
March 29 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- These Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs) are based on PMF IAS Daily Current Affairs.
- The daily current affairs are uploaded every day by 8 PM. You can read the Daily Current Affairs from here.
- Subscribers of the “Current Affairs” course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC from here.
[Quiz] Daily Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs) – March 29 2024
0 of 11 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Information
These MCQs are based on PMF IAS Daily Current Affairs. The daily current affairs are uploaded every day by 8 PM. You can read the Daily Current Affairs from here. Subscribers of the “Current Affairs” course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC from here.
You have already completed the Test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the Test.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this Test:
Your results are here!! for" [Quiz] Daily Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs) – March 29 2024 "
0 of 11 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
Your Final Score is : 0
You have attempted : 0
Number of Correct Questions : 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions : 0 and Negative marks 0
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
-
Not categorized
You have attempted: 0
Number of Correct Questions: 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions: 0 and Negative marks 0
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 11
1. Question
Q1. {IR – Development} Consider the following statements with respect to Investment Facilitation for Development:
- It is a joint Initiative launched International Monetary Fund and World Economic Forum at the 2024 Davos Summit.
- The agreement aims to create legally binding provisions to facilitate investment flows.
- India is a member to the Investment Facilitation for Development Agreement.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are not correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD) is a joint Initiative launched at the 11th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC11) in December 2017 on a plurilateral basis by 70 countries.
- This was done through a process known as the Joint Statement Initiative.
- A core objective of the framework is to facilitate greater participation by developing and least-developed WTO Members in global investment flows.
- The IFD agreement was finalised in November 2023 and at present around 120 of 166 WTO member countries (more than 70% of the membership) back this agreement.
Statement 2 is correct
- This agreement aims to create legally binding provisions to facilitate investment flows.
- It also aims to develop predictable, transparent and open investment rules that will contribute to more efficient investment flows and increased business confidence and it is now in a formal negotiation phase.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- India is not a part of this initiative.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD) is a joint Initiative launched at the 11th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC11) in December 2017 on a plurilateral basis by 70 countries.
- This was done through a process known as the Joint Statement Initiative.
- A core objective of the framework is to facilitate greater participation by developing and least-developed WTO Members in global investment flows.
- The IFD agreement was finalised in November 2023 and at present around 120 of 166 WTO member countries (more than 70% of the membership) back this agreement.
Statement 2 is correct
- This agreement aims to create legally binding provisions to facilitate investment flows.
- It also aims to develop predictable, transparent and open investment rules that will contribute to more efficient investment flows and increased business confidence and it is now in a formal negotiation phase.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- India is not a part of this initiative.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Investment Facilitation for Development (IFD) is a joint Initiative launched at the 11th WTO Ministerial Conference (MC11) in December 2017 on a plurilateral basis by 70 countries.
- This was done through a process known as the Joint Statement Initiative.
- A core objective of the framework is to facilitate greater participation by developing and least-developed WTO Members in global investment flows.
- The IFD agreement was finalised in November 2023 and at present around 120 of 166 WTO member countries (more than 70% of the membership) back this agreement.
Statement 2 is correct
- This agreement aims to create legally binding provisions to facilitate investment flows.
- It also aims to develop predictable, transparent and open investment rules that will contribute to more efficient investment flows and increased business confidence and it is now in a formal negotiation phase.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- India is not a part of this initiative.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 2 of 11
2. Question
Q2. {Polity – Statutory Bodies} Consider the following statements with respect to Lokpal:
- The selection committee is composed of the Prime Minister, Speaker of Lok Sabha, Chairman of Rajya Sabha and Chief Justice of India.
- The term of office for Lokpal Chairman and Members is 5 yrs or till the age of 65 yrs.
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal has been vested with the powers of a civil court.
- In 1966, India became the first developing nation to adopt the concept of the ombudsman.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- The members are appointed by the president on the recommendation of a Selection Committee.
