be covered to improve connectivity & make Indian businesses more competitive.
- It will also leverage technology extensively, including spatial planning tools with ISRO imagery developed by BiSAG-N (Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics).
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
- The PLI Scheme is a policy to promote domestic manufacturing to enhance India’s self-reliance and global competitiveness.
- The scheme provides financial incentives to eligible companies based on their incremental sales of products manufactured in India over a base year.
- The scheme covers 13 key sectors, including electronics, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, textiles, food processing, telecom, solar PV modules and white goods.
- The scheme has a total budgetary outlay of Rs 1.97 lakh crore for a period of five years.
One District One Product (ODOP) Scheme
- The ODOP Program is a project operating under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), which falls under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The program identifies distinctive and culturally significant products from each district, encompassing handicrafts, handloom, and agricultural goods.
- The idea is to select, brand, and promote One Product from each District of the country.
- It is a CSS shared by the central government and states in 60:40 contributions.
- It is operationally merged with the ‘Districts as Export Hub’ initiative.
- States will identify the ODOP food product for a district.
Foreign Trade Policy, 2023
- It came into effect on 1st April 2023.
- It focuses on taking forward the Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative to promote exports at the district level.
- It provides a roadmap for establishing e-commerce hubs and related elements such as payment reconciliation, bookkeeping, returns policy, and export entitlements.
- It provides for an Amnesty Scheme for exporters as those unable to meet their obligations under EPCG (Export Promotion Credit Guarantee) and Advance Authorizations can be regularised on payment of all customs duties exempted.
Nirvik Scheme
- Also called the Export Credit Insurance Scheme (ECIS), it aims at enhancing loan availability and easing the lending process to the exporters.
- It provides 90% coverage of the principal and interest of the loan, for both pre- and post-shipment credit.
- It also subsidizes the premium to be paid by exporters of certain key sectors.
- Enhanced insurance cover will ensure that Foreign and Rupee export credit interest rates will be low for exporters.
National Logistics Policy, 2022
- It aims to develop a technologically enabled, integrated, cost-efficient, resilient, sustainable, and trusted logistics ecosystem for accelerated and inclusive growth.
- 4 Features:
- Integration of Digital System (IDS): Under it, 30 different systems of 7 departments are integrated – including data from the road transport, railways, customs, aviation, and commerce departments.
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): It will bring all the digital services related to the transportation sector into a single portal, freeing the exporters from a host of cumbersome processes.
- Ease of Logistics: It is a digital portal for industry associations to directly take up matters with government agencies regarding issues in their operations and performance.
- System Improvement Group (SIG): It will monitor all logistics-related projects regularly.
- Key action areas for policy implementation: Integrated Digital Logistics Systems, Standardization of physical assets and benchmarking of service quality standards, EXIM Logistics, Logistics Parks etc.
National Industrial Corridor Development Programme
- It is aimed at the development of futuristic industrial cities that can compete with the best manufacturing and investment destinations in the world.
- It is developed as part of the PM Gati Shakti – National Master Plan.
- Objective: To provide plug-and-play infrastructural facilities for setting up large-scale manufacturing.
- Each Industrial Corridor is envisaged to be implemented by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) in the form of a company set up under the Companies Act, 2013 as a joint venture between the central and state governments.
- Implementing Agency: The National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation Limited (NICDC).
- Monitoring and Review Mechanism: by National Industrial Corridor Development and Implementation Trust (NICDIT).
- State governments contribute by providing land as their share of equity in the programme.
- The NICP envisages the development of 11 industrial corridors in four phases.
Startup India
- It is a flagship initiative of GoI announced in 2016 to build a strong ecosystem for fostering entrepreneurship, nurturing innovation, driving sustainable economic growth and generating large-scale employment opportunities.
- Objective: To make India a nation of ‘job creators’ rather than job seekers.
- It is based on the following 3 pillars:
- Simplification and Handholding through faster exits.
- Funding Support and Incentives through credit guarantee fund, tax exemptions on Capital Gains and income-tax.
- Industry-Academia Partnership and Incubation through Building Innovation Centres, Technology Business Incubators (TBIs), and Research Parks in National institutes and in private sector.
{GS3 – Infra – Urban Development} Protests over DRP
Dharavi
- Dharavi is Asia’s largest slum cluster on a 300-hectare prime land near the premium Bandra-Kurla Complex (BKC) area.
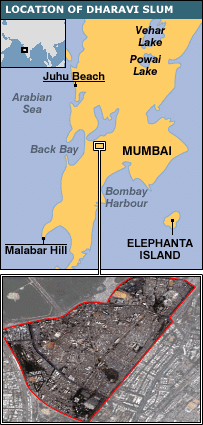
- Dharavi grew as an unplanned locality after its initial foundation in 1882.
- With around 58,000 families, mostly migrants, Dharavi also houses small commercial establishments.
- Poor living conditions and unplanned urbanisation demand redevelopment of Dharavi.
|
Dharavi Redevelopment Project
- The redevelopment plan is an integrated residential, commercial, and industrial development approach with a floor space index of over 4.
- After the initial proposal in 1999, the Dharavi Redevelopment Authority was constituted under the Slum Redevelopment Authority (SRA) in 2004.
- Despite several global tenders in the past, the project never took off.
- The 2018 tender by Seclink Technologies Corporation was cancelled due to a delay in transferring required land by railways.
- Finally, in November 2022, Adani Properties Private Limited secured the 259-hectare redevelopment project through competitive bidding.
|
Recent Controversy
- Seclink Technologies Corporation has alleged improper termination of the 2018 tender in favour of Adani Group.
- An issue regarding the Transferable Development Rights notification is also being raised.
|
Current Status of Project
- Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL) as a special purpose vehicle (SPV) was formed with an 80:20 developer and state government stake, respectively.
- The project is expected to finish in 7-10 years after next year’s commencement.
{Prelims – Awards} Sahitya Akademi Awards
- Context (TH): Lakshmisha Tolpadi bags the Sahitya Akademi Award in the essays category.
- Tolpadi’s work is a collection of essays on Vyasa Mahabharatha which are Vyasa’s commentaries on worldview through the eyes of Kannada scholar.
- Other works of Tolpadi: Mahamadana Balige Baradiddare, Sampige Bhagavatha, Balu, Mahayuddhakke Munna, Anandalahari, and Bhakthina Nepadalli.
- Sahitya Akademi Awards is a literary honor conferred annually by the Sahitya Akademy, the National Academy of Letters.
- It was established in 1954.
- It is the 2nd highest literary honor after the Jnanpith Award.
- It is conferred for literary works in 24 languages (22 Official Languages of the 8th Schedule of IC, English and Rajasthani).
- The awardees are presented with cash prize of Rs 10 lakh and a plaque.
Criteria
- The author must be of Indian Nationality.
- The book must be an outstanding contribution to the language and literature to which it belongs.
- In case of similar worth of two works, factors such as overall literary contribution and author’s standing would be considered.
Other Sahitya Akademi Awards
- Sahitya Akademi Bal Sahitya Puraskar: Honors authors for contribution to Children’s literature
- Sahitya Akademi Yuva Puraskar: Honors novels written by authors below the age of 35 years.
Sahitya Akademi
- Founded in 1954, it is an organization dedicated to the promotion of literature in the Indian languages.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Culture.
- Its office is located in Delhi.
- It initially functioned under executive order but was subsequently registered as a society under the Indian Societies Registration Act of 1860.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)