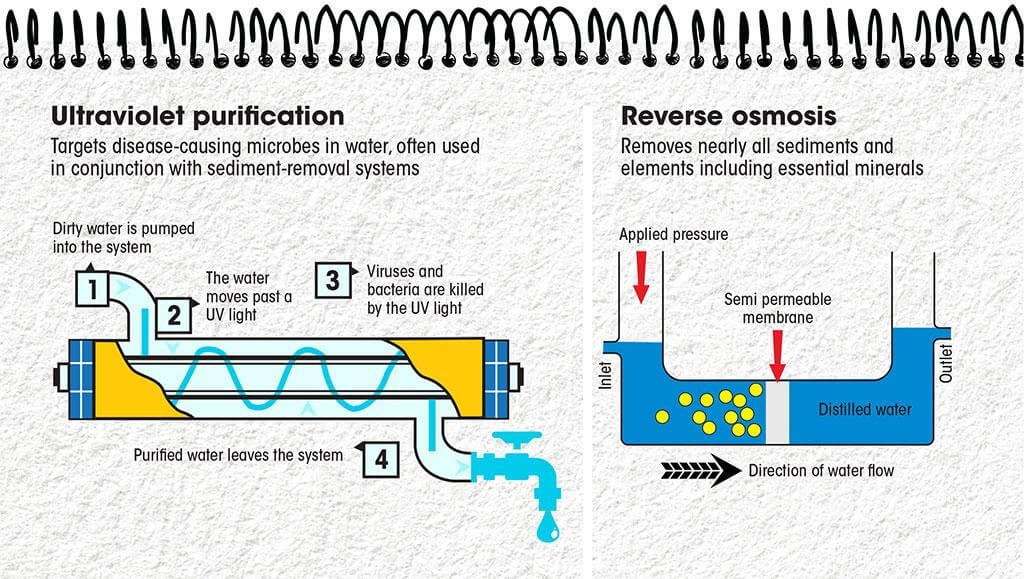
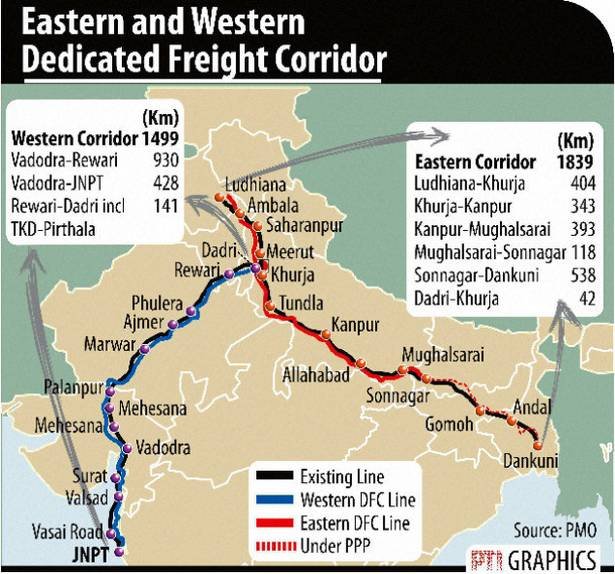
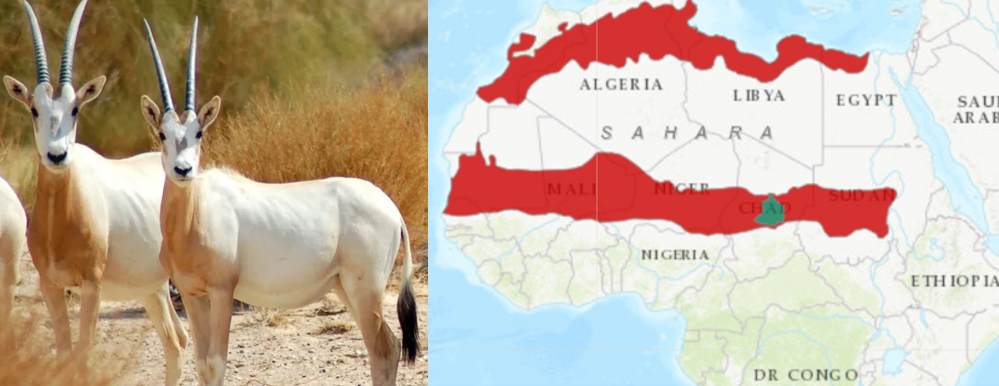
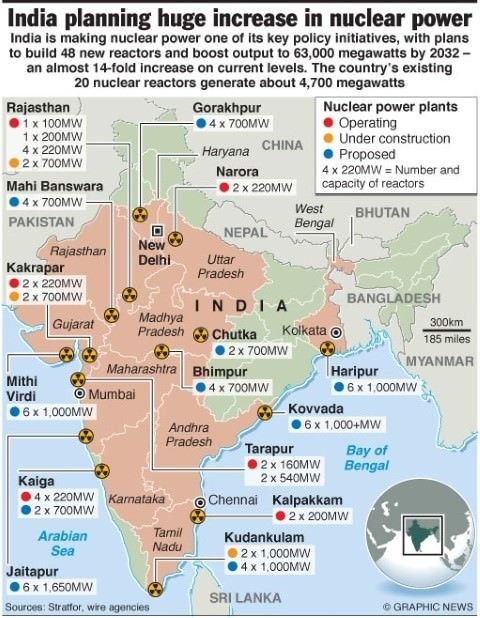
Discovery of Obelisks
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
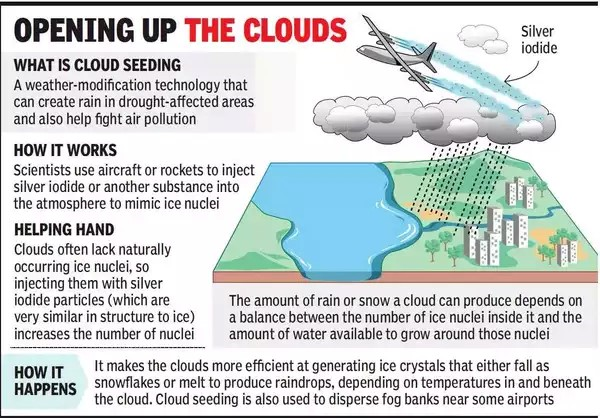
- Context (TH): Researchers recently discovered obelisks, which are biological entities within the human mouth and gut.
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was employed to analyze existing datasets from human microbiomes, facilitating the discovery of obelisks.
|
What are Obelisks?
- Obelisks are circular bits of genetic material containing one or two genes, self-organizing into a rod-like shape.
- The Obelisks’ genetic sequences are only around 1,000 characters (nucleotides) in size.
- They are made of RNA and proteins which facilitates self-replication within bacterial cells. Obelisks rely on microbial host cells, possibly bacteria or fungi, for replication.
- Obelisk genes perform identical functions across diverse bacterial strains.
- They are capable of vertically propagating from parent to offspring cells along with the host bacteria.
- Integrate loosely into the bacterial genome without disrupting standard cellular mechanisms.
- Obelisks fall between viruses and viroids in terms of classification.
- Similar to viroids, obelisks are circular single-stranded RNA genomes without a protein coat.
- Like viruses, obelisks contain genes predicted to code for proteins.
What is the difference between viruses and viroids?
| Features | Viruses | Viroids |
| Structure | Nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat (capsid) | Short, circular RNA molecule (250-400 nucleotides) |
| Living or Non-Living? | Non-living;
lack cellular structures and independent metabolic processes |
Non-living;
lack protein coats and protein-encoding capability |
| Replication | Require host cells for replication, hijack host machinery | Replicate within host cells using cellular enzymes |
| Genetic Material | DNA or RNA | RNA |
| Protein Synthesis | Do not synthesize proteins independently; rely on host cells | Do not encode proteins |
| Pathogenicity | Infect animals, plants, and other organisms | Infect plants and cause plant diseases |
| Examples | Influenza virus, HIV, SARS-CoV-2 | Potato spindle tuber viroid, Coconut cadang-cadang viroid |
To know more about Viruses and Viroids, refer to PMF IAS CA June 5, 2021.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)