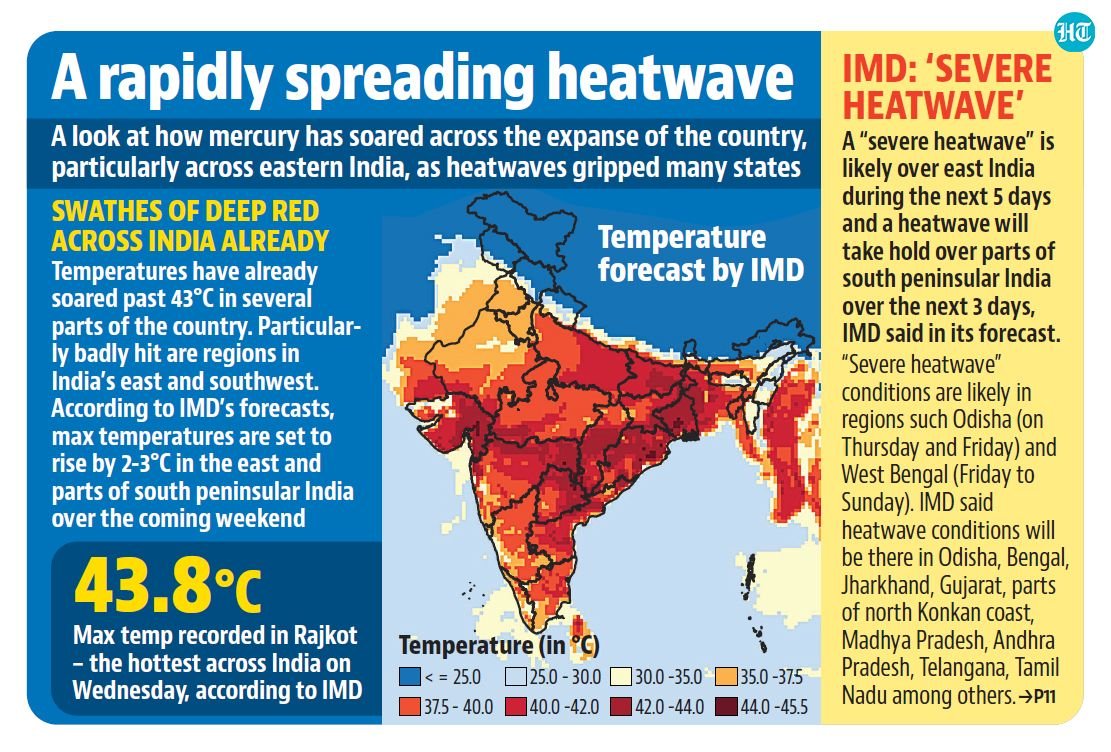
RO water purification systems
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (DTE): Experts warn that Reverse Osmosis (RO) water with dangerously low levels of mineral content can have an adverse impact on health.
- Reasons to prefer RO water: Concerns about tap water quality, contaminated groundwater, and irregular water supplies.
- The water purifier market in India is expected to double from $3,080.7 million in 2023 to $6,880.3 million by 2032.
- Despite its dominance, the effects of RO water on health and industry regulations remain unclear.
Need for RO water purification systems
- Water contains helpful microscopic organisms and essential minerals like calcium and magnesium, which aid in muscle and heart function.
- Sodium, potassium, copper, iron, and zinc are also present in small amounts.
- Polluted water can carry disease-causing microbes, fertilisers, and heavy metals like chromium and lead.
- Groundwater may contain elements like fluorides and heavy metals such as chromium, arsenic, and lead, which can cause health issues if consumed in large amounts.
- The presence of minerals and heavy metals in water is known as total dissolved solids (TDS), responsible for its taste and hardness.
- High levels of total dissolved solids (TDS) in water can cause unpalatable taste and hardness.
