Malware (Malicious Software), Types of Malware & Akira Ransomware
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE | TH ): Computer Emergency Response Team of India (CERT-In) issued an alert for ransomware malware named “Akira”.
Malware (malicious software)
- Malware is any program (computer code)/file that is harmful to the user of an electronic device.
- Malware can monitor/steal/encrypt/alter/delete data and hijack core computing functions.
- Mobile malware can access the device’s components, such as the camera, microphone, GPS, etc.
How does malware enter a device?
- Malware can be delivered to a device with a USB drive or can spread over the internet through downloads, softwares, applications, etc.
- Phishing attacks are a common type of malware delivery where emails/SMS/Whatsapp messages disguised as legitimate messages contain malicious links/attachments that deliver the malware.
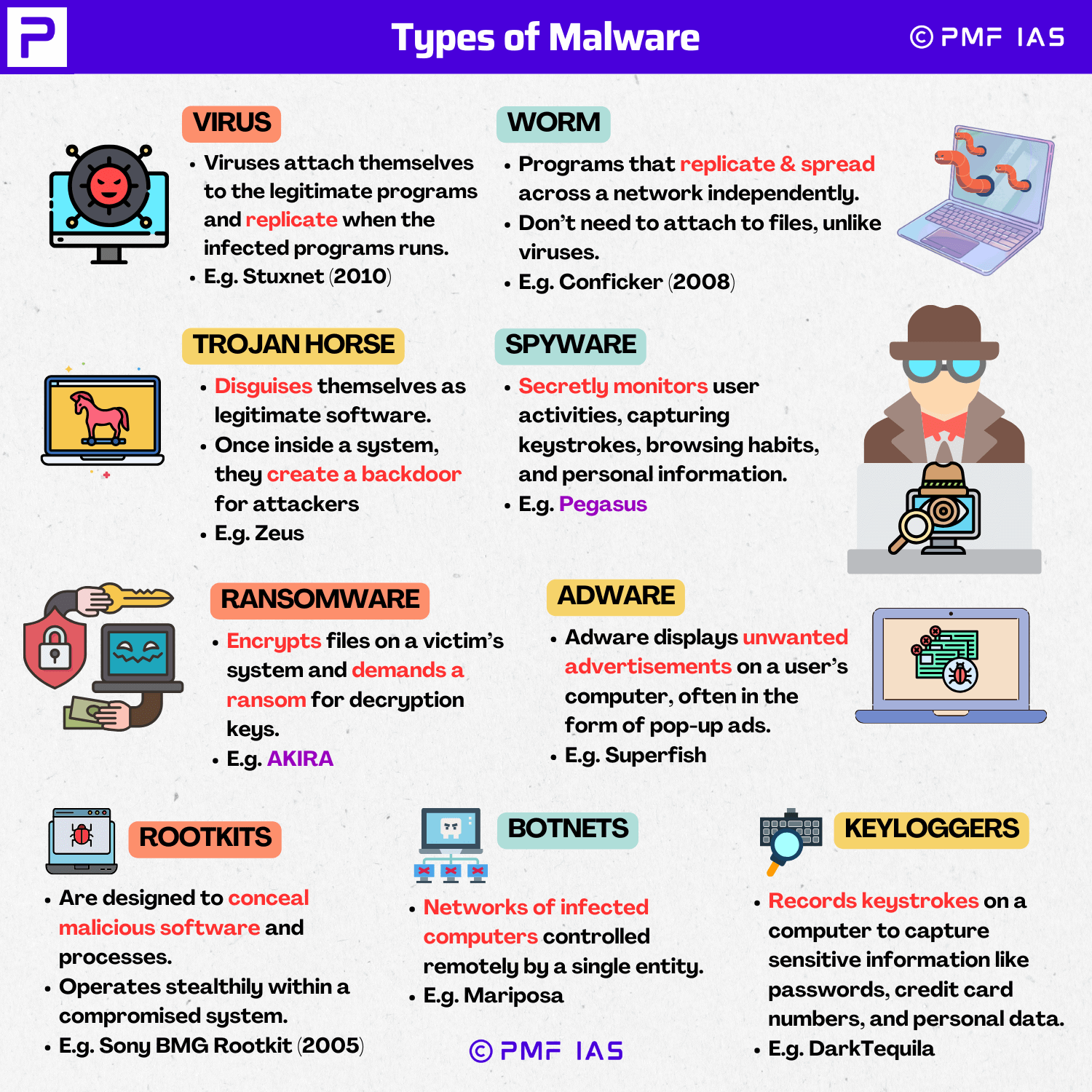
Different types of malware
- Virus: malware which can execute itself and spread by infecting other programs or files.
