
Origin and Evolution of Life on Earth
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Origin of Life on Earth – Evolution of Life on Earth – Adaptive Radiation – Biological Evolution – Origin and Evolution of Man – Timeline of Evolution.
Source | Credits | Picture Credits: NCERT General Science
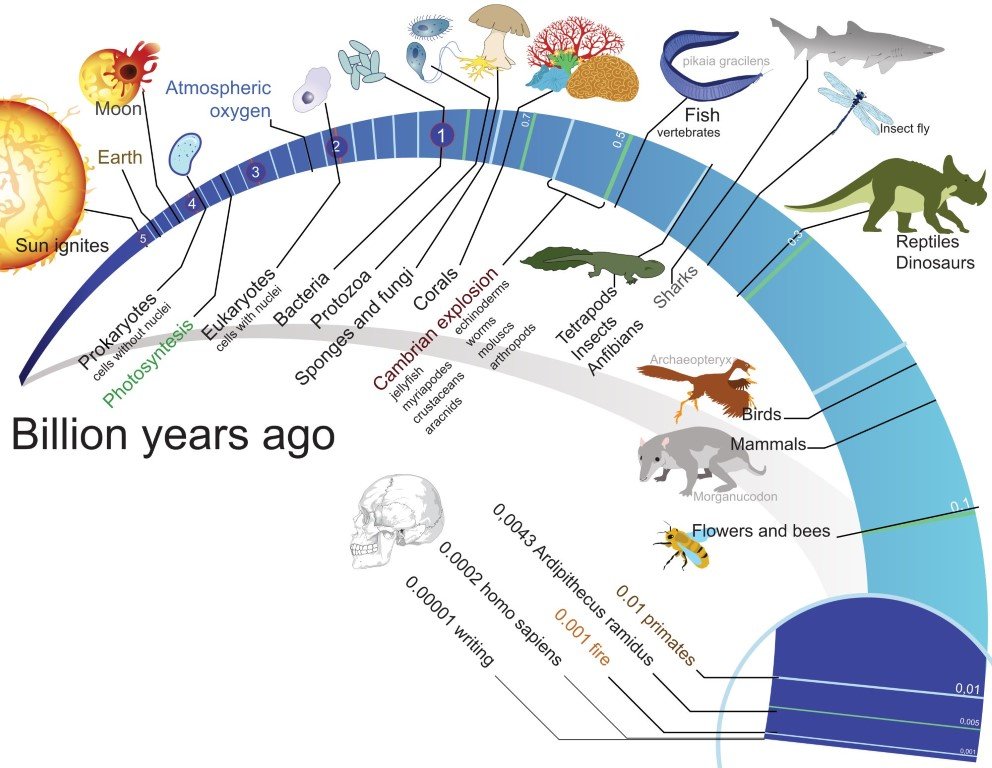
Origin Of Life on Earth
- The universe is very old – almost 13 billion years old. Huge clusters of galaxies comprise the universe.
- The Big Bang theory attempts to explain to us the origin of universe. It talks of a singular huge explosion unimaginable in physical terms.
- The universe expanded and hence, the temperature came down. Hydrogen and Helium formed sometime later.
- The gases condensed under gravitation and formed the galaxies of the present day universe.
- In the solar system of the milky way galaxy, earth was supposed to have been formed about 5 billion years back.
- There was no atmosphere on early earth. Methane, carbondioxide and ammonia released from molten mass covered the surface.
- The UV rays from the sun brokeup water into Hydrogen and Oxygen and the lighter H2 escaped. Oxygen combined with ammonia and methane to form water, CO2 and others.
- The ozone layer was formed. As earth cooled, the water vapor fell as rain, to fill all the depressions and form oceans.
- Life appeared 500 million years after the formation of earth, i.e., almost four billion years back. Some scientists believe that the life came from outerspace.
- The first non-cellular forms of life could have originated 3 billion years back. They would have been giant molecules (RNA, Protein, Polysaccharides, etc.). These capsules reproduced their molecules perhaps.