- The selection committee is composed of the Prime Minister who is the Chairperson, Speaker of Lok Sabha, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, Chief Justice of India or a Judge nominated by him/her and One eminent jurist.
- For selecting the chairperson and the members, the selection committee constitutes a search panel of at least eight persons.
- Under the Lokpal Act of 2013, the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) is supposed to put together a list of candidates interested to be the chairperson or members of the Lokpal.
- This list would then go to the proposed eight-member search committee, which would shortlist names and place them before the selection panel headed by the Prime Minister.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Lokpal is a multi-member body, that consists of one chairperson and a maximum of 8 members.
- Chairperson of the Lokpal should be either the former Chief Justice of India or the former Judge of Supreme Court or an eminent person with impeccable integrity and outstanding ability, having special knowledge and expertise of minimum 25 years in the matters relating to anti-corruption policy, public administration, vigilance, finance including insurance and banking, law and management.
- The term of office for Lokpal Chairman and Members is 5 years or till the age of 70 years.
Statement 3 is correct
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal has been vested with the powers of a civil court.
- Lokpal has powers of confiscation of assets, proceeds, receipts and benefits arisen or procured by means of corruption in special circumstances.
- Lokpal has the power to recommend transfer or suspension of public servant connected with allegation of corruption.
- Lokpal has the power to give directions to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry.
Statement 4 is incorrect
- In 1966, Guyana became the first developing nation to adopt the concept of the ombudsman.
- Subsequently, it was further adopted by Mauritius, Singapore, Malaysia, and India as well.
- In India, the concept of constitutional ombudsman was first proposed by the then law minister Ashok Kumar Sen in parliament in the early 1960s.
- The term Lokpal and Lokayukta were coined by Dr. L. M. Singhvi.
- In 1966, the First Administrative Reforms Commission recommended the setting up of two independent authorities- at the central and state level, to look into complaints against public functionaries, including MPs.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- The members are appointed by the president on the recommendation of a Selection Committee.
- The selection committee is composed of the Prime Minister who is the Chairperson, Speaker of Lok Sabha, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, Chief Justice of India or a Judge nominated by him/her and One eminent jurist.
- For selecting the chairperson and the members, the selection committee constitutes a search panel of at least eight persons.
- Under the Lokpal Act of 2013, the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) is supposed to put together a list of candidates interested to be the chairperson or members of the Lokpal.
- This list would then go to the proposed eight-member search committee, which would shortlist names and place them before the selection panel headed by the Prime Minister.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Lokpal is a multi-member body, that consists of one chairperson and a maximum of 8 members.
- Chairperson of the Lokpal should be either the former Chief Justice of India or the former Judge of Supreme Court or an eminent person with impeccable integrity and outstanding ability, having special knowledge and expertise of minimum 25 years in the matters relating to anti-corruption policy, public administration, vigilance, finance including insurance and banking, law and management.
- The term of office for Lokpal Chairman and Members is 5 years or till the age of 70 years.
Statement 3 is correct
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal has been vested with the powers of a civil court.
- Lokpal has powers of confiscation of assets, proceeds, receipts and benefits arisen or procured by means of corruption in special circumstances.
- Lokpal has the power to recommend transfer or suspension of public servant connected with allegation of corruption.
- Lokpal has the power to give directions to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry.
Statement 4 is incorrect
- In 1966, Guyana became the first developing nation to adopt the concept of the ombudsman.
- Subsequently, it was further adopted by Mauritius, Singapore, Malaysia, and India as well.
- In India, the concept of constitutional ombudsman was first proposed by the then law minister Ashok Kumar Sen in parliament in the early 1960s.
- The term Lokpal and Lokayukta were coined by Dr. L. M. Singhvi.
- In 1966, the First Administrative Reforms Commission recommended the setting up of two independent authorities- at the central and state level, to look into complaints against public functionaries, including MPs.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- The members are appointed by the president on the recommendation of a Selection Committee.