- Worm: self-replicating malware that typically spreads without any human interaction.
- Trojan horse: designed to appear as a legitimate program in order to gain access to a system. Once activated, Trojans can execute their malicious functions.
- Spyware: malware that collects data on the device and spy on activities of unsuspecting users.
- Ransomware: malware that infects a user’s system and encrypts the data. Cybercriminals then demand a ransom payment from the victim in exchange for decrypting the system’s data.
- Rootkit: malware created to obtain administrator-level access to the victim’s system. Once installed, the program gives threat actors root or privileged access to the system.
- Adware: malware used to track a user’s browser and download history with the intent to display pop-up or banner advertisements that lure the user into making a purchase.
- Keyloggers: also called system monitors, are used to see nearly everything a user does on their computer. This includes emails, opened web pages, programs and keystrokes.
Ransomware
- Ransomware encrypts the victim’s data or locks them out of their computer systems.
- The attackers then demand a ransom from the victim (usually payable in cryptocurrency like Bitcoin) in exchange for providing the decryption key or restoring access to the system.
- It typically spreads through phishing emails that contain malicious attachments.
- Ransomware attacks are a significant cybersecurity threat, causing disruptions, financial losses, and data breaches to individuals, businesses, and organisations worldwide.
How Akira Ransomware Works?
- Akira ransomware target both Windows and Linux devices.
- It uses Virtual Private Network (VPN) services to trick users into downloading malicious files.
- After infecting a sytem, it shuts down Windows services that restrict it from encrypting files.
- Once it steals/encrypts sensitive data, the group behind the attack extorts the victims for a ransom, threatening to release the data on their dark web blog.
|
Spyware as Threat to Democracy of India
- Context (TH | IE | TH | IE): Apple alerted opposition leaders of a “potential state-sponsored spyware attack” on their iPhones.
Why Spyware is a Threat to Indian Democracy
- Undermining trust in elections: Spyware can manipulate public opinion, gather information on political opponents, or spread disinformation.
- Silencing dissent: Spyware can monitor and track dissidents, activists, and journalists.
- Surveillance of political figures: State-sponsored spyware can monitor political opponents.
- Violates privacy: It undermines the personal freedoms and civil liberties the Constitution grants.
Safeguards Available in India Against Spyware
Legal Safeguard: Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
- The IT Act 2000 is the primary law governing cybercrime in India. Certain provisions of the Act can be used to prosecute spyware developers and users.
- The IT Act
- Prohibits sending unsolicited commercial communications, which could include spyware
- Prohibits the sending of offensive messages, which could also include spyware
- Prohibits the hacking of computer systems, which could include the installation of spyware.
