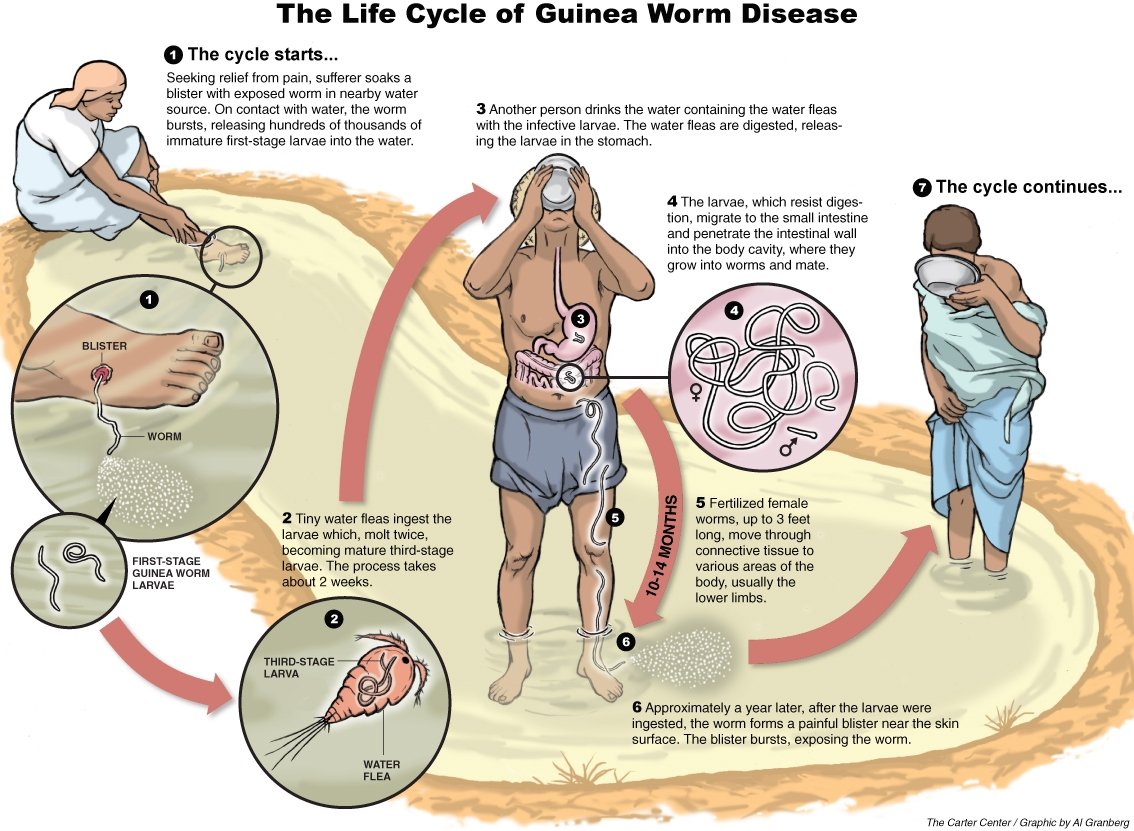
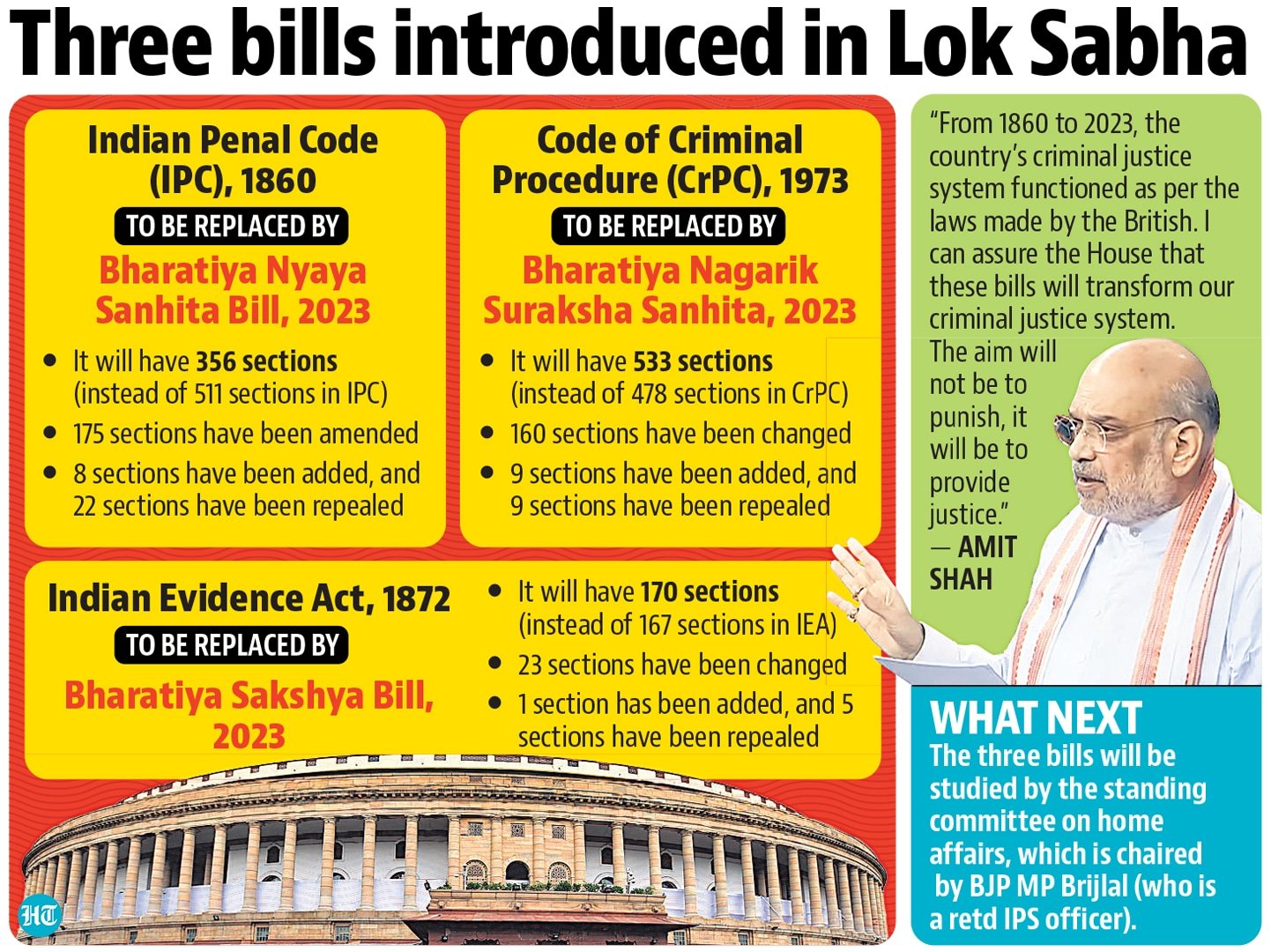
Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – March 08, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Governance – Initiatives} NITI For States
- Context (PIB): The Minister of Communications, Railways, and Electronics & Information Technology will inaugurate the NITI for States platform developed by NITI Aayog.
- NITI For States is a cross-sectoral knowledge platform designed to serve as a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Policy and Good Governance.
- Sector Coverage: Agriculture, Education, Energy, Health, Livelihoods, Manufacturing, MSME, Tourism, urban and Water Resources, and WASH.
- The platform also covers two cross-cutting themes: Gender and Climate Change.
Features
- Extensive Knowledge Base: 7,500 curated best practices, 5,000 policy documents, 900+ datasets, 1,400 data profiles, and 350 NITI Aayog publications.
- Multilingual Accessibility: In the near future the platform will be available in 22 major Indian languages and 7 foreign languages, ensuring inclusivity for diverse user groups.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Tailored digital training modules for officials at various levels (block, district, and state) in collaboration with relevant institutions.
- Expert Help Desk: Specialised guidance through partnerships with leading institutions allows states and UTs to address specific challenges.
- Data Integration: Leverages data from the National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP) for comprehensive and actionable insights, fostering data-driven decision-making.
Benefits
- Accelerate digital transformation of governance by equipping officials with robust knowledge, actionable insights, and user-friendly digital tools.
- Empower frontline functionaries at the district and block levels to replicate successful initiatives and address local challenges effectively.
- Foster cooperative federalism and strengthen good governance practices through knowledge sharing and cross-learning among states and UTs.
{GS2 – MoSJE – Schemes} NAMASTE Scheme
- Context (PIB): Urban Local Body (ULB) nodal officers and surveyors are trained in the profiling process and the NAMASTE mobile application.
- National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) Scheme is a joint initiative by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- It has replaced the Self-Employment Scheme for the Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS).
- It is a central sector scheme launched in 2022.
- It aims to eliminate the manual engagement of sanitation workers in hazardous tasks related to sewer and septic tank cleaning.
- The scheme will be implemented by the National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC) for a period of 3 years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2025-26).
Components of the Scheme
- Profiling of Sewer and Septic Tank Workers (SSWs): Creating a national database with a unique NAMASTE ID for each worker.
- Health Insurance: SSWs will be covered under the PM-JAY health insurance scheme.
- Safety Measures: They will receive Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) kits and access to safety devices.
- Training: Occupational safety training will be provided.