- The selection committee is composed of the Prime Minister who is the Chairperson, Speaker of Lok Sabha, Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha, Chief Justice of India or a Judge nominated by him/her and One eminent jurist.
- For selecting the chairperson and the members, the selection committee constitutes a search panel of at least eight persons.
- Under the Lokpal Act of 2013, the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) is supposed to put together a list of candidates interested to be the chairperson or members of the Lokpal.
- This list would then go to the proposed eight-member search committee, which would shortlist names and place them before the selection panel headed by the Prime Minister.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Lokpal is a multi-member body, that consists of one chairperson and a maximum of 8 members.
- Chairperson of the Lokpal should be either the former Chief Justice of India or the former Judge of Supreme Court or an eminent person with impeccable integrity and outstanding ability, having special knowledge and expertise of minimum 25 years in the matters relating to anti-corruption policy, public administration, vigilance, finance including insurance and banking, law and management.
- The term of office for Lokpal Chairman and Members is 5 years or till the age of 70 years.
Statement 3 is correct
- The Inquiry Wing of the Lokpal has been vested with the powers of a civil court.
- Lokpal has powers of confiscation of assets, proceeds, receipts and benefits arisen or procured by means of corruption in special circumstances.
- Lokpal has the power to recommend transfer or suspension of public servant connected with allegation of corruption.
- Lokpal has the power to give directions to prevent the destruction of records during the preliminary inquiry.
Statement 4 is incorrect
- In 1966, Guyana became the first developing nation to adopt the concept of the ombudsman.
- Subsequently, it was further adopted by Mauritius, Singapore, Malaysia, and India as well.
- In India, the concept of constitutional ombudsman was first proposed by the then law minister Ashok Kumar Sen in parliament in the early 1960s.
- The term Lokpal and Lokayukta were coined by Dr. L. M. Singhvi.
- In 1966, the First Administrative Reforms Commission recommended the setting up of two independent authorities- at the central and state level, to look into complaints against public functionaries, including MPs.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 3 of 11
3. Question
Q3. {Prelims – In News} Which of the following is not true about Mekong river?
Correct
Explanation
- Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia.
- It is the world’s twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia.
- It originates from the Sanjiangyuan in the Tibetan Plateau in China.
- High on the Tibetan Plateau, Sanjiangyuan covers an area approximately the size of England in the south of Qinghai province.
- This is the largest uninterrupted snow leopard habitat anywhere in the world.
- The river drains into the South China Sea.
- It flows through six Asian countries: China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam and covers a total length of 2700 km.
- Capitals cities on its banks – Vientiane– the capital of Laos and Phnom Penh-the capital of Cambodia.
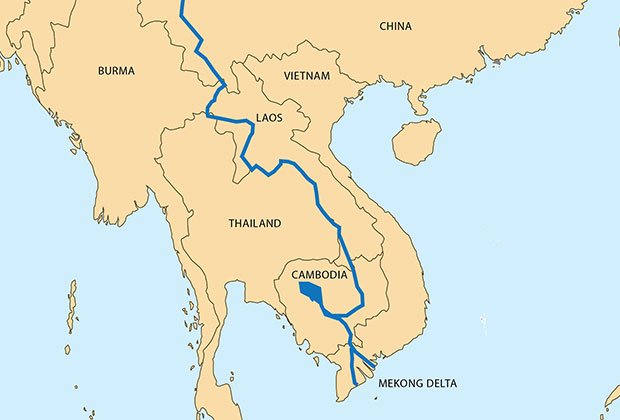
Answer: (d) It originates in the Tanggula Mountains in the central Tibetan Plateau; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
- Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia.
- It is the world’s twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia.
- It originates from the Sanjiangyuan in the Tibetan Plateau in China.
- High on the Tibetan Plateau, Sanjiangyuan covers an area approximately the size of England in the south of Qinghai province.
