Effective Exchange Rate (EER)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): The last 10 years have seen the Indian currency fall more against the dollar than during the previous 10 years.
- Since April-end 2014, the rupee has depreciated by 27.6% against the US dollar. However, the rupee strengthened in real terms when its exchange rate with all major global currencies was taken.
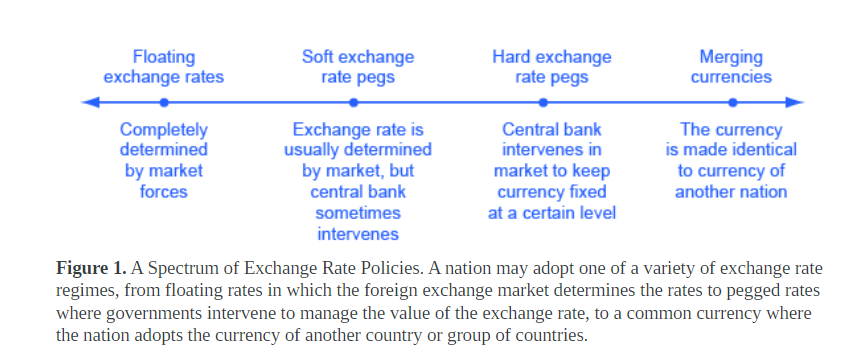
Effective Exchange Rate (EER)
- The rupee’s strength or weakness depends on its exchange rate with the US dollar and other global currencies. This includes a basket of currencies from India’s major trading partners, known as the rupee’s effective exchange rate or EER.
- The Effective Exchange Rate (EER) is measured using an index similar to the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- The CPI calculates the average retail price of a standard consumer basket of goods and services for a specific period compared to a fixed base period.
- Similarly, the EER measures the weighted average of the rupee’s exchange rates against the currencies of India’s major trading partners.
- Currency weights in the EER are determined by each country’s share in India’s total foreign trade.
- There are two measures of Effective Exchange Rate (EER).
- Nominal EER or NEER.
- Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER).
Nominal EER or NEER
- RBI has developed NEER indices for the rupee against two baskets of currencies.
- One basket has six currencies: US dollar, euro, Chinese yuan, British pound, Japanese yen, and Hong Kong dollar.
- The other NEER index covers a larger basket of 40 currencies, representing countries contributing to about 88% of India’s annual trade.
- NEER indices are calculated based on a reference base year value of 100 for 2015-16.
|
Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)
- While the Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) reflects movements in the rupee’s external value against a basket of currencies, it doesn’t consider inflation, which affects the rupee’s internal value.
- For example, the Indonesian rupiah has fallen by 8.5% against the US dollar in the past year, while the Indian rupee depreciated by only 1.7%.
- However, India’s March annual CPI inflation rate of 4.9% was higher than Indonesia’s 3.1%.
- This means the Indonesian currency’s domestic purchasing power suffered less erosion compared to its international purchasing power, while it was the opposite for the rupee.
- REER adjusts the NEER for inflation differentials between the home country and its trading partners.
|
Analysis of the last 10 years
The rupee weakened less relative to other currencies
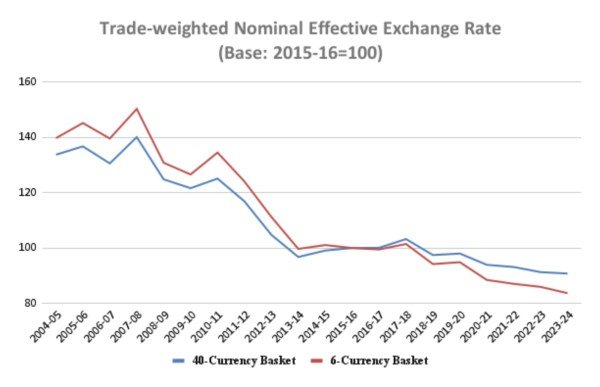
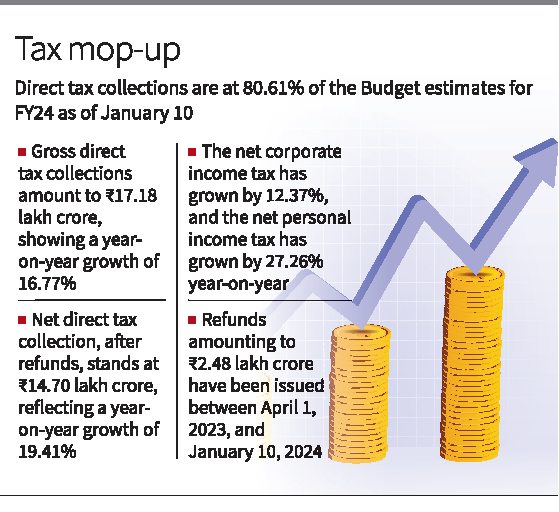
- The NEER against the 40-currency basket decreased by approximately 32.2% from 2004-05 to 2023-24, falling from 133.8 to 90.8.
- The decline was even steeper for the narrower 6-currency basket NEER, around 40.2%, from 139.8 to 83.7 during the same period.
- Meanwhile, the rupee’s average exchange rate against the US dollar decreased by 45.7%, from Rs 44.9 to Rs 82.8.
The rupee has strengthened in real terms
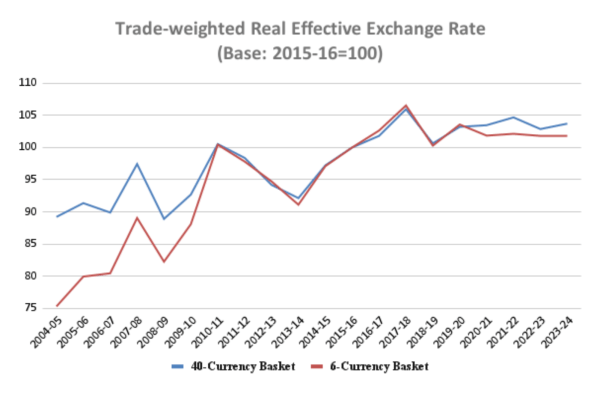
- During 9 out of the 10 years from 2014 to 2024, the rupee’s REER has been at 100 or above.
- This trend contrasts with the weakening trend observed when considering only the rupee’s Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) or its exchange rate against the US dollar.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)