- Capital subsidy of up to Rs. 5 lakh for sanitation-related vehicles/equipment will create livelihood opportunities through subsidized machinery.
- Sanipreneurship: Capacity building will encourage SSWs to start their sanitation enterprises.
{GS3 – S&T – AI} IndiaAI Mission
- Context (PIB): The government approved the IndiaAI mission.
- Implemented by ‘IndiaAI’ Independent Business Division (IBD) under Digital India Corporation (DIC).
Objectives of IndiaAI Mission
- Establish a comprehensive AI ecosystem for innovation.
- Democratize computing access and improve data quality.
- Develop indigenous AI capabilities and attract top talent.
- Enable industry collaboration and provide startup risk capital.
- Ensure socially impactful AI projects and bolster ethical AI.
Components of IndiaAI Mission
- IndiaAI Compute Capacity: Establishment of a high-end, scalable AI computing ecosystem with 10,000 or more GPUs.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre: Development and deployment of indigenous Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) and foundational models.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: Streamline access to quality non-personal datasets for AI innovation.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative: Promote AI applications in critical sectors sourced from Central Ministries, State Departments, and other institutions.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills: Increase AI courses in educational programs and set up Data and AI Labs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Support and accelerate deep-tech AI startups with streamlined access to funding.
- Safe & Trusted AI: Enable responsible development, deployment, and adoption of AI with indigenous tools and frameworks.
Impact and Benefits
- Propel innovation and build domestic capacities for tech sovereignty.
- Create highly skilled employment opportunities.
- Demonstrate transformative technology for social good and enhance global competitiveness.
{GS3 – S&T – Tech} Bengaluru’s First Driverless Metro Train
- Context (IE): Bengaluru Metro Rail Corporation Limited (BMRCL) received the first set of driverless metro train coaches, which are part of the Communication-based Train Control (CBTC) system.
- The 18.8 km-long line, connecting south of Bengaluru to the city’s tech hub, will be the first to have a driverless train.
- These coaches are manufactured by Chinese firm CRRC Nanjing Puzhen Co Ltd, along with their domestic partners Titagarh Rail Systems Ltd., as part of the Make in India Initiative.
- AI is employed for track monitoring and analyzing sensor data for safety concerns, while cameras on trains aid real-time analysis of visual data for safety measures.
CBTC System
- CBTC technology is a modern communication-based system that uses radio communication to transfer timely and accurate train control information.
- CBTC is “one train talking to another train”.
- It will have Unattended Train Operations (UTO), which enable full automation in tasks like door operations and train movement.
- The Operations Control Centre (OCC) provides enhanced supervision capability.
![PDF] Radio Communication for Communications-Based Train Control (CBTC): A Tutorial and Survey | Semantic Scholar](http://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Picture-1-12.png)
{GS3 – S&T – Tech} Frontier Technology Labs
- Context (PIB): Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog, and Meta announce the launch of Frontier Technology Labs (FTLs) to democratize future technologies and empower youth to innovate.
- FTLs, an advanced version of ATLs, aim to equip students with state-of-the-art infrastructure to innovate using AI, Augmented & Virtual Reality (AR, VR), Blockchain, Cybersecurity, Robotics, 3D Printing, and IoTs.
- Funded by: Meta, with AIM as the knowledge partner.
- The labs will be managed by Meta’s partner 1M1B (One Million for One Billion), further facilitating the initiative’s implementation and impact.
- It aligns with Vision Education to Entrepreneurship initiative, launched in September 2023, aims to connect students, youth, and micro-entrepreneurs.
- Establishing FTLs aligns with AIM’s vision to create a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in schools across India, contributing to the building of a skilled workforce for the future.
Education to Entrepreneurship Initiative
|
{GS3 – S&T – Tech} Pine Needles-based Fuel-making Technology
- Context (PIB): Under the “Adarsh Champawat“ mission, CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum (IIP) and UCOST signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to implement pine needle-based fuel-making technology.
- The MoU aims to drive sustainable development, energy conservation, employment generation, skill development, and women’s empowerment in Champawat, Uttarakhand.
- CSIR-IIP will deploy two major technologies:
- A briquetting unit capable of producing 50 kg per hour based on pine needles.
- 500 units of Improved Cookstoves for rural households.
- The briquettes can be used for domestic cooking and as direct or co-firing fuel in brick kilns and thermal power plants.
- CSIR-IIP has developed improved technology for pine needle briquetting and energy-efficient biomass cookstoves, which can reduce household pollution by 70%.
|
{Prelims – Awards} National Creators Award
- Context (PIB): PM presents the first-ever National Creators Award on 8th March 2024.
- Objective: To recognize creators’ excellence in storytelling, advocacy, sustainability, education, gaming, and impact across domains, fostering positive change.