- This is the largest uninterrupted snow leopard habitat anywhere in the world.
- The river drains into the South China Sea.
- It flows through six Asian countries: China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam and covers a total length of 2700 km.
- Capitals cities on its banks – Vientiane– the capital of Laos and Phnom Penh-the capital of Cambodia.

Answer: (d) It originates in the Tanggula Mountains in the central Tibetan Plateau; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
- Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia.
- It is the world’s twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia.
- It originates from the Sanjiangyuan in the Tibetan Plateau in China.
- High on the Tibetan Plateau, Sanjiangyuan covers an area approximately the size of England in the south of Qinghai province.
- This is the largest uninterrupted snow leopard habitat anywhere in the world.
- The river drains into the South China Sea.
- It flows through six Asian countries: China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam and covers a total length of 2700 km.
- Capitals cities on its banks – Vientiane– the capital of Laos and Phnom Penh-the capital of Cambodia.

Answer: (d) It originates in the Tanggula Mountains in the central Tibetan Plateau; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 4 of 11
4. Question
Q4. {Envi – Conservation} With reference to Greywater Reuse, consider the following statements about greywater:
- Greywater is sewage water contaminated with chemicals and urine or fecal matter.
- Greywater can be filtered and cleaned for reuse in the garden or irrigation purposes if properly treated.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are not correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Grey water is defined as wastewater that is produced from household processes (e.g. washing dishes, laundry and bathing).
- Grey water can contain harmful bacteria and even faecal matter that contaminates soil and groundwater.
- The Centre plans to replicate Karnataka’s KC Valley project nationwide to accelerate wastewater reuse.
- The KC Valley project supplies treated water from Bengaluru to fill lakes in dry districts like Bengaluru Rural, Kolar, and Chikkballapura.
- The project’s success in recharging groundwater prompted the Ministry to consider its implementation in other states for lake rejuvenation with recycled treated water.
Statement 2 is correct
- The Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organisation (CPHEEO) has specified permitted discharge standards for treated water; use of treated wastewater in agriculture and horticulture (MoHUA, 2012).
- When you use greywater for irrigation, your garden becomes a natural water treatment plant.
- As the water filters through the soil, it is purified by the plants and microorganisms in the soil.
- This process helps to remove pollutants and other contaminants from the water, making it safer for the environment.
- The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB, 2000) directs that treated wastewater can be used as a source of artificial ground water recharge once it meets standards and is compatible with existing groundwater.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Grey water is defined as wastewater that is produced from household processes (e.g. washing dishes, laundry and bathing).
- Grey water can contain harmful bacteria and even faecal matter that contaminates soil and groundwater.
- The Centre plans to replicate Karnataka’s KC Valley project nationwide to accelerate wastewater reuse.
- The KC Valley project supplies treated water from Bengaluru to fill lakes in dry districts like Bengaluru Rural, Kolar, and Chikkballapura.
- The project’s success in recharging groundwater prompted the Ministry to consider its implementation in other states for lake rejuvenation with recycled treated water.
Statement 2 is correct
- The Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organisation (CPHEEO) has specified permitted discharge standards for treated water; use of treated wastewater in agriculture and horticulture (MoHUA, 2012).
- When you use greywater for irrigation, your garden becomes a natural water treatment plant.
- As the water filters through the soil, it is purified by the plants and microorganisms in the soil.
- This process helps to remove pollutants and other contaminants from the water, making it safer for the environment.
- The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB, 2000) directs that treated wastewater can be used as a source of artificial ground water recharge once it meets standards and is compatible with existing groundwater.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Grey water is defined as wastewater that is produced from household processes (e.g. washing dishes, laundry and bathing).
- Grey water can contain harmful bacteria and even faecal matter that contaminates soil and groundwater.
- The Centre plans to replicate Karnataka’s KC Valley project nationwide to accelerate wastewater reuse.
