Recycling of Rare Earth Metals
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE | NT): A new study by Chinese and Dutch researchers reveals that reusing or recycling Rare earth metals can meet 40% of their demand in the US, China, and Europe by 2050.
Significance of Rare Earth Metals
- Rare earths play a crucial role in green technologies like electric vehicles and wind turbines.
- Industries such as aircraft, missile, and satellite manufacturing rely on rare earth metals.
- Unlike fossil fuels, rare earths can be recovered and reused.
- They have unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties.
Significance of recycling
- Recycling rare earths can reduce the environmental impact of mining operations. Mining often pollutes soil and water with toxic heavy metals, posing environmental and health risks.
- Rare earth mining operations are sometimes associated with local conflicts and human rights violations. E.g. Myanmar–China Border Region. Reusing already-mined rare earths can contribute to ethical sourcing and conflict-free supply chains.
- Using our old stuff for rare earth metals can make our supply chains safer and reduce risks.
- Reduce the cost of renewable energy There can be a 60 per cent reduction in mining of Neodymium and dysprosium (REM) (used in wind turbines) by 2050 through effective reuse and recycling.
Challenges
- Only about 1% of rare earths in old products are currently reused or recycled. While common metals like iron, copper, and aluminium are widely recycled.
- Rare earths are frequently mixed with other metals, making their extraction challenging.
- Some rare-earth recycling methods involve the use of hazardous chemicals.
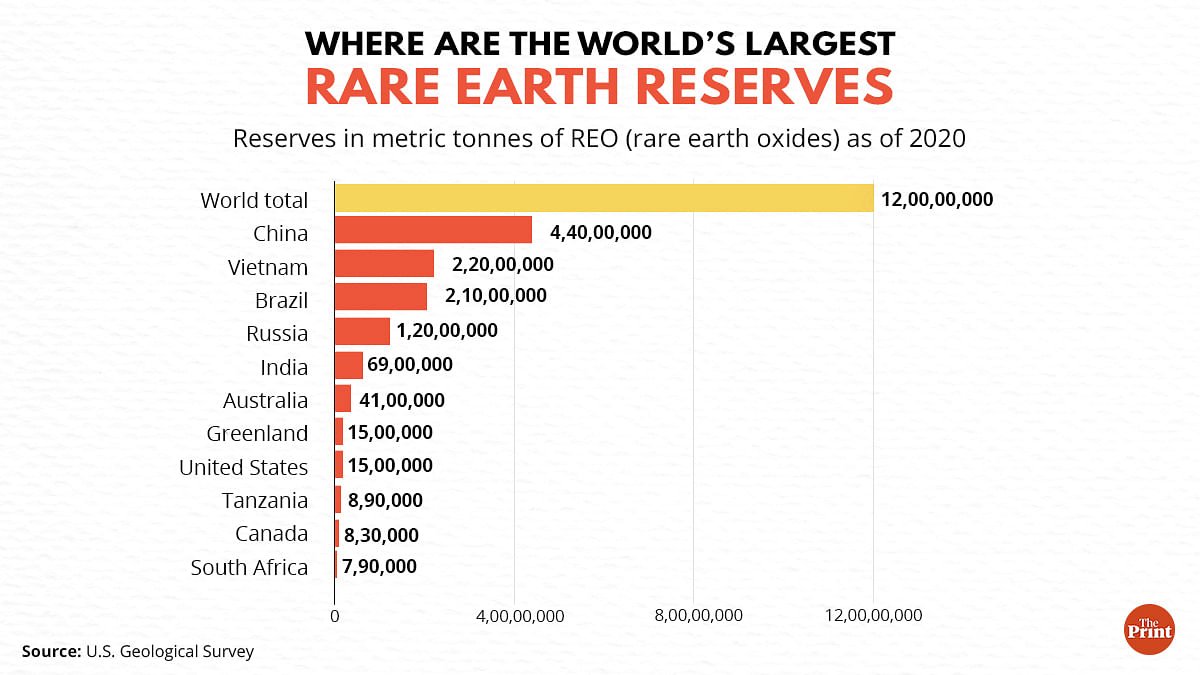
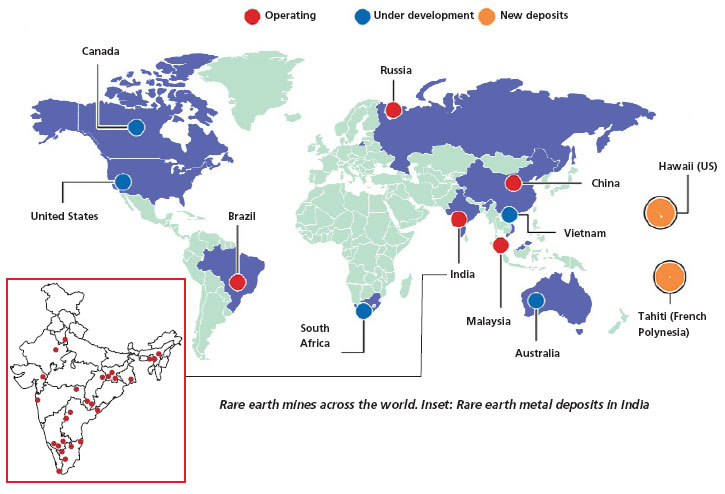
India & Rare Earth Metals
Principal sources of Rare Earth Elements (REE)
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)