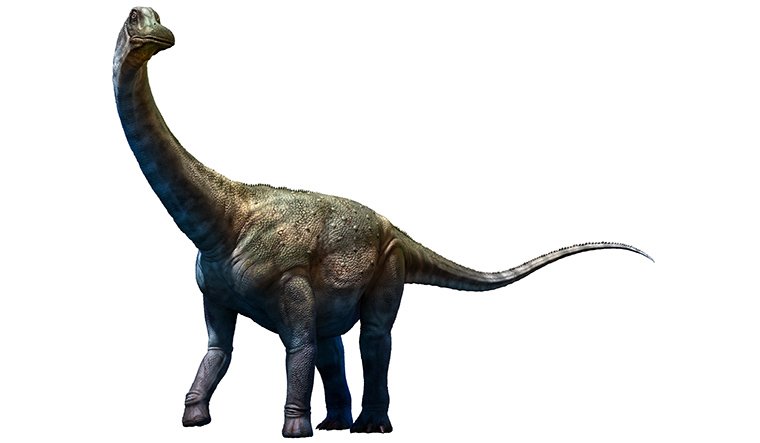Current Affairs September 20, 2023: Jainism, Samvatsari, India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, Khalistan Movement, Bureau of Indian Standards, Women’s Reservation Bill, Bima Sugam platform, Operation Sajag, Vibhav Anti-Tank Munition, MOXIE, Tharosaurus Indicus
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – A&C – Religion – 2023/09/20} Samvatsari
- Context (PIB | TOI): PM greets people on the occasion of Samvatsari.
- Samvatsari is an auspicious day for the Jain community.
- It is celebrated as the last day of the Paryushan festival.
- During this day, people say “Michami Dukkadam” and seek forgiveness from others.
|
Jainism (GS1, His, AIH)
- Jainism is an ancient religion based on the teachings of 24 Tirthankaras (or great teachers).
- Rishabnath (or Adinath) was the first Tirthankara and was the founder of Jainism.
- Jainism came into prominence in the 6th century B.C. when Lord Mahavira propagated the religion.
- Lord Mahavira was the 24th and the last Tirthankara.
- The word ‘Jain’ is derived from jina or jaina, meaning the ‘conqueror’.
Vardhamana Mahavira
|
Jain Philosophy
Three Jewels or Triratna
- Jainism believes that salvation can be attained by following the three-fold path:
- Right Faith (Samyakdarshana)
- Right Knowledge (Samyakjnana)
- Right Action (Samyakcharita)
- One of the three cannot exist exclusive of the others, and all are required for spiritual liberation.
Five Doctrines of Jainism
- To attain salvation, Jains must follow five doctrines:
- Ahimsa (non-violence)
- Satya (truthfulness)
- Asteya (not stealing)
- Aparigraha (non-acquisition)
- Brahmacharya (chaste living) — propounded by Mahavira.
Anekantavada and Syadvada
Anekantavada
- It is the doctrine that the ultimate truth and reality are complex and have multiple aspects.
- It believes in non-absolutism or pluralism, which means no single, specific statement can describe the nature of existence and the absolute truth.
Syadvada
- It is the doctrine that all judgments are conditional, holding good only in certain conditions, circumstances, or senses.
- According to it, ways of looking at a thing (called naya) are infinite in number, so there will be infinite judgments. Hence, all judgments are relative.
Sects of Jainism
- There are two major sects in Jainism: Digambaras (sky-clad) and Svetambaras (white-clad).
| Digambaras | Svetambaras |
| Believes in complete nudity, and males do not wear clothes. Female monks wear unstitched plain white sarees and are called Aryikas. | Monks wear simple white clothing and carry a begging bowl, a brush to remove insects from their path, books and writing materials with them. |
| Follow the preachings of Mahavira, i.e., they believe in all five constraints (Ahimsa, Satya, Asteya, Aparigraha and Brahmacharya). | Follow the preachings of Parshvanatha, i.e., they believe in only four constraints (except Brahmacharya). |
| Bhadrabahu was an exponent of the Digambara sect, and he moved to Karnataka along with his disciples after predicting a long famine. | Sthulabhadra was an exponent of the Svetambara sect, and he and his disciples stayed in Magadha. |
| Believe that women cannot be Tirthankaras and say that Malli was a man. | Believe Tirthankaras can be men or women, and say that Malli began her life as a princess. |
| Believe that Tirthankaras did not marry. | Believe that the 23rd & 24th Tirthankara did marry. |
| Monasticism rules are more rigid. | Monasticism rules are less rigid. |
| Sub-sects: Mula Sangh, Terapanthi, Taranpathi, and Bispanthi | Sub-sects: Sthanakavasi and Murtipujaka |
{GS2 – IR – Groupings – 2023/09/20} India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC)
- Context (IE): IMEC has immense potential to put India, the Middle East and Europe on the collective path to growth, triggering regional and global cooperation.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
- IMEC is a network of transport corridors (railway lines and sea lanes).