- The KC Valley project supplies treated water from Bengaluru to fill lakes in dry districts like Bengaluru Rural, Kolar, and Chikkballapura.
- The project’s success in recharging groundwater prompted the Ministry to consider its implementation in other states for lake rejuvenation with recycled treated water.
Statement 2 is correct
- The Central Public Health and Environmental Engineering Organisation (CPHEEO) has specified permitted discharge standards for treated water; use of treated wastewater in agriculture and horticulture (MoHUA, 2012).
- When you use greywater for irrigation, your garden becomes a natural water treatment plant.
- As the water filters through the soil, it is purified by the plants and microorganisms in the soil.
- This process helps to remove pollutants and other contaminants from the water, making it safer for the environment.
- The Central Ground Water Board (CGWB, 2000) directs that treated wastewater can be used as a source of artificial ground water recharge once it meets standards and is compatible with existing groundwater.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 5 of 11
5. Question
Q5. {Prelims – Envi – Conservation} Ecocide has been in the news recently, it means?
Correct
Explanation
- The scale and long-term impact of the destruction in Gaza have led to calls for it to be investigated as a potential war crime, and to be classed as ecocide, which covers damage done to the environment by deliberate or negligent actions.
- Under the Rome Statute, which governs the international criminal court, it is a war crime to intentionally launch an excessive attack knowing that it will cause widespread, long-term and severe damage to the natural environment.
- The Geneva conventions require that warring parties do not use methods of warfare that cause “widespread, long-term and severe damage to the natural environment”.
- The full extent of the damage in Gaza has not yet been documented, but analysis of satellite imagery provided to the Guardian shows the destruction of about 38-48% of tree cover and farmland.
- Olive groves and farms have been reduced to packed earth; soil and groundwater have been contaminated by munitions and toxins; the sea is choked with sewage and waste; the air polluted by smoke and particulate matter.
- Researchers and environmental organisations say the destruction will have enormous effects on Gaza’s ecosystems and biodiversity.
- The scale and potential long-term impact of the damage have led to calls for it to be regarded as “ecocide” and investigated as a possible war crime.
- The lack of fuel has led to people in Gaza having to cut down trees wherever they can find them to burn for cooking or heating.
- The continuing conflict and siege conditions have resulted in the total collapse of Gaza’s already fragile civil infrastructure, including waste disposal, sewage treatment, fuel supplies and water management.
Answer: (c) Unlawful acts committed with potential to cause widespread or long-term damage to environment; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
- The scale and long-term impact of the destruction in Gaza have led to calls for it to be investigated as a potential war crime, and to be classed as ecocide, which covers damage done to the environment by deliberate or negligent actions.
- Under the Rome Statute, which governs the international criminal court, it is a war crime to intentionally launch an excessive attack knowing that it will cause widespread, long-term and severe damage to the natural environment.
- The Geneva conventions require that warring parties do not use methods of warfare that cause “widespread, long-term and severe damage to the natural environment”.
- The full extent of the damage in Gaza has not yet been documented, but analysis of satellite imagery provided to the Guardian shows the destruction of about 38-48% of tree cover and farmland.
- Olive groves and farms have been reduced to packed earth; soil and groundwater have been contaminated by munitions and toxins; the sea is choked with sewage and waste; the air polluted by smoke and particulate matter.
- Researchers and environmental organisations say the destruction will have enormous effects on Gaza’s ecosystems and biodiversity.
- The scale and potential long-term impact of the damage have led to calls for it to be regarded as “ecocide” and investigated as a possible war crime.
- The lack of fuel has led to people in Gaza having to cut down trees wherever they can find them to burn for cooking or heating.
- The continuing conflict and siege conditions have resulted in the total collapse of Gaza’s already fragile civil infrastructure, including waste disposal, sewage treatment, fuel supplies and water management.
