Environment Impact Assessment (EIA)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): According to the EIA report, the trapping of workers in the Silkyara-Barkot tunnel collapse in Uttarakhand might not have happened if there had been a separate escape tunnel.
- The project had dismissed the idea of a separate escape tunnel, citing increased construction time, cost, and low anticipated traffic volume.
|
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA)
- EIA is a tool to anticipate the likely environmental impacts of the proposed developmental activities and suggest mitigation measures and strategies.
- EIA was introduced in India in 1978 for river valley projects.
- Later, the EIA legislation was enhanced to include other developmental sections.
- EIA comes under Notification on EIA of Developmental Projects 1994 under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 provisions.
- EIA is now mandatory for more than 30 categories of projects, and these projects get Environmental Clearance (EC) only after the EIA requirements are fulfilled.
- EC is granted by the Impact Assessment Agency in the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEF&CC).
Salient Features of the 2006 Amendment to EIA Notification
- The EIA Notification of 2006 has decentralised the environmental clearance projects by categorising the developmental projects into two categories:
- Category A (national-level appraisal)
- Category B (state-level appraisal)
Drawbacks of the EIA
- Applicability: Certain projects with significant environmental impacts are exempted due to category classification or investment thresholds provided in the notification.
- Lack of expertise: EIA teams may lack diverse expertise from environmental science, wildlife, and social sciences, leading to incomplete assessments.
- Ineffective public hearings: Public comments are not considered at the early stage, which often leads to conflict at the later stage of project clearance.
- Weak compliance monitoring
- Biased EIA reports
- Data and information gaps
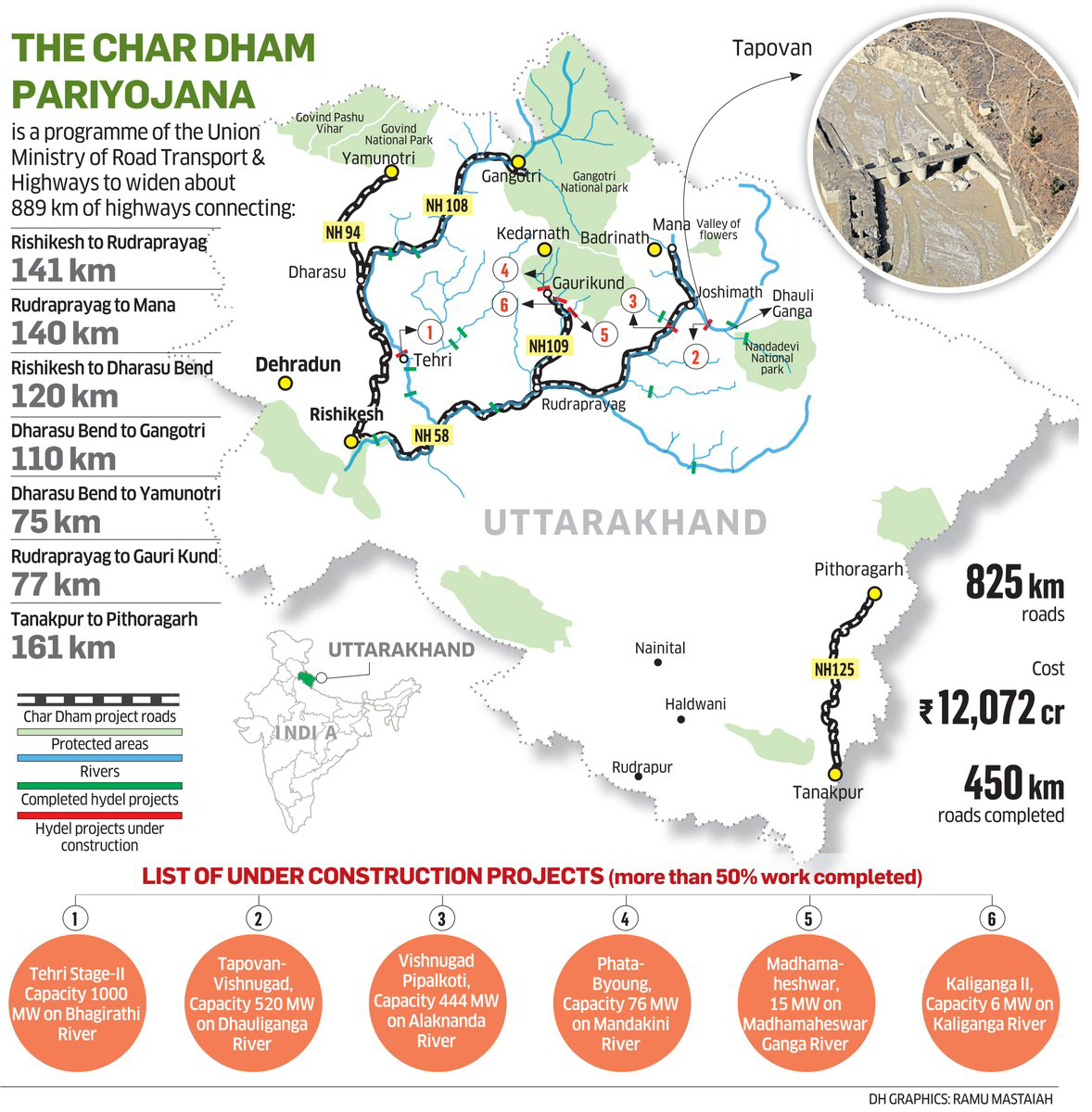
Case Study: Char Dham Project
- Chardham Mahamarg Vikas Pariyojna seeks to improve connectivity between four pilgrimage sites – Kedarnath, Badrinath, Yamunotri, and Gangotri – in Uttarakhand.
- The project was started in 2016 and is now nearing completion.
- It focuses on the widening of the existing roads in the region.
- The entire length of the highways will be two-laned with paved shoulder.
- It is implemented by three executing agencies of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways:
- Uttarakhand State Public Works Department
- Border Road Organization (BRO)
- National Highway and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL)
How the Char Dhan Project Escaped EIA?
- The Char Dham project was broken down into “53 civil works” to avail the exemption from environmental clearance provided to all linear projects under 100 km since 2013.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)