- It consists of two separate corridors:
- East Corridor, which connects India to West Asia.
- North Corridor that connects West Asia to Europe.
- It is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure Investment.

Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment
- It is a joint initiative to fund infrastructure projects in developing countries.
- It was launched by G7 countries in 2022.
- It aims to counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
|
Significance of IMEC
- Ancient Trade Route Revival: IMEC resurrects historic trade routes, notably the Red Sea, fostering cultural and economic exchange.
- India’s Reaffirmed Role: IMEC underscores India’s historical significance in global trade networks.
- Geopolitical Influence: IMEC’s establishment elevates the geopolitical importance of connected regions, including India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Challenges of IMEC
- Infrastructure Development: IMEC faces complexities in building essential infrastructure at major Gulf and Mediterranean ports.
- Cross-Border Connectivity: Achieving seamless cross-border connectivity demands international cooperation, particularly in the Middle East.
- Environmental Sustainability: Addressing environmental considerations, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, is crucial for IMEC’s long-term viability.
- Coordination and Financing: Effective coordination among participating nations and securing financing are pivotal challenges for the corridor’s sustainability.
{GS2 – IR – India-Canada – 2023/09/20} India-Canada and Khalistan Movement
- Context (TH): Canadian PM Justin Trudeau alleged a potential link between the GoI and the killing of pro-Khalistan leader Hardeep Singh Nijjar.
- Canada expelled a diplomat from the Indian High Commission in Ottawa.
- In response, India also expelled a Canadian diplomat.
India-Canada Bilateral Relations
- India-Canada bilateral relations elevated to a strategic partnership in 2015.
People-to-People Relations
- Canada hosts one of the largest Indian Diasporas in the world.
- Seven lakh NRIs & 1.6 million people of Indian origin live in Canada (total population 38.8 million).
- The present House of Commons (total strength of 338) has 19 MPs of Indian origin.
Economic Relations
- India’s total trade with Canada (goods and services) in 2021-22 was US$11.68 billion.
- Canadian Pension Funds have substantial investments in India.
- India became the 10th largest trading partner of Canada in 2022.
Agriculture
- The bilateral MoU on agriculture cooperation was signed in 2009.
- A Joint Working Group has been set up under the MoU.
- A Joint Working Group for Pulses has been set up separately.
- Canada is one of India’s largest sources of pulses (in 2021, almost 30% of our total pulses imports were from Canada).
India-Canada strained ties
- India criticised the Canadian government for:
- Proximity to individuals sympathetic to Khalistan activities.
- Incitement of violence against Indian diplomats
- Damage to diplomatic premises
- Threats to the Indian community and places of worship
- Extremist elements in Canada and their nexus with:
- Organised crime
- Drug syndicates
- Human trafficking
- In response to India’s concerns, Justin Trudeau stated that Canada would defend:
- Freedom of expression
- Peaceful protest and Conscience
- The defence of Khalistanis under the aspect of “free speech” is selective and hypocritical.
Domestic Politics Impacting Relations
- Trudeau’s domestic political considerations have negatively impacted Canada’s relations with India.
- Trudeau’s Liberal Party relies on the support of Jagmeet Singh’s New Democratic Party.
- Singh’s party includes members with ties to Khalistani extremism.
Effect of strained relations
- India and Canada paused their Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) negotiations.
- Canada cancelled a trade mission to India scheduled to arrive in Mumbai in October.
Khalistan Movement
- The Khalistan movement is a fight for a separate, sovereign Sikh state in present-day Punjab (both India and Pakistan).
- The movement was crushed in India following Operation Blue Star (1984).
- It continues to evoke sympathy and support among sections of the Sikh population, especially in the Sikh diaspora in countries such as Canada, the UK, and Australia.
Timeline of the Khalistan Movement
India’s Independence and Partition
- The movement’s origins have been traced back to India’s independence and subsequent partition along religious lines.
