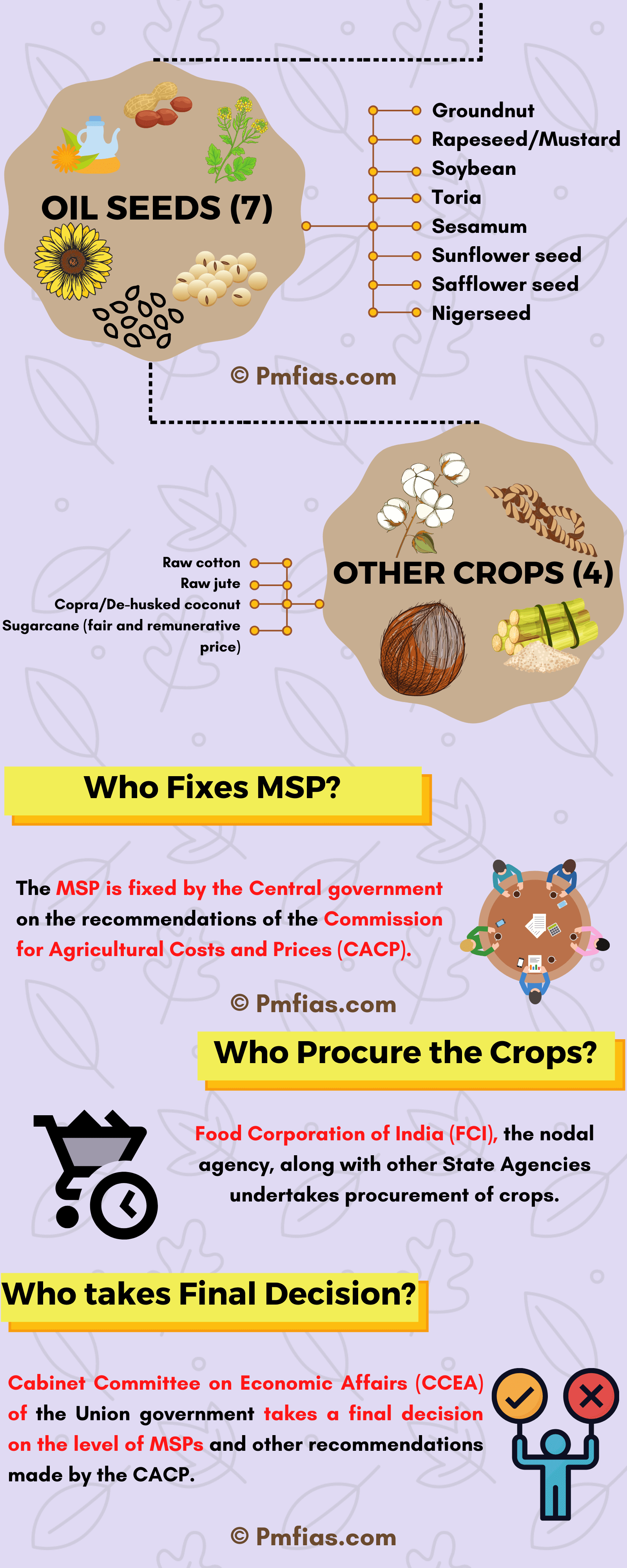
Total Solar Eclipse
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE | HT): On April 8, a total solar eclipse will cross North America, passing over Mexico, the United States, and Canada.

What is an Eclipse?
- An eclipse occurs when one body passes in front of and obscures another body.
- In general, an eclipse typically refers to the Sun being blocked by the Moon (a solar eclipse) or the Earth blocking the Sun (a lunar eclipse).
- In order for this to occur, the three bodies (Sun, Moon, and Earth) have to be in a nearly perfectly straight line.

