
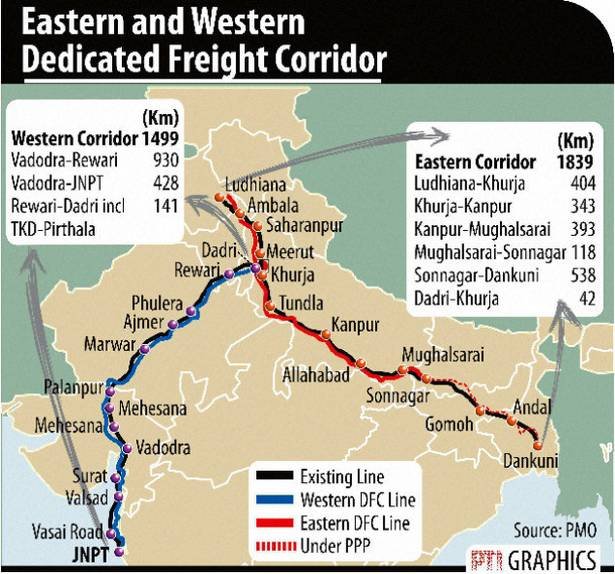
Dedicated Freight Corridor: Western & Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridors
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
PIB | Prelims + Mains | GS3 > Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
- Context: PM dedicated to the nation the 306 Km New Rewari-New Madar Section of the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC).
- It is situated in Haryana & Rajasthan.
- The opening of this stretch will benefit various industries in the surrounding areas of Rajasthan & Haryana.
What is a Dedicated Freight Corridor?
- It is a high speed & high-capacity railway corridor that is exclusively meant for the transportation of freight (goods & commodities).
- On the normal lanes, goods trains must make way for passenger trains, thereby delaying freight movement.
- The surging power needs requiring heavy coal movement, booming infrastructure construction, & growing international trade has led to the conception of the Dedicated Freight Corridors.
- DFC involves the seamless integration of better infrastructure & state of the art technology.
- It will allow for efficient & fast movement of freight (very important for the horticulture sector).
Dedicated Freight Corridor Project
- Under Ministry of Railways.
- The project involves the construction of six freight corridors traversing the entire country.
- The purpose of the project is to provide a safe & efficient freight transportation system.
- Initially, the construction of two freight corridors,
- Western DFC connecting the states of Haryana & Maharashtra &
- Eastern DFC connecting the states Punjab & West Bengal, is being undertaken.
- The other four corridors include
- North-South (Delhi-Tamil Nadu),
- East-West (West Bengal-Maharashtra),
- East-South (West Bengal-Andhra Pradesh) &
- South-South (Tamil Nadu-Goa).
- These four corridors are still in the planning stage.
- In 2006, the Government of India established a dedicated body to implement the project, called the Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India (DFCCIL).

Significance
- The diversion of freight to DFCs on trunk routes will free up the existing network for the kind of capacity expansion needed for passenger movement.
- It will also integrate the Industrial Corridors.
In short
- Logistics costs will be reduced.
- Reduction in the unit cost of transportation,
- Smaller organization & management cost,
- Higher efficiency & lower energy consumption.
- Faster movement of goods.
- It is environmentally friendly.
- Helps in generating more employment.
Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC)
- Dadri, U.P to Jawaharlal Nehru Port, Mumbai-1,468 km
- The WDFC covers Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra & Uttar Pradesh.
- It is being funded by the Japan International Cooperation Agency.
Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC)
- Ludhiana Punjab to Dankuni West Bengal-1,760 km
- The EDFC route covers Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand & West Bengal
- The EDFC route has coal mines, thermal power plants & industrial cities.
- Feeder routes are also being made for these.
- EDFC is being funded by the World Bank.
- Connecting Link for Eastern & Western Arm is under construction between Dadri & Khurja.












Well done team PMF IAS
Religiously I’m following your Initiatives and will utilise of the utmost importance.