- The Punjab province saw some of the worst communal violence.
- After the partition, the following cities went to Pakistan:
- Lahore (capital of Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s great Sikh Empire)
- Nankana Sahib (birthplace of Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism)
Demand for Autonomous Punjabi Suba
- At the time of Independence, the Punjabi Suba Movement demanded the creation of a Punjabi-speaking state. In 1966, Punjab was reorganised to reflect the Punjabi Suba demand.
- The erstwhile Punjab state was trifurcated into:
- Hindi-speaking, Hindu-majority states of Himachal Pradesh and Haryana
- Punjabi-speaking, Sikh-majority Punjab.
Anandpur Sahib Resolution
- In 1973, Akali Dal in Punjab presented the Anandpur Sahib Resolution.
- It asked Punjab to have more control over its affairs, decide its own borders, and make its own rules.
|
Rise of Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale
- Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale emerged and positioned himself as the authentic voice of the Sikhs.
Dharam Yudh Morcha
- In 1982, Bhindranwale launched a civil disobedience movement (Dharam Yudh Morcha) with support from the Akali Dal’s leadership.
- The movement was geared towards the demands articulated in the Anandpur Sahib Resolution.
- He took up residence inside the Golden Temple, directing demonstrations and clashes with the police.
- GoI declared the movement tantamount to secession.
Operation Bluestar
- Operation Blue Star began on June 1, 1984, to flush out militants from the Golden Temple and neutralise Bhindranwale.
- Bhindranwale was killed, and the Golden Temple was freed of militants.
- It gravely wounded the Sikh community worldwide and galvanised the demand for Khalistan.
Current Status
- Punjab has been peaceful for a long time, but the Khalistan movement still exists in some Sikh communities abroad. Many in the Sikh diaspora still support Khalistan.
- Some still support Khalistan due to memories of the troubled 1980s.
{GS2 – MoCAFPD – Initiatives – 2023/09/20} Standard Clubs
- Context (PIB): The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has established 6,467 Standard Clubs in educational institutions across India.
- The Standard Clubs initiative was launched in 2021 under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution (MoCAFPD).
- It sensitises young members of society to the importance of standards in improving quality of life.
Eligibility
- Students of class IX and above and studying science subjects are eligible to be part of the Clubs.
- Standards Clubs can be formed in any educational institution in India comprising teachers (mentors) and students (members) from:
- High and Higher Secondary schools
- Engineering colleges
- Science colleges
- Polytechnics
- Professional institutions
- A minimum of fifteen student members shall be required to form a Standards Club.
Objectives
- Youth Sensitization: Instil an appreciation for quality, standards, and scientific temperament among young individuals.
- Quality Consciousness: Promote quality-consciousness rooted in standardisation principles as a driver of economic development.
Features
- Diverse Activities: Students participate in standards writing competitions, quizzes, debates, essay writing, and industrial visits.
- Financial Support: The financial support for Standards Clubs in:
- Engineering Institutions: limited to a maximum of Rs 1,00,000/- per year.
- Other than Engineering Institutions: limited to a maximum of Rs 10,000/- per year.
- Laboratory Grants: High and higher secondary Government Schools with Standard Clubs can receive up to Rs. 50,000 for upgrading Science Labs.
- ‘Manak Kaksha’ Initiative: Provides up to Rs. 1,00,000 to establish innovative learning spaces in government institutions.
- Under it, one room in the school shall be renovated by providing basic amenities like smart TVs, audio video systems, proper illumination, etc.
{GS2 – Vulnerable Sections – Women – 2023/09/20} Women’s Reservation Bill
- Context (TH): The Women’s Reservation Bill was introduced in LS.
128th Constitution Amendment Bill (Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam)
- It proposes to introduce three new articles:
- Article 330A of IC
- Article 332A of IC
- Article 334A of IC
- It provides the reservation of one-third of seats in the LS and state Assemblies for women for fifteen years.
- There will be a quota for SC/STs within the reserved seats for women.
- The seats reserved for women will be rotated after every delimitation exercise.
- It will be implemented after the delimitation exercise is completed based on the figures of the first census after this constitutional amendment.
- The provisions of this amendment also apply to the legislative assembly of the NCT of Delhi.
|
Timeline
- In 1987, Rajiv Gandhi’s government constituted a 14-member committee under Margaret Alva.
- The committee presented the National Perspective Plan for Women, 1988-2000.
- The committee recommended the reservation of seats for women in elected bodies.
