Satellite-Based Internet Connectivity
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): SpaceX launches first ‘direct-to-cell’ Starlink satellites.
- Satellite based internet connectivity refers to the use of artificial satellites positioned in space to facilitate communication over long distances.
Working Mechanism
- Satellite communication works by using satellites to relay signals between two points on Earth.
- The satellites are placed in orbit around the Earth, and they act as a mediator between the two points.
- When a signal is sent from one point to the satellite, the satellite amplifies the signal and retransmits it to the other point.

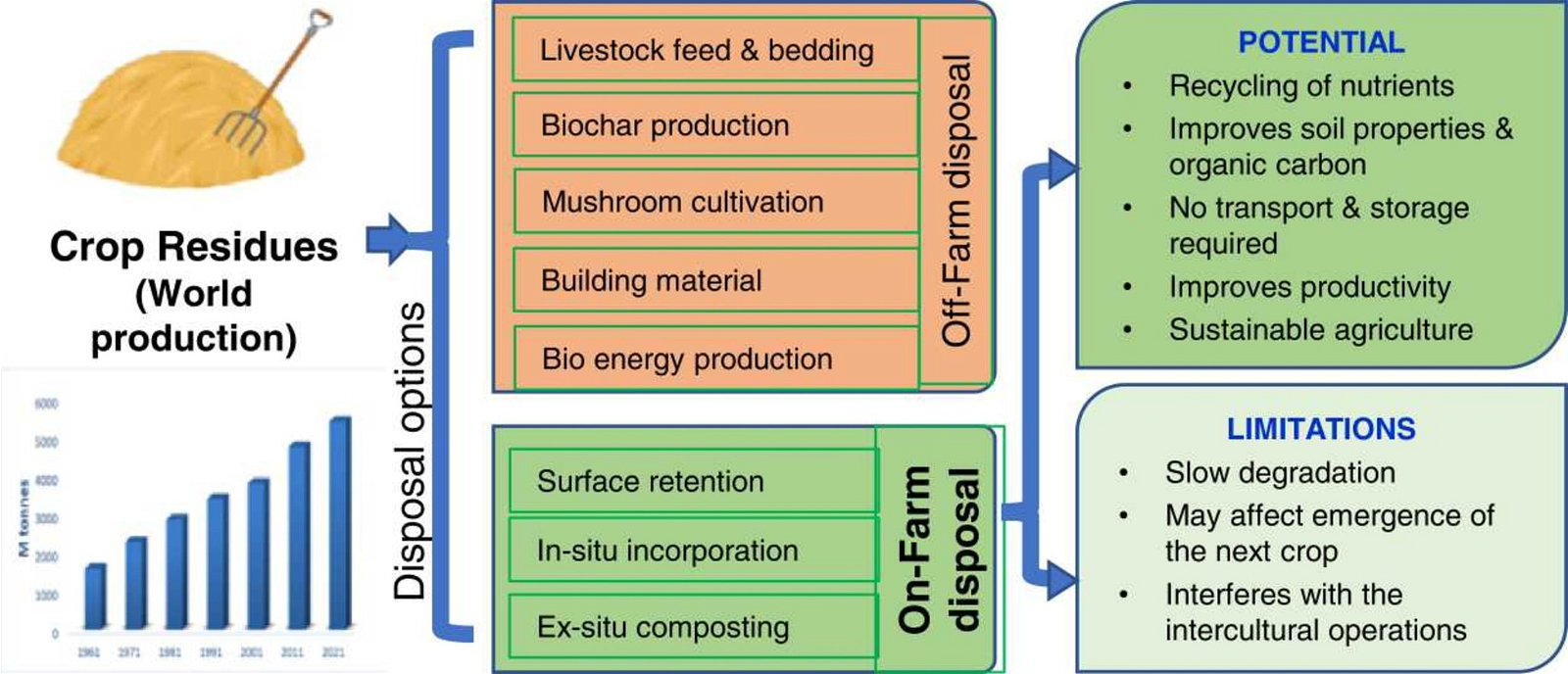
Benefits
- Global coverage: Satellites can provide coverage to remote and under served areas where terrestrial infrastructure is limited or non-existent.
- Scalability: Satellite networks can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate increasing user demand, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Security: Satellite communication can be more secure than terrestrial communication, as it is less susceptible to interception.
- Reliable communication: Independence from terrestrial infrastructure enables seamless communication in challenging terrains making them more resilient to disasters or physical communication.
- Low Latency makes satellite communication more suitable for applications that require real-time interaction, e.g. high-frequency trading, and teleconferencing.
Challenges associated with space satellite communication
- High cost involved for deployment, operation, and launching satellites into space, building ground station infrastructure, and associated maintenance expenses.
- Risk of Debris: Satellite communication requires a network of satellites for internet coverage raising the problem of space debris and their collision (Kessler Syndrome) hindering space exploration.
- Signal Interference: Weather conditions like storms and other atmospheric disturbances can degrade the quality and reliability leading to disruptions, reduced data rates, or signal loss.
- Latency: Transmitting signals from Earth to satellites in space and back results in a noticeable delay in communication making it problematic for real-time applications.
- Limited bandwidth: They can only transmit a limited amount of data at a time posing problem for applications that require high bandwidth, e.g. streaming video or online gaming.
- Coverage gaps: Physical features like mountains, tall buildings, etc can obstruct the requirement of a clear line of sight path leading to signal attenuation.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)