- 23 winners were selected, including three international creators, reflecting public choice and engagement.
- The award spans 20 categories, including The Best Storyteller Award, The Disruptor of the Year, Celebrity Creator of the Year, Green Champion Award, Best Creator For Social Change, etc.
- Awards: Awards will be presented across 20 distinct categories. In 19 of these categories, a single winner will be selected for each. In International Creator Award category would have three winners.
Eligibility
- Age Requirement: Participants must be 18 years of age or above at the time of nomination.
- Nationality and Residency: 19 categories are open exclusively to individuals of Indian nationality. One category is dedicated to international digital creators
- Platforms: Content must be published on one or more of the following digital platforms: Instagram, YouTube, Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, ShareChat, Koo, Roposo, or Moj
- Language: Content submission can be in English or any other Indian language.
- Nomination Limits: Creators can self-nominate in a maximum of three categories. Those nominating others can nominate in all 20 categories.
Nominations
- Self-Nomination: Creators are allowed to nominate themselves. The nomination must include links to the content on the eligible platforms, description of the content’s impact, etc.
- Nomination Limits: Creators can self-nominate in a maximum of three categories. Those nominating others can propose nominations across all 20 categories.
{Prelims – In News} ChipIN Centre
- Context (PIB): Semiconductor leaders back ChipIN Centre, which will boost India’s semiconductor hub potential through enhanced chip design infrastructure.
- It has been set up at C-DAC Bangalore.
- It acts as one-stop centre to provide semiconductor design tools, fab access, virtual prototyping hardware lab access to fabless chip designers from Startups and Academia.
- It aims to provide access of state-of-the-art Electronic Design Automation (EDA) Tools to 85,000 students at B.Tech, M.Tech and PhD level to design semiconductor chips.
- It aims to bring advanced chip design infrastructure to the doorstep of the semiconductor design community in the country.
{Prelims – In News} Shankaracharya Temple
- Context (PIB): PM paid obeisance to Shankaracharya Hill during his visit to Jammu & Kashmir.

- The Shankaracharya Temple is perched atop Shankaracharya Hill, also called the Hill of Solomon, on the Zabarwan Mountain in Srinagar, Kashmir.
- The temple’s origins date back to around 200 BCE, although the present structure likely dates to the 9th century CE.
- Initially known as Takht-i-Sulaiman, which means Throne of Solomon, it was later renamed after a saint Adi Shakaracharya who attained enlightenment here in AD 750.
- It is considered the oldest temple in the Kashmir valley. It follows the indigenous early Kashmiri style of architecture.
- The early Shikhara style is evident, characterized by a horseshoe arch pattern.
- The temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva and is situated at a height of 1,000 feet above the plain, providing a commanding view of the city of Srinagar.
- Buddhists refer it as the Jyesteshwara Temple or Pas-Pahar.
Kashmiri style of architecture
- The development of Kashmiri architecture can be broadly divided into the early medieval Hindhu phase and Muslim rule from the 14th century onwards.
- It is renowned for its exquisite stone carvings.
- Due to its location on important trade routes, the architectural style is inspired by many foreign sources.
- Main Features of Kashmiri style of architecture:
- Trefoil arched (Gandhara influence)
- Cellular layout and enclosed courtyard
- Straight-edged Pyramidal roof
- Column walls (Greek influence)
- Triangular pediments (Greek influence)
- More number of steps
{Prelims – PIN} Ayya Vaikundar: The Visionary Reformer
- Context (IE): Recently, the TN Governor referred to Ayya Vaikundar as a ‘Sanatan Dharma saviour’, which sparked controversy because Ayyavazhi is distinct from mainstream Hinduism.

- Ayya Vaikundar was born in 1809 CE in a poor Nadar family in the village of Poovandan Thoppu, near the town of Tamaraikkulam, about five miles from Kanyakumari.
- He was the founder of the Ayyavazhi sect, primarily in southern Tamil Nadu.
- While it shares some concepts with Hinduism, it significantly differs in its views on good and evil and dharma.
- He was the first person to lead religious and social reform as a people’s movement.
Teachings
- His teachings focused on equality, fraternity, and the eradication of caste-based discrimination, challenging the established religious and social hierarchies of the time.
- He did not engage in any religious conversion. He spearheaded the reform without distorting the culture and culture of the communities.
- He organised Samapanthi-bhojana or community eateries for people from all backgrounds.
- He also encouraged all devotees to wear turbans and dhotis, promoting equality.
- He established Nizhal Thangals as community worship spaces, which did not have any idol or deity, and only Tamil was used for worship.
- He pioneered education for the lower castes and opposed discriminatory taxes.
- He introduced simplified, inclusive marriage customs without a Brahmin priest or Sanskrit mantras.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)