Liver Fluke Parasite
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
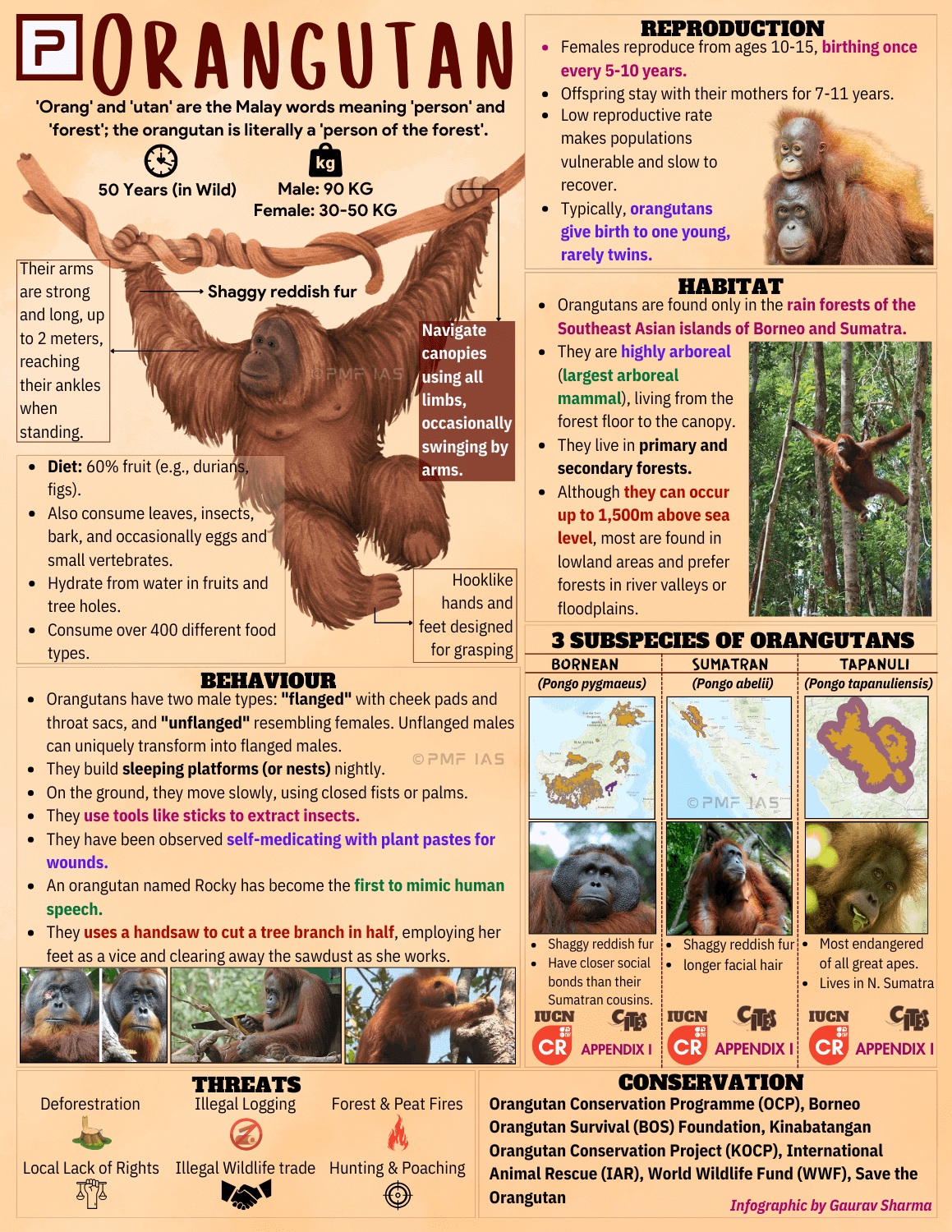
- Context (DTE): Liver fluke parasite found in southern California’s Colorado River.
- Also called Heterobilharzia americana, it infects dogs when they wade or swim in freshwater inhabited by infected snails, which serve as the intermediate host.
- The parasite enters the dog’s body through the skin and migrates to the veins of the intestinal lining.
- It then develops into an adult and mates, laying eggs that can affect the lungs, spleen, liver, and heart.
- This condition is known as canine schistosomiasis, causing severe debilitation.
Liver fluke
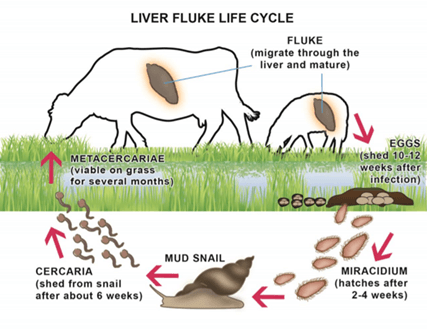
- Liver flukes are parasitic worms that cause a disease.
- Habitat: It primarily parasitizes the liver of various mammals, including humans. It can also be found in bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver parenchyma.
- Pathological Effects: Liver flukes induce pathological lesions in the liver and associated organs, leading to parasitic diseases.
- Movement: They are capable of moving along the blood circulation, allowing them to migrate to different parts of the liver and associated structures.
- Life Cycle: Liver flukes have complex life cycles that typically involve 2 or 3 different hosts. They have free-living larval stages in water, indicating an aquatic phase of their life cycle.
Colorado River
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)