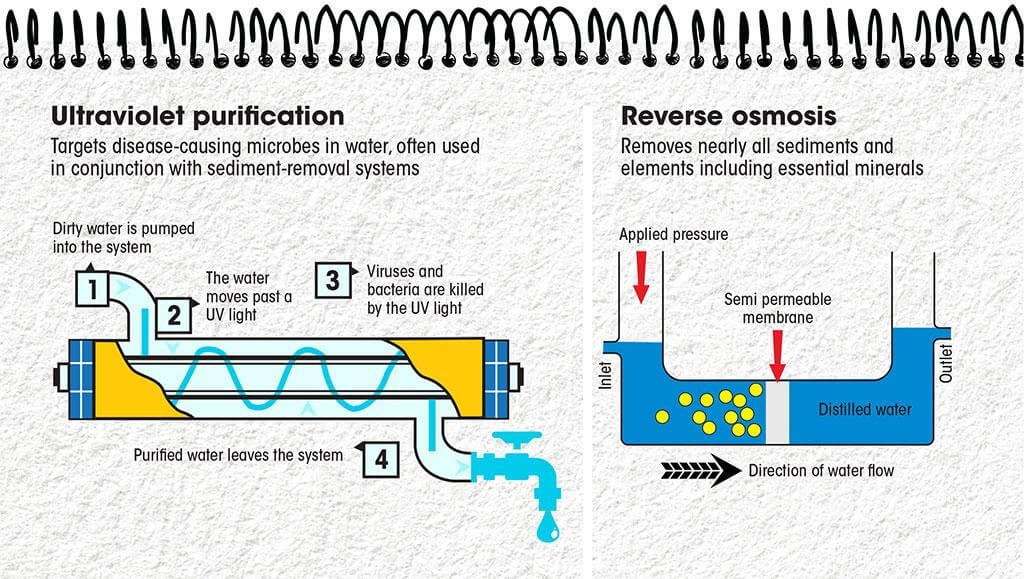
- Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are becoming popular for purifying water as they can remove impurities and lower TDS levels.
- An RO system consists of a semi-permeable membrane with tiny pores (0.0001 to 0.001 microns in size) that separate dissolved salts and impurities from water under pressure.
- As untreated water passes through the membrane under applied external pressure, dissolved salts, impurities, and germs are separated, providing clean and sweet water.
Issues with RO systems
- RO systems claim to remove 90-100% of TDS. However, essential minerals like calcium and magnesium are also lost in the process.
- This loss could be a public health concern as many people in the country suffer from micronutrient deficiency.
- In most houses surveyed by SPECS, RO water has TDS levels of 18 to 25 mg/l, which is considered unsuitable for drinking. ( PECS, an NGO in Dehradun
- According to SPECS, drip candle filters can be used for purification in many areas. However, due to a lack of awareness, people opt for RO systems unnecessarily.
- In August 2023, a study by researchers from Medical College Baroda found that RO systems remove 90-92% of beneficial calcium and magnesium.
- The study, published in the Journal of the Indian Medical Association, linked RO water usage to joint pain among urban citizens of Vadodara.
- Another study in Vadodara, published in January 2022, found that RO water causes micronutrient deficiency.
- It analysed patients at SSG Hospital in 2017-18 and found a significant association between RO water usage and vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Factors like a vegetarian diet, dark complexion, and socio-economic status were also linked to vitamin B12 deficiency.
- In a 2005 paper, the World Health Organization (WHO) documented cases from the Czech and Slovak populations.
- They began using RO systems in home taps around 2000-02.Shortly after, complaints of cardiovascular disorders, tiredness, weakness, and muscular cramps emerged.
- The WHO paper suggests acute magnesium (and possibly calcium) deficiency as the cause.
- BIS cautioned in its 2015 standards that RO systems aren’t suitable for areas where arsenic levels exceed 0.1 mg/l and fluoride levels surpass 8.0 mg/l, but this was removed from the updated 2023 standards.
Various Methods to Remove impurities from Water



Steps taken
- National Green Tribunal (NGT) in May 2019, the Union Environment Ministry directed the issuance of a notification to prohibit the use of RO purifiers where TDS in water is less than 500 mg/l. Wherever RO is allowed, a requirement was set for more than 60% water recovery.
- The report stated that RO systems are not useful if TDS is less than 500 mg/l.
- It also highlighted the removal of important minerals and wastage of water by RO in such cases.
- In March 2022, the Supreme Court stayed the NGT order following a challenge by the Water Quality India Association, a non-profit in Mumbai.
- The Union environment ministry issued the Water Purification System (Regulation of Use) Rules, 2023, In November.
- These rules provide guidelines for managing reject water and discarded elements from purification systems. RO companies have one year to comply with these rules.
- WHO’s 2017 drinking water standards recommend TDS levels between 600 and 1,000 mg/l. However, there’s limited data on whether high or low TDS affects health.
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has set the maximum TDS limit at 500 mg/l since 1991. Europe, the US, and Canada set TDS standards at 500 to 600 mg/l
Way forward
- Experts suggest that the necessity of RO depends on the region and water condition, recommending it only for areas with hard surface or groundwater.
- In places where surface water is used for drinking, a combination of candles, activated carbon, and UV filters is usually sufficient to purify the water.
- Experts urge that the water supplied through pipes to every household should meet BIS standards, eliminating the need for RO in such areas.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)