Natural Gas, First Strategic Natural Gas Reserves in India
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
First Strategic Natural Gas Reserves
- Context (TH): GAIL is looking at building India’s first strategic natural gas reserves by using old, depleted hydrocarbon wells.
- India has 5 million tonnes of strategic petroleum reserves but no storage facilities for natural gas.
Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL)
|
Natural Gas
- Natural gas is a fossil fuel that primarily consists of methane.
- Natural gas reserves are deep inside the earth near other solid and liquid hydrocarbon beds like coal and crude oil.
- It is not used in its pure form; it is processed and converted into cleaner fuel for consumption.
- By-products extracted: Propane, ethane, butane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen etc.
- It also contains nonhydrocarbon gases, such as carbon dioxide and water vapour.
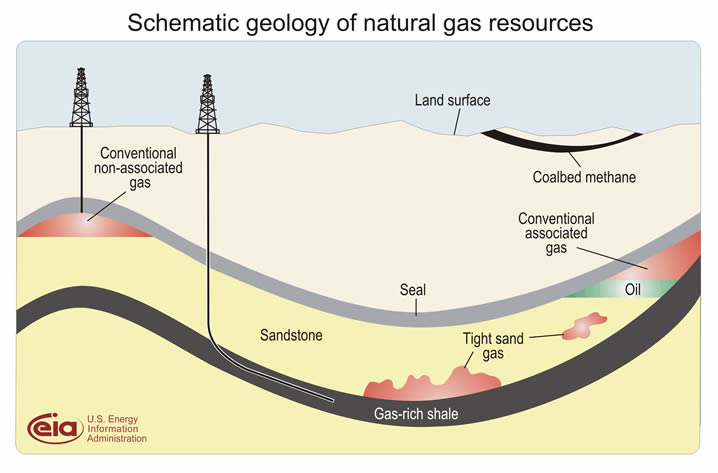
Types of Natural Gas
- Wet gas or Associated gas: Natural gas found in association with crude oil.
- Dry gas or Non-associated gas: When reservoirs contain only gas and no oil.
- Coalbed methane: Natural gas found in coal deposits.
- Sour gas: Natural gases that contain hydrogen sulfide or other organic sulfur compounds.
- Sweet gas: Coalbed methane is called ‘sweet gas’ because it lacks hydrogen sulfide.
- Shale gas or Tight gas: Natural gas that occurs in the pores of shale, sandstone, and other sedimentary rocks.
Benefits of Natural Gas as Fuel
- Clean burning: Natural gas burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, emitting fewer air pollutants and greenhouse gases.
- Efficient: It has a high energy conversion efficiency, minimising waste and maximising utilisation.
- Versatile: It can be used for various purposes like cooking, generating electricity, and powering industrial processes.
- Flexible: Liquified and compressed natural can be easily transported and stored.
Disadvantages of Natural Gas as Fuel
- Contributes to greenhouse gas emissions despite cleaner burning.
- Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, can leak during natural gas extraction, processing, and transportation.
- Natural gas extraction from shale and tight formations often relies on fracking, which can have environmental impacts like water contamination and seismic activity.
- Non-renewable: Natural gas is a finite resource that cannot be replenished.
- Transportation: Its transportation requires specialised infrastructure.
Natural Gas Storage
- Underground storage: Utilising depleted gas fields, salt caverns, and other geological formations.
- Above-ground storage: Utilising specially designed tanks for smaller-scale storage.
Benefits of Underground Storage of Natural Gas
- Large capacity
- Higher energy efficiency: Natural pressure and temperature in underground formations maintain stored gas in a condensed state, minimising energy losses during storage and retrieval.
- Cost-effective
- Safe and secure: It minimises the risk of leaks and ensures the safety of the surrounding environment.
- Long-term storage
- Grid reliability: Underground storage ensures a reliable natural gas supply during peak demand, maintaining grid stability and preventing power outages.
|
Four Basic Forms of Natural Gas
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)