- These recommendations paved the way for the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts (P V Narasimha Rao government).
- The amendments mandated the reservation of one-third of seats for women in
- Panchayati Raj institutions
- Urban local bodies.
- Deve Gowda’s government brought the first women’s reservation Bill in 1996.
- In 2008 the UPA government introduced the Constitution (108th Amendment) Bill in RS.
- The Bill sought to reserve one-third of all seats for women in LS and the state legislative Assemblies.
- The RS passed the Bill on March 9. However, it was never brought to LS, and it lapsed with the dissolution of the LS.
- In May 2013, the Ministry of Women and Child Development constituted a committee on the status of women.
- The committee recommended at least 50 per cent reservation of seats for women in:
- Local bodies
- State Legislative Assemblies
- Parliament
- Ministerial levels
- All government decision-making bodies.
- The committee recommended at least 50 per cent reservation of seats for women in:
Women’s representation in Parliament
- Currently, Women MPs constitute less than 15% of LS members (78/545) as against the global average of 25.8%.
|
Women’s representation in Panchayat
- Article 243D of IC mandates a reservation of a minimum of one-third of seats to women.
- In 2006, Bihar became the first state to provide 50% reservation to women at the Panchayat level.
- Currently, at least 20 Indian states have given 50% reservation to women at the Panchayat.
|
Benefits of feminisation of political governance
- Diverse Perspectives: Women bring more diversity to decision-making.
- Gender-Specific Issues: Women-related issues (safety of women, nutrition) will come to the forefront.
- Equality and Inclusivity: It promotes gender equality and inclusivity in governance.
- Enhanced Social Services: Female representation often leads to improved education, healthcare, and social services as these issues are given higher priority.
- Reducing Stereotypes: Women in politics help to break down gender stereotypes and biases.
- Peace and Conflict Resolution: Women’s involvement in politics contributes to peacebuilding and conflict resolution efforts.
{GS3 – Agri – Crops – 2023/09/20} Basmati Reaping the Rewards of Research
- Context (IE): Annual exports of basmati rice from India have soared by nearly $5 billion due to the contribution of scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI).
- Significance: India’s basmati rice export success is a testimony to what good public sector breeding and collaboration with industry can achieve.

Progress of Basmati Rice in India
First Revolution
- Till the late 1980s, Indian farmers grew traditional basmati varieties having tall plants, prone to lodging and low yielding. E.g., Taraori (or Karnal Local) and Dehraduni (Type-3).
- In 1989, IARI scientists released the Pusa Basmati-1 (PB-1) variety, which has short plants that did not lodge, yielded high, and matured in fewer days.
- Result: Basmati rice export fetched $400-450 million annually, with PB-1’s share at roughly 60%.
|
Second Revolution
- In 2003, IARI released Pusa Basmati-1121 (PB-1121), whose unique selling point was grain quality.
- It was billed as the world’s longest rice grain, and more volume of rice is obtained from a few kernels.
- KRBL Ltd realised its true potential by creating the India Gate Classic brand for export.
- Result: Basmati rice export fetched $4.9 billion annually, with PB-1121’s share at roughly 70%.
|
Third Revolution
- In 2013, released Pusa Basmati-1509 (PB-1509) which was high-yielding like PB-1 and had good grain quality like PB-1121. Moreover, PB-1509’s maturing time was much less (115-120 days).
- Result: This early-maturing high-yielding enables farmers to take up an extra crop now.
Breeding for Disease Resistance
- The improved basmati varieties have also become susceptible to diseases.
- So, in the last few years, IARI scientists have focused on preserving the yield gains from their improved basmati varieties by incorporating genes for disease resistance.
- To control it, scientists have sought to transfer genes from landrace cultivars and wild relatives of paddy that are resistant to diseases.
- Recently, five new varieties of seeds of Basmati rice were developed by the IARI.
- Three varieties resist bacterial leaf blight (BLB) and fungal blast (leaf and collar).
- Two varieties resist herbicides and save water using the Direct Sowing of Rice (DSR) method.
|
| IARI New Varieties | Features |
| Pusa Basmati 1847 |
|
| Pusa Basmati 1885 | |
| Pusa Basmati 1886 | |
| Pusa Basmati 1979 |
|
| Pusa Basmati 1985 |
Concerns with Basmati Rice Cultivation in India
No Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- There is no minimum support price (MSP) for basmati paddy. Though the basmati cultivators earn more by selling it at market price, they are also exposed to the vagaries of the market and climate. So, without MSP, these farmers are more vulnerable to adverse situations.