- The first cellular form of life did not possibly originate till about 2000 million years ago. These were probably single-cells. All life forms were in water environment only.
- The version of a biogenesis, i.e., the first form of life arose slowly through evolutionary forces from non-living molecules is accepted by majority.
- However, once formed, how the first cellular forms of life could have evolved into the complex biodiversity of today is the fascinating story that will be discussed below.
Evolution of Life on Earth
- Evolutionary Biology is the study of history of life forms on earth.
- Homology indicates common ancestry. In the context of biology, homology is the existence of shared ancestry between a pair of structures, or genes, in different species.
- A common example of homologous structures in evolutionary biology are the wings of bats and the arms of primates.
- Homology is based on divergent evolution whereas Analogy refers to a situation exactly opposite [convergent evolution].
- Wings of butterfly and of birds look alike. They are not anatomically similar structures though they perform similar functions.
- Hence, analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution – different structures evolving for the same function and hence having similarity.
- Other examples of analogy are the eye of the octopus and of mammals or the flippers of Penguins and Dolphins.
- One can say that it is the similar habitat that has resulted in selection of similar adaptive features in different groups of organisms but toward the same function: Sweet potato (root modification) and potato (stem modification) is another example for analogy.
Q1. Which one of the following is a modified stem? [1996]
- Carrot
- Sweet potato
- Coconut
- Potato
Carrot → Modified root
Coconut → Modified seed
Adaptive Radiation
- During his journey, Charles Darwin went to Galapagos Islands. There he observed an amazing diversity of creatures.
- Of particular interest, small black birds later called Darwin’s Finches amazed him.
- He realized that there were many varieties of finches in the same island. All the varieties, he conjectured, evolved on the island itself.
- From the original seed-eating features, many other forms with altered beaks arose, enabling them to become insectivorous and vegetarian finches. This process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography (habitats) is called adaptive radiation.
Biological evolution
- The essence of Darwinian theory about evolution is natural selection. The rate of appearance of new forms is linked to the life cycle or the life span.
- Microbes that divide fast have the ability to multiply and become millions of individuals within hours.
- A colony of bacteria (say A) growing on a given medium has built- in variation in terms of ability to utilise a feed component.
- A change in the medium composition would bring out only that part of the population (say B) that can survive under the new conditions.
- In due course of time this variant population outgrows the others and appears as new species. This would happen within days.
- For the same thing to happen in a fish or fowl would take million of years as life spans of these animals are in years.
- Hence, there must be a genetic basis for getting selected and to evolve.
- Another way of saying the same thing is that some organisms are better adapted to survive in an otherwise hostile environment. Adaptive ability is inherited. It has a genetic basis. Fitness is the end result of the ability to adapt and get selected by nature.
A Brief Account of Evolution
- About 2000 million years ago (mya) the first cellular forms of life appeared on earth.
- The mechanism of how non-cellular aggregates of giant macromolecules could evolve into cells with membranous envelop is not known.
- Some of these cells had the ability to release O2. The reaction could have been similar to the light reaction in photosynthesis where water is split with the help of solar energy captured and channelized by appropriate light harvesting pigments.