Solar Eclipse
- A solar eclipse is an astronomical phenomenon where the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun and blocks the Sun’s light either entirely or partially.
- The Moon blocks the light of the Sun, either fully or partially, which casts a huge shadow on some parts of the world.
- When the moon completely covers the sun, it casts a shadow on Earth, forming what is called a “path of totality.” This path is a relatively narrow band that moves across the surface.
|
Types of Solar Eclipse
![Burning Issues] Eclipses This Year - Civilsdaily](http://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Picture-9.jpeg)
- Partial solar eclipses occur when the Moon only partially obscures the Sun’s disk and casts only its penumbra on Earth.
- Annular solar eclipses take place when the Moon’s disk is not big enough to cover the entire disk of the Sun, and the Sun’s outer edges remain visible to form a ring of fire in the sky.
- An annular eclipse of the Sun takes place when the Moon is near apogee, and the Moon’s antumbra falls on Earth.
- Total solar eclipses happen when the Moon completely covers the Sun, and it can only take place when the Moon is near perigee, the point of the Moon’s orbit closest to Earth.
- One can only see a total solar eclipse if he is in the path where the Moon casts its darkest shadow, the umbra.
- Hybrid Solar Eclipses, also known as annular-total eclipses, are the rarest type.
- They occur when the same eclipse changes from an annular to a total solar eclipse, and/or vice versa, along the eclipse’s path.
What happens during a solar eclipse?
- The Moon casts two shadows – a lighter, outer shadow known as the penumbra and a darker, inner shadow known as the umbra.
- Eclipse viewers located in the larger penumbra shadow will only witness a partial solar eclipse.
- The closer to the umbra (the darker, inner shadow of the Moon), the more of the Sun that is obscured and the longer the partial eclipse.
What can be observed during a solar eclipse?
Corona
- Corona is the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere.
- The corona is made up of ionized gas called plasma, with its temperatures upto many millions of degrees.
- The corona is visible to the naked eye only during a total solar eclipse.
Solar Chromosphere
- The part of the edge of the Moon looks like it is highlighted by a very thin, deep-red crescent.
- This glowing red feature is the lower portion of the Sun’s atmosphere, which is known as the chromosphere. Named for its stark colouration, the chromosphere is approximately 10,000 degrees Celsius and is comprised of hydrogen gas emitting its distinctive red colour.

Prominences
- Immediately after the diamond ring and during totality, Prominences may be seen.
- They appear as pink fiery features extending out from the black disc of the moon, held in place by the Sun’s magnetic field.
- They are actually giant gaseous extensions from the Sun.

Bailey’s Beads
- Bailey’s Beads are named after English astronomer Francis Baily, who is credited as the first person to describe them after seeing an annular eclipse in 1836.
- The beads are due to the irregularities on the Moon’s surface that allow slight portions of the Sun’s surface (the photosphere) to shine through.
- The beads are typically most visible along the edge of the path of totality but can sometimes be observed in the few seconds before and after totality.

Diamond Ring
- The Diamond Ring effect occurs during the few seconds before and after totality while an extremely small fraction of the Sun’s photosphere is still visible.

How often does a solar eclipse takes place?
- A solar eclipse is witnessed only during the new moon — when the Moon and Sun are aligned on the same side of Earth.
- Although a new moon occurs about 29.5 days (the time taken by the Moon to orbit Earth), a solar eclipse takes place only two to five times annually. But why?
- It is because the Moon does not orbit Earth in the same plane as the Earth orbits the Sun.
- The Moon is tilted by about five degrees with respect to Earth. As a result, most of the time when the Moon is in between the Sun and Earth, its shadow is either too high or too low to fall on the Earth.
Total Solar Eclipse

Factors affecting the duration of total solar eclipse
Distance of the Moon from Earth
- The closer the Moon is, the larger it will appear in the sky, and the longer it will be able to cover the Sun.
- If the Moon is near its farthest point from Earth (apogee), totality is not possible because the Moon is too small to completely cover the Sun.
Distance of the Earth from the Sun
- The farther Earth is from the Sun, the smaller it will appear, and the easier it will be for the Moon to cover the solar disk.
Location of the observer in the umbra
- If one is near the center of the path of totality, the widest part of the shadow passes over and totality is longer.
- If one is near the edge of totality, then there may be only a few seconds of total eclipse.
- If one is near where the umbra shadow just comes into contact with the Earth, totality will be very short due to the shadow racing over the curved surface of the planet.
Why is a total solar eclipse so rare?
- While there can be between two and five solar eclipses every year, total eclipses only happen about once every 18 months or so and a particular spot on Earth witnesses a total solar eclipse only once in 400 years.
- This is because a total eclipse is only visible if one is standing in the umbra — the other part of the shadow is called the penumbra, which is not as dark as the umbra.
- The umbral shadow is very small, covering only a small part of Earth. In fact, the entire path of the umbral shadow during a solar eclipse will only cover less than one per cent of the globe.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)