- Empowers the GoI to intercept, monitor, or decrypt computer data for national security, public order, or crime prevention
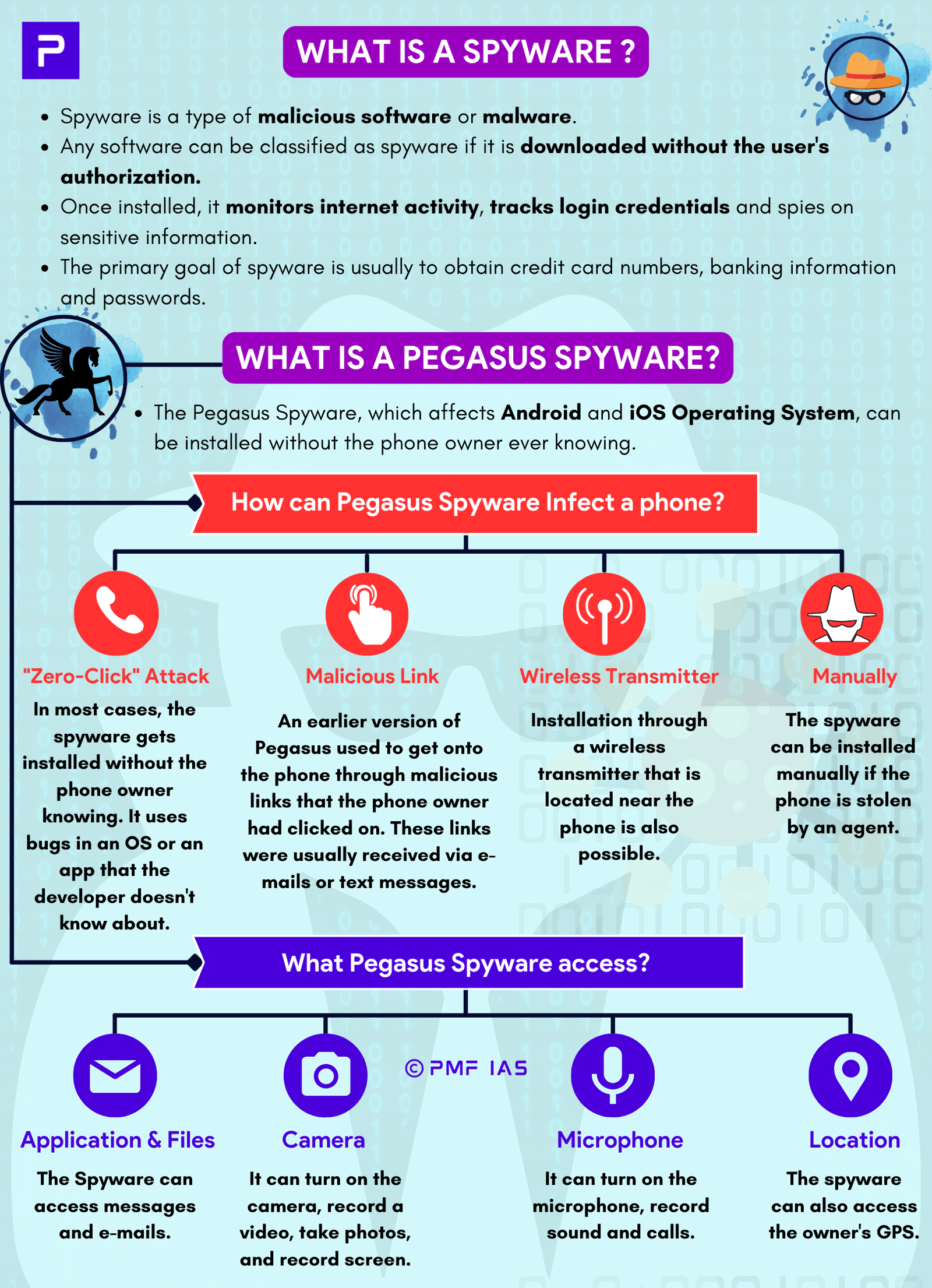
Pegasus Spyware Case: Case Study
- In 2021, Pegasus spyware created by the Israeli cybersecurity firm NSO Group allegedly targeted mobile phones in multiple countries, including India.
- The Supreme Court formed an Expert Committee led to investigate Pegasus spyware allegations.
- The committee did not find conclusive evidence of Pegasus spyware on the examined phones.
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- CERT-In is the national nodal agency to deal with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing.
- It is an office within the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It was formed in 2004 under Information Technology Act, 2000.
Practices Recommended by CERT-In Against Ransomware Attack
- Maintaining regular offline data backups which are encrypted.
- All accounts should have strong and unique passwords.
- Multi-factor authentication (verifying logins with SMS/Email OTP)
- Separate administrative network.
- A host-based firewall.
- Disable remote desktop connections.
- Spam-proof email validation system.
- Anti-virus software should be updated.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)