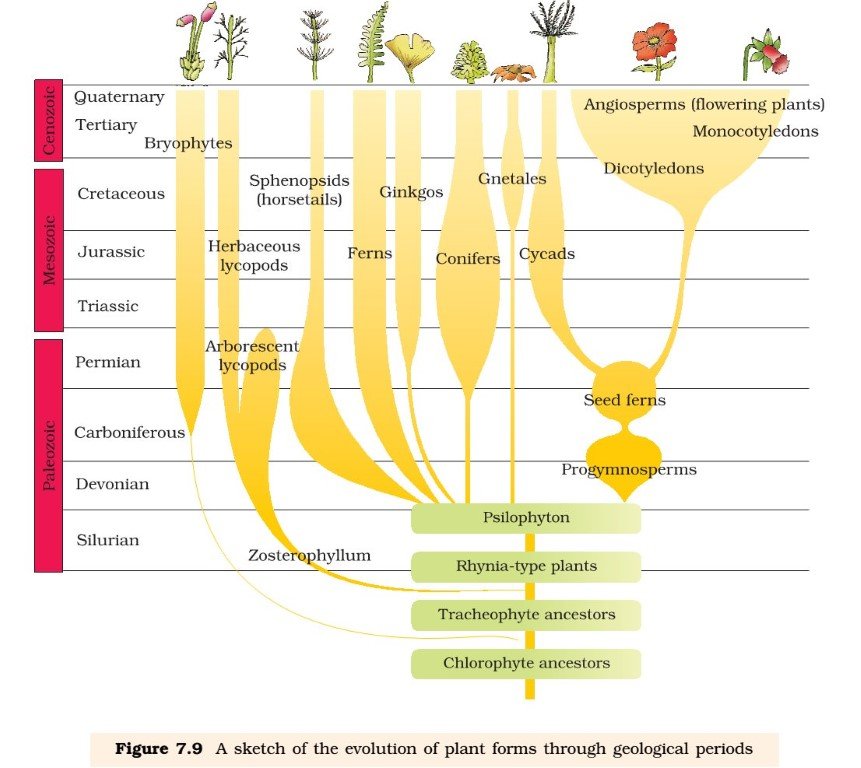
- Slowly single-celled organisms became multi-cellular life forms. By the time of 500 mya, invertebrates were formed and active. Jawless fish probably evolved around 350 mya. Sea weeds and few plants existed probably around 320 mya.
- We are told that the first organisms that invaded land were plants. They were widespread on land when animals invaded land.
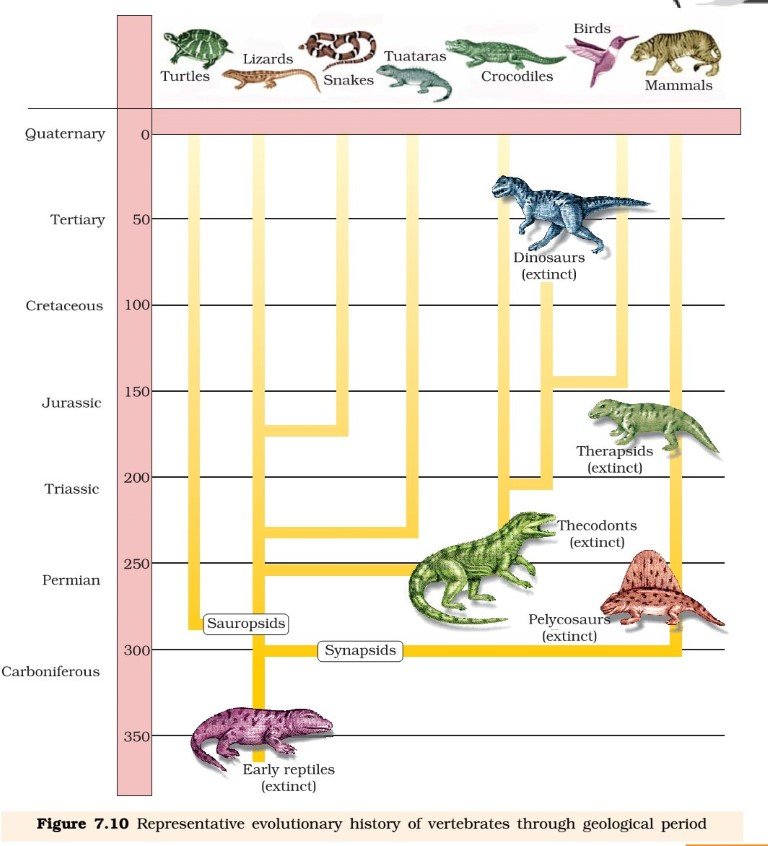
- Fish with stout and strong fins could move on land and go back to water. This was about 350 mya. These animals called lobefins evolved into the first amphibians that lived on both land and water. These were ancestors of modern day frogs and salamanders.