Answer: (c) Unlawful acts committed with potential to cause widespread or long-term damage to environment; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
- The scale and long-term impact of the destruction in Gaza have led to calls for it to be investigated as a potential war crime, and to be classed as ecocide, which covers damage done to the environment by deliberate or negligent actions.
- Under the Rome Statute, which governs the international criminal court, it is a war crime to intentionally launch an excessive attack knowing that it will cause widespread, long-term and severe damage to the natural environment.
- The Geneva conventions require that warring parties do not use methods of warfare that cause “widespread, long-term and severe damage to the natural environment”.
- The full extent of the damage in Gaza has not yet been documented, but analysis of satellite imagery provided to the Guardian shows the destruction of about 38-48% of tree cover and farmland.
- Olive groves and farms have been reduced to packed earth; soil and groundwater have been contaminated by munitions and toxins; the sea is choked with sewage and waste; the air polluted by smoke and particulate matter.
- Researchers and environmental organisations say the destruction will have enormous effects on Gaza’s ecosystems and biodiversity.
- The scale and potential long-term impact of the damage have led to calls for it to be regarded as “ecocide” and investigated as a possible war crime.
- The lack of fuel has led to people in Gaza having to cut down trees wherever they can find them to burn for cooking or heating.
- The continuing conflict and siege conditions have resulted in the total collapse of Gaza’s already fragile civil infrastructure, including waste disposal, sewage treatment, fuel supplies and water management.
Answer: (c) Unlawful acts committed with potential to cause widespread or long-term damage to environment; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 6 of 11
6. Question
Q6. {Prelims – S&T – Tech} Consider the following statements:
- Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) stores information that uniquely identifies a cellular subscription.
- Embedded SIM cards include less customer freedom to adjust the device from one provider to another.
- Electronic SIM is a SIM that can load new carrier profiles digitally.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- A SIM (Subscriber Identity Module), also called a Universal Integrated Circuit Card or UICC, stores information that uniquely identifies a cellular subscription.
- SIM holds the credentials and security keys necessary to identify a subscriber.
- That identity comes in the form of a so-called IMSI number, or International Mobile Subscriber Identity, which is unique for every user or device on or off the network.
Statement 2 is correct
- An embedded SIM is a SIM card that cannot be removed from a device.
- Traditional SIM cards are made so that they can easily be swapped out of a phone, so that core service information can get ported from one physical device to another.
- With an embedded SIM, the chips are made to allow for information switching, so that the actual physical chip would not get removed from the device.
- When using embedded SIM, customers would not need to order replacement SIM cards and physically integrate them into their phones.
- The idea is that manufacturers would use the same SIM card across the industry.
- However, embedded SIM cards include less customer freedom to adjust the device from one provider to another.
Statement 3 is correct
- eSIM is a hardware that runs an application called eUICC, which has storage to hold multiple SIM profiles at the same time (but only one can be active), and can be provisioned remotely, over the air (OTA).
- eSIM is a SIM that can load new carrier profiles digitally, over the air, which means one no longer need to physically swap SIM cards in their devices.
- The profiles stored on an eSIM can be modified remotely, through software and API calls, without needing to physically swap SIMs.
- An eSIM can hold multiple SIM profiles at the same time, which can give a device access to multiple completely different carriers, however, only one SIM can be active at a time.
Answer: (c) All three; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- A SIM (Subscriber Identity Module), also called a Universal Integrated Circuit Card or UICC, stores information that uniquely identifies a cellular subscription.
- SIM holds the credentials and security keys necessary to identify a subscriber.
- That identity comes in the form of a so-called IMSI number, or International Mobile Subscriber Identity, which is unique for every user or device on or off the network.
Statement 2 is correct
- An embedded SIM is a SIM card that cannot be removed from a device.
- Traditional SIM cards are made so that they can easily be swapped out of a phone, so that core service information can get ported from one physical device to another.
- With an embedded SIM, the chips are made to allow for information switching, so that the actual physical chip would not get removed from the device.