Limited Domestic Market
- Most Indian basmati rice is exported, and its domestic market is limited.
- Government policies and international situations control the export of basmati rice. Recently, GoI has restricted the export of basmati shipments priced below $1,200 per tonne.
- Such policies without domestic demand will adversely affect the farmers.
Adulteration
- Adulteration of basmati includes undeclared blending of non-basmati varieties of rice.
- Such practices will lower the reputation of Indian basmati in the market.
Basmati Rice
Diseases of Basmati RiceBacterial Leaf Blight (BLB) Disease
Blast (Leaf and Collar) Disease
Indian Agriculture Research Institute (IARI)
|
{GS3 – IE – Insurance – 2023/09/20} Bima Sugam platform
- Context (IE I IE): The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) claims that the proposed Bima Sugam is a “game changer” and a “UPI moment” for the insurance segment.
- Bima Sugam is an online platform where customers can choose a suitable scheme from multiple options given by various companies.
- All insurance requirements, including those for life, health, and general insurance (including motor and travel), will be met by Bima Sugam.
- This platform will help in the settlement of claims, whether it’s health coverage or death claims, in a paperless manner based on policy numbers.
- Life insurance and general insurance companies will own a 47.5 per cent stake each, while brokers and agent bodies will own 2.5 per cent each in the Bima Sugam Platform.
Bima Sugam platform – Role and Utility
- Single window for policyholders to manage insurance coverage.
- End-to-end solutions for purchase, service, and settlement.
- Real-time access to validated data for insurance companies.
- Intermediary interface to sell policies and reduce paperwork.
{GS3 – IS – Security Forces – 2023/09/20} Operation Sajag
- Context (PIB I TP): The Indian Coast Guard recently conducted ‘Operation Sajag‘ a Coastal Security Drill along the Western Coast.
- This operation involves all stakeholders of the Indian coastal security construction, including 118 ships from Customs, Marine Police, Ports, and the Indian Navy.
- It revalidates the coastal security mechanism, raises awareness among fishermen, and involves extensive document verification of sea vessels. Biometric card readers are used for this purpose.
Indian Coast Guard
- It is an armed force that protects India’s maritime interests and enforces maritime law over the territorial waters of India, including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone.
- History: it was established in 1978 by the Coast Guard Act 1978 as an independent armed force.
- Parent ministry: It operates under the Ministry of Defence.
- Administration: The organisation is headed by the Director General of the Indian Coast Guard.
{GS3 – S&T – Defence – 2023/09/20} Vibhav Anti-Tank Munition
- Context (TOI): Vibhav Anti-Tank Munition is a self-neutralising anti-tank mine designed and developed indigenously in a joint venture with the DRDO in India.
- It is a point-attack anti-tank munition designed to immobilise all enemy armoured vehicles.
- The Kalyani Group produces the munition for the Indian Army.

Key Features of Vibhav Anti-Tank Munition
- Laid manually or mechanically.
- Safety mechanisms for handling, lethality, and reliability.
- Integrated safety measures for operator protection.
- Self-neutralizing with mechanical timers after 120 days.
- 10-year storage life without special requirements.
{GS3 – S&T – Space – 2023/09/20} MOXIE Generates Oxygen in Mars
- Context (NDTV): NASA’s MOXIE (Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilisation Experiment) has successfully converted Martian CO2 into oxygen.
- Oxygen produced is of 98% purity or better, making it suitable for both fuel and breathing purposes.
- MOXIE is aboard the NASA’s Perseverance Rover.
Perseverance rover
- It is a part of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission and has landed on Mars in 2021.
- The rover is exploring Jezero Crater on Mars in search of signs of ancient life on Mars.
{Prelims – In News – 2023/09/20} Tharosaurus Indicus
- Context (IE | TH): The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has discovered the fossils of a sauropod in Jaisalmer. A dinosaur egg fossil is also found in Jethwai-Gajroop Sagar hills in Jaisalmer.
- The sauropod dinosaur is named ‘Tharosaurus indicus’ with Tharo deriving from the Thar desert, saurus from the Greek ‘sauros’, or lizard, and indicus from its Indian origin.
- Significance of the discovery:
- This is the first diplodocoid sauropod fossil to have been found in India.
- This is the oldest fossil of diplodocoid sauropod found to date (167 million years old).
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)