- The amphibians evolved into reptiles. They lay thick-shelled eggs which do not dry up in sun unlike those of amphibians. Again we only see their modern day descendents, the turtles, tortoises and crocodiles.
- In the next 200 million years or so, reptiles of different shapes and sizes dominated on earth. Giant ferns (pteridophytes) were present along with reptiles but they all fell to form coal deposits slowly.
- Some of these land reptiles went back into water to evolve into fish like reptiles probably 200 mya (e.g. Ichthyosaurs).
- The land reptiles were, of course, the dinosaurs. The biggest of them were Tyrannosaurus and Ultrasaurus.
- About 65 mya, the dinosaurs suddenly disappeared from the earth. We do not know the true reason. Some say climatic changes killed them. Some say most of them evolved into birds. The truth may live in between. Small sized reptiles of that era still exist today.
- The first mammals were like shrews. Their fossils are small sized. Mammals were viviparous and protected their unborn young inside the mother’s body.
- Mammals were more intelligent in sensing and avoiding danger at least. When reptiles came down mammals took over this earth. T
- here were in South America mammals resembling horse, hippopotamus, bear, rabbit, etc. Due to continental drift, when South America joined North America, these animals were overridden by North American fauna. Due to the same continental drift pouched mammals of Australia survived because of lack of competition from any other mammal.
Q2. With reference to the evolution of living organisms, which one of the following sequences is correct? [2009]
- Octopus-Dolphin-Shark
- Pangolin-Tortoise-Hawk
- Salamander-Python-Kangaroo
- Frog-Crab-Prawn
Answer: Evolution == Single cellular → Multicellular → Fishes → Amphibians → Reptiles → Birds → Mammals.
- Octopus (Mollusc) – Dolphins and Whales (Mammals) – Shark (Fish)
- Pangolin (Mammal – always in news as it is an endangered one – its meat is consumed in some South-East Asian countries) – Tortoise (Reptile) – Hawk (Bird)
- Salamander (Amphibian) – Python (Reptile) – Kangaroo (Mammal)
- Frog (Amphibian) – Crab (Crustaceans) – Prawn (Crustaceans)
Picture Credits: Wikipedia
Origin and Evolution of Man
- About 15 mya, primates called Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus were existing. They were hairy and walked like gorillas and chimpanzees. Ramapithecus was more man-like while Dryopithecus was more ape-like.
- Few fossils of man-like bones have been discovered in Ethiopia and Tanzania. These revealed hominid features leading to the belief that about 3-4 mya, man-like primates walked in eastern Africa. They were probably not taller than 4 feet but walked up right.
- Two mya, Australopithecines probably lived in East African grasslands. Evidence shows they hunted with stone weapons but essentially ate fruit.
- Some of the bones among the bones discovered were different. This creature was called the first human-like being the hominid and was called Homo habilis. The brain capacities were between 650-800cc. They probably did not eat meat.
- Fossils discovered in Java in 1891 revealed the next stage, i.e., Homo erectus about 1.5 mya. Homo erectus had a large brain around 900cc. Homo erectus probably ate meat.
- The Neanderthal man with a brain size of 1400cc lived in near east and central Asia between 1,00,000-40,000 years back. They used hides to protect their body and buried their dead.
- Homo sapiens arose in Africa and moved across continents and developed into distinct races. During ice age between 75,000-10,000 years ago modern Homo sapiens arose.
- Pre-historic cave art developed about 18,000 years ago. Agriculture came around 10,000 years back and human settlements started. The rest of what happened is part of human history of growth and decline of civilisations.










Sir
Here it is written that Tyrannosaurus were the biggest reptile… But it’s not…. Rather Ultrasaurus were the biggest reptile.. It was not just the biggest dinosaur but also the the biggest land animal.. It was about 50 m in length…. Please correct me if I m wrong…
Its given in NCERT.
But I verified over the internet and found that Ultrasaurus is much bigger. So Corrected!