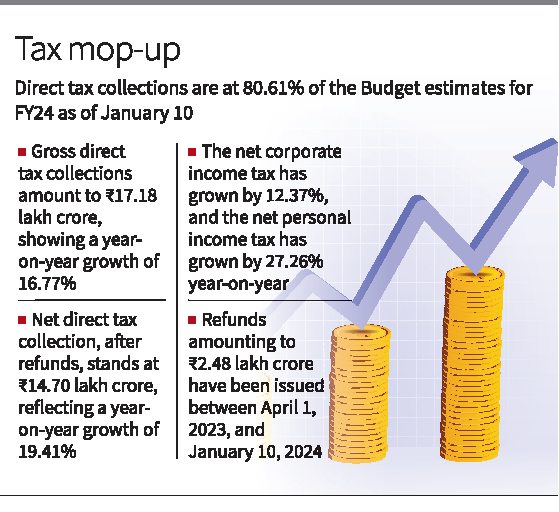
Direct Tax
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): According to the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), provisional direct tax collections continue to register ‘steady growth.
Types of Direct Taxes
Income Tax
- Income Tax Act, 1961 imposes tax on the income of the individuals or Hindu undivided families or firms or co-operative societies (other than companies) and trusts (identified as bodies of individuals associations of persons) or every artificial juridical person.
- The inclusion of a particular income in the total incomes of a person for income-tax in India is based on his residential status.
Corporation Tax
- The companies and business organizations in India are taxed on the income from their worldwide transactions under the provision of Income Tax Act, 1961.
- A corporation is deemed to be resident in India if it is incorporated in India or if it’s control and management is situated entirely in India.
- In case of non-resident corporations, tax is levied on the income which is earned from their business transactions in India or any other Indian sources depending on bilateral agreement of that country.
Minimum Alternate Tax
- It was created to bring the ‘zero-tax paying companies’ within the ambit of income tax and make them pay a minimum amount in tax to the government.
- It was introduced in the budget of 1986-87 when the applicable rate was 15.75 %.
- Introduced by the Finance Act of 1987, MAT came into effect from the assessment year 1988-89.
- Discontinued from 1990-91 and reintroduced in 1996-97 when the effective rate was 11.87%
- MAT credit is the difference between the tax the company pays under MAT and the regular tax.
Dividend Distribution Tax
- It is a tax levied on dividends that a company pays to its shareholders out of its profits.
- It has been abolished from April 1, 2020.
Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
- STT is a tax being levied on all transactions done on the stock exchanges.
- STT is applicable on the purchase or sale of equity shares, derivatives, equity-oriented funds and equity oriented Mutual Funds.
- It was introduced in 2004.
- The reason behind levying STT is to curb evasion of capital gains tax on profits earned by transacting in securities.
Suggestion to improve Direct Tax collection
- Expand the tax base by bringing more individuals and businesses into the formal economy. For example, real estate and agriculture.
- Consider reintroducing a wealth tax targeting high levels of wealth, assets, and property. This will also help address wealth inequality.
- Rationalise tax deductions, exemptions, and incentives to eliminate outdated provisions.
- Encourage voluntary compliance and introduce incentives for timely and accurate tax filing.
- Introduce anti-avoidance provisions to prevent aggressive tax planning.
- Conduct regular and transparent audits to deter tax evasion and improve compliance.
Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)