PSLV C56 Mission, Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), New Space India Ltd (NSIL)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
PSLV C56 Mission
- Context (TH | LM ): During PSLV C56 mission, ISRO’s PSLV successfully placed seven Singaporean satellites into intended orbits.
Significance of PSLV C56 Mission
- PSLV C56 mission is the second commercial mission of ISRO’s NSIL.
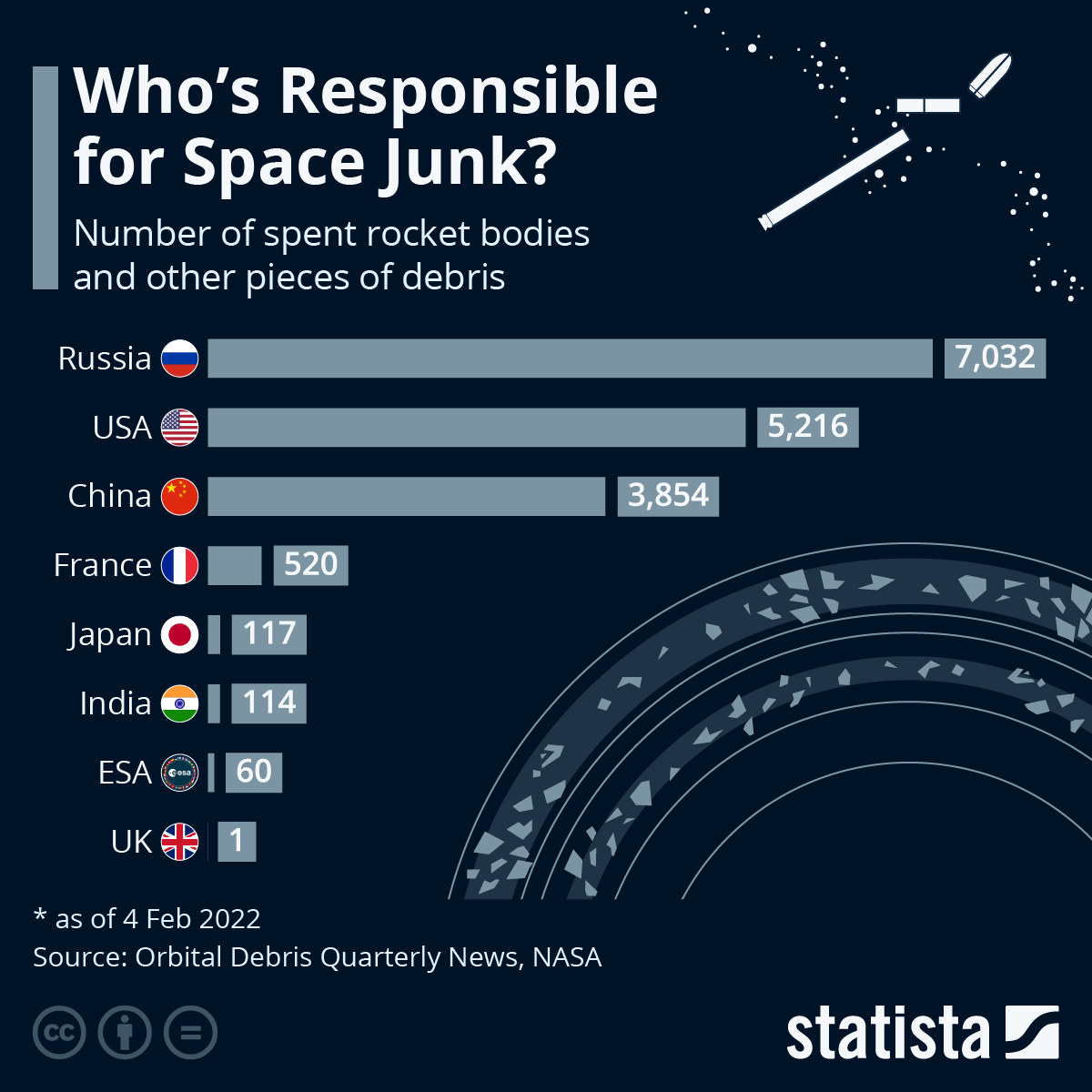
- The mission is designed to mitigate the space debris problem.
- Normally, after a successful mission, a rocket stays in orbit for “decades” as space debris, before re-entering into Earth’s atmosphere.
- But in this mission after placing customer satellites at an altitude of 536 km, the rocket will be lowered into a 300 km high orbit.
- Due to the orbit-lowering, the duration of space debris generated from this mission in space will be reduced to two months.
|
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)
- PSLV is an indigenous expendable launch system developed in the 1990s by ISRO.
- It is called the ‘workhorse of ISRO’ because it has the highest number of successful launches.
|

Orbits in which PSLV Places Satellites
Polar and Near Polar (e.g. sun-synchronous orbit) Lower Earth Orbits
- PSLV was developed to place satellites (mostly remote sensing satellites) in polar and near polar (e.g. sun-synchronous orbit) Lower Earth Orbits.
- E.g., Astrosat (India’s first space observatory)
Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits
- Initially PSLV was developed to place satellites only on Low Earth Orbits. But, in the last decade, PSLV was successful in sending several satellites also toward geosynchronous transfer orbits.
- E.g. Chandrayaan-1 (India’s first lunar probe) and Mars Orbiter Mission or Mangalyaan (India’s first interplanetary mission).
Stages of PSLV
- PSLV is a four stage launch vehicle.
- First stage and third stage are solid-fuelled stages.
- Second stage and fourth stage are liquid-fuelled stages.
- The second stage engine, Vikas, is a derivative of France’s Viking engine.
New Space India Ltd (NSIL)
- New Space India Ltd (NSIL) is a Public Sector Enterprise (under the Companies Act, 2013).
- It is under the administrative control of the Department of Space.
- It is the commercial wing of the ISRO.
- Objective: to commercially exploit the Research and Development work of the ISRO.
Space Business Activities of NSIL
- Owning satellites for Earth Observation and Communication applications.
- Building satellites and launching them as per demand.
- Providing launch services for satellite belonging to customer.
- Building launch vehicles through Indian Industry and Launch as per satellite customer requirement.
- Space-based services related to Earth Observation and Communication on a commercial basis.
- Satellite building through Indian Industry
- Technology Transfer to Indian Industry
- Marketing spin-off (commercial) technologies and products/services emanating out of ISRO.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)