Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport in Tamil Nadu
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): On February 28, Prime Minister laid the foundation stone for ISRO’s second rocket launchport in Kulasekarapattinam, Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu.
- It will be exclusively used for commercial, on-demand, and small satellite launches in the future.
Why does India need a new launchport?
- To handle the expected increase in commercial launches due to the new space sector policy, ISRO is building a second rocket launchport.
- It will ensure that the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR is not overburdened.
- SHAR will be only used for launching bigger and heavy-lift-off missions like those to the Moon, Venus, and the Gaganyaan human-flight mission.
- Whereas the new launchport will handle smaller payloads and accommodate private players for satellite building and facilitate dedicated launch infrastructure for commercial launches.
Why is the new launchport located in Tamil Nadu?
To avoid Dogleg manoeuvre
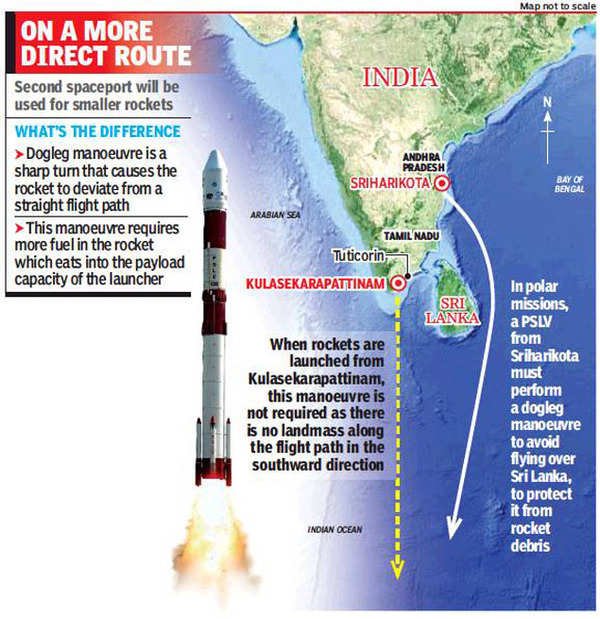
- Currently, the trajectory followed by all launches from SHAR are longer as they follow a path which requires the vehicle to skirt eastwards around Sri Lanka before taking the actual southward flight.
- The rule is that you cannot fly over a land mass when you are not in orbit. This consumes additional fuel.
- Future launches from Kulasekarapattinam, positioned west of Colombo, will have a more direct southward flight path, avoiding the eastward route around Sri Lanka.
Geographic advantage of being more closer to the equator
- The surface velocity of rotation varies from point to point on the Earth.
- It is about 1600 km per hour or about 460 meters in a second near the equator.
- The velocity gradually reduces as we move to the poles and it is practically zero there.
- A satellite launched from the sites near the equator towards the east direction will get an initial boost (approximately 460 m/s) equal to the velocity of Earth surface.
- Why East? The Earth rotates from west to east (anti-clockwise).
- The initial boost helps in cutting down the cost of rockets used to launch the satellites. This is the major reason for launching satellites in the east ward direction.
Exceptions
- The above benefit can be taken only for such satellites which are placed in geo-stationary orbit or which circle the Earth parallel to the equator.
- Such satellites are usually communication satellites or satellites used for scientific research.
- There are other satellites which are placed in polar orbits moving across the equator in a north south direction.
- Such satellites are generally launched in a south ward or north ward direction and therefore cannot take advantage of the Earth’s rotation. They are used mainly for mapping or spying.
|
Small satellite launch vehicle
- SSLV is a recent addition to ISRO’s launch capabilities.
- It is a three-stage launch vehicle (3 solid propulsion stages & a liquid propulsion terminal stage).
- It’s specifically designed to launch small satellites, ranging from 10 to 500kg, into Low Earth Orbit.
- These satellites are often referred to as mini, micro, or nano satellites.
- SSLV missions are cost-effective, and they enable quicker satellite insertion into orbit.
- SSLV are best suited for commercial and on-demand launches.
-
SSLV mission so far
- First mission (SSLV-D1) in August 2022, carrying EOS-02 and AzaadiSat, was unsuccessful due to a deviation in the satellite insertion orbit.
- Second mission (SSLV-D2) in February 2023, successfully inserted three satellites into the intended orbit. Both launches occurred at SHAR.

Sriharikota Range (SHAR)
- SHAR is located 80 km off Chennai on the east coast of Andhra Pradesh.
- It serves as the primary launch infrastructure for all ISRO missions.
- SHAR features facilities for solid propellant processing, static testing, and launch vehicle integration.
- The center includes telemetry services, a mission control center, and a tracking and command network for launch oversight.
- SHAR has two launch complexes, the First Launch Pad operational since September 1993, and the Second Launch Pad operational since May 2005.
- It is used for launching various ISRO vehicles, including PSLV, GSLV, and LVM3.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)