- When using embedded SIM, customers would not need to order replacement SIM cards and physically integrate them into their phones.
- The idea is that manufacturers would use the same SIM card across the industry.
- However, embedded SIM cards include less customer freedom to adjust the device from one provider to another.
Statement 3 is correct
- eSIM is a hardware that runs an application called eUICC, which has storage to hold multiple SIM profiles at the same time (but only one can be active), and can be provisioned remotely, over the air (OTA).
- eSIM is a SIM that can load new carrier profiles digitally, over the air, which means one no longer need to physically swap SIM cards in their devices.
- The profiles stored on an eSIM can be modified remotely, through software and API calls, without needing to physically swap SIMs.
- An eSIM can hold multiple SIM profiles at the same time, which can give a device access to multiple completely different carriers, however, only one SIM can be active at a time.
Answer: (c) All three; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- A SIM (Subscriber Identity Module), also called a Universal Integrated Circuit Card or UICC, stores information that uniquely identifies a cellular subscription.
- SIM holds the credentials and security keys necessary to identify a subscriber.
- That identity comes in the form of a so-called IMSI number, or International Mobile Subscriber Identity, which is unique for every user or device on or off the network.
Statement 2 is correct
- An embedded SIM is a SIM card that cannot be removed from a device.
- Traditional SIM cards are made so that they can easily be swapped out of a phone, so that core service information can get ported from one physical device to another.
- With an embedded SIM, the chips are made to allow for information switching, so that the actual physical chip would not get removed from the device.
- When using embedded SIM, customers would not need to order replacement SIM cards and physically integrate them into their phones.
- The idea is that manufacturers would use the same SIM card across the industry.
- However, embedded SIM cards include less customer freedom to adjust the device from one provider to another.
Statement 3 is correct
- eSIM is a hardware that runs an application called eUICC, which has storage to hold multiple SIM profiles at the same time (but only one can be active), and can be provisioned remotely, over the air (OTA).
- eSIM is a SIM that can load new carrier profiles digitally, over the air, which means one no longer need to physically swap SIM cards in their devices.
- The profiles stored on an eSIM can be modified remotely, through software and API calls, without needing to physically swap SIMs.
- An eSIM can hold multiple SIM profiles at the same time, which can give a device access to multiple completely different carriers, however, only one SIM can be active at a time.
Answer: (c) All three; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 7 of 11
7. Question
Q7. {Prelims – In News} Consider the following statements:
- D-SIIs are insurance companies which are perceived as ‘Too Big or Too Important to Fail’.
- At present, Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) is the only D-SII in India.
- State Bank of India (SBI), ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank have been classified as domestic systemically important banks (D-SIBs).
How many of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- D-SIIs are insurance companies which are perceived as ‘too big or too important to fail’ (TBTF) based on their size, market importance, and domestic and global interconnectedness.
- Therefore, the continued functioning of D-SIIs is critical for the uninterrupted availability of insurance services to the national economy.
- Given the nature of their operations and the systemic importance of the D-SIIs, these insurers have to carry forward their efforts on the following:
- Raise the level of corporate governance.
- Identify all relevant risks and promote a sound risk management framework and culture.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- LIC and New India are the largest life and general insurance companies in the country, respectively and General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC Re) is the sole Indian reinsurer.
Statement 3 is correct
- The Reserve Bank had issued the Framework for dealing with Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
- D-SIB framework requires the RBI to disclose the names of banks designated as D-SIBs starting from 2015 and place these banks in appropriate buckets depending upon their Systemic Importance Scores (SISs).
- Based on the bucket in which a D-SIB is placed, an additional common equity requirement has to be applied to it.
- State Bank of India, ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank have been classified as domestic systemically important banks (D-SIBs).
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- D-SIIs are insurance companies which are perceived as ‘too big or too important to fail’ (TBTF) based on their size, market importance, and domestic and global interconnectedness.
