Crop Residue Management (CRM) Guidelines 2023-24
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (DTE): The GoI released Crop Residue Management (CRM) operational guidelines 2023-24 for UP, Haryana, Punjab, MP and the NCT of Delhi in July 2023.
- It aims to decrease pollution from stubble burning and involve more farmers in supplying agri-residue to support bioenergy plants.
Release of major pollutants in to the atmosphere during residue burning |
Crop Residue Management Operational Guidelines 2023-24
- Techno-commercial pilot projects for the Paddy Straw Supply Chain will be established under bilateral agreements between the Beneficiary/Aggregator and industries using paddy straw.
- Beneficiary/Aggregator means Farmers, rural entrepreneurs, Cooperative Societies of Farmers, Farmers Producer Organizations (FPOs), and Panchayats.
- Financial Assistance: Government will provide financial aid for machinery & equipment capital costs.
- The industry and the beneficiary can finance the working capital together or through sources like the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund, NABARD, or financial institutions.
- The beneficiary needs to arrange and prepare the land for storage of the collected paddy straw.
- Financial assistance for supply chain equipment like higher HP tractor, cutters, balers, rakers, loaders, grabbers, and telehandlers.
- Setting up machinery for the paddy straw supply chain costs approximately Rs 1 crore for 3,000 tonnes and Rs 1.8 crore for 4,500 tonnes per season.
- The government provides a subsidy on the rounded-off amount of Rs 1.5 crore.
- Project Approval: State Governments will approve projects via project sanctioning committees.
- Cost Distribution: The government (Central and State jointly) will contribute 65% of the project cost, the industry will contribute 25%, and the beneficiary will contribute the remaining 10%.
- The central regulatory bodies: The Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) and State Agricultural Departments.
- Objective: To collect 1.5 million tonnes of paddy straw in the next three years by the establishment of 333 collection centres with a total financial assistance of Rs 600 crore.
| CRM 2023-24 | CRM 2020-21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
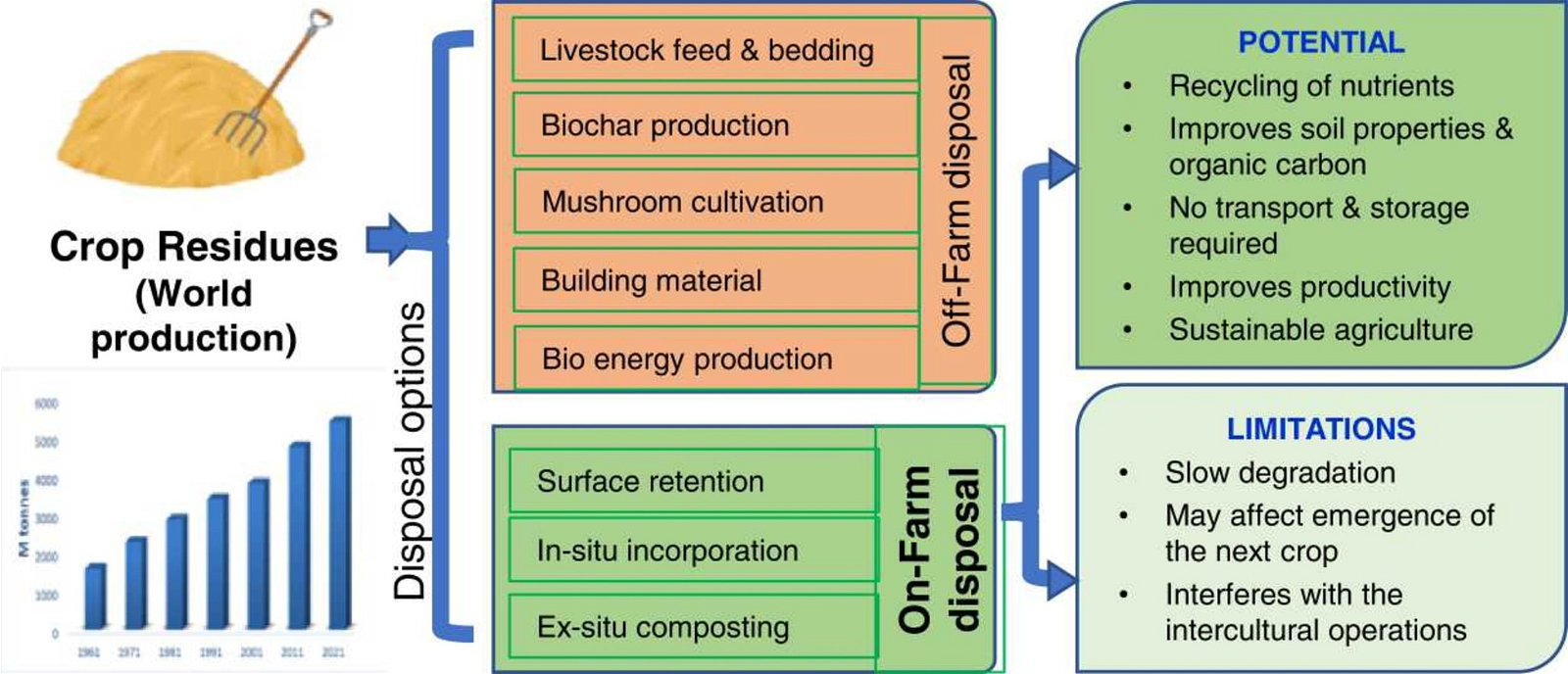
Crop residue management
Crop residue management Techniques (On Farm/Off Farm) Disposal
On field ManagementSurface retention and mulching
Composting
Off-field managementsBaling and removing the straw
Livestock feed
Production of the mushroom crop
Biochar production
Biogas production
Industrial uses of CR (Rice,Wheat)Straw
Farmers’ Producer Organisation (FPO)
|
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)