- Therefore, the continued functioning of D-SIIs is critical for the uninterrupted availability of insurance services to the national economy.
- Given the nature of their operations and the systemic importance of the D-SIIs, these insurers have to carry forward their efforts on the following:
- Raise the level of corporate governance.
- Identify all relevant risks and promote a sound risk management framework and culture.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- LIC and New India are the largest life and general insurance companies in the country, respectively and General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC Re) is the sole Indian reinsurer.
Statement 3 is correct
- The Reserve Bank had issued the Framework for dealing with Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
- D-SIB framework requires the RBI to disclose the names of banks designated as D-SIBs starting from 2015 and place these banks in appropriate buckets depending upon their Systemic Importance Scores (SISs).
- Based on the bucket in which a D-SIB is placed, an additional common equity requirement has to be applied to it.
- State Bank of India, ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank have been classified as domestic systemically important banks (D-SIBs).
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- D-SIIs are insurance companies which are perceived as ‘too big or too important to fail’ (TBTF) based on their size, market importance, and domestic and global interconnectedness.
- Therefore, the continued functioning of D-SIIs is critical for the uninterrupted availability of insurance services to the national economy.
- Given the nature of their operations and the systemic importance of the D-SIIs, these insurers have to carry forward their efforts on the following:
- Raise the level of corporate governance.
- Identify all relevant risks and promote a sound risk management framework and culture.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- LIC and New India are the largest life and general insurance companies in the country, respectively and General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC Re) is the sole Indian reinsurer.
Statement 3 is correct
- The Reserve Bank had issued the Framework for dealing with Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs).
- D-SIB framework requires the RBI to disclose the names of banks designated as D-SIBs starting from 2015 and place these banks in appropriate buckets depending upon their Systemic Importance Scores (SISs).
- Based on the bucket in which a D-SIB is placed, an additional common equity requirement has to be applied to it.
- State Bank of India, ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank have been classified as domestic systemically important banks (D-SIBs).
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 8 of 11
8. Question
Q8. {Agri – Issues} Consider the following statements about Food Waste Index Report, 2024:
- Food Waste Index tracks both the global and national generation of food and inedible parts wasted at the retail and consumer levels.
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is the custodian of the Index.
- Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 13 is associated with food waste.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- World wastes 1 billion meals a day, says UN’s Food Waste Index Report, 2024.
- The report is jointly authored by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and WRAP (Waste and Resources Action Programme), a U.K.-based non-profit.
- The report was released ahead of the International Day of Zero Waste, observed on March 30.
- The Food Waste Index tracks the global and national generation of food and inedible parts wasted at the retail and consumer (household and food service) levels.
- The report defines food waste as food and the associated inedible parts removed from the human food supply chain.
- Food loss is defined as all the crop and livestock human-edible commodities that directly/indirectly, completely exit the post-harvest production, excluding, the retail level.
Statement 2 is correct
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is its custodian.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- The report pointed out that many low and middle income countries continue to lack adequate systems for tracking progress to meet Sustainable Development Goal 12.3.
- Sustainable Development Goal 12.3
- By 2020, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses.
- Hotter countries appear to generate more food waste per capita in households, potentially due to higher consumption of fresh foods with substantial inedible parts and a lack of robust cold chains.
- The report found that food loss and waste generated 8-10% of annual global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, almost 5 times that of the aviation sector.
- Food waste also contributes to significant biodiversity loss by taking up the equivalent of almost a third of the world’s agricultural land.
- It is estimated the roll of both food loss and waste on the global economy at $1 trillion.
- At present, only four G-20 countries (Australia, Japan, U.K., and U.S.) and the European Union have food waste estimates suitable for tracking progress to 2030.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- World wastes 1 billion meals a day, says UN’s Food Waste Index Report, 2024.
- The report is jointly authored by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and WRAP (Waste and Resources Action Programme), a U.K.-based non-profit.
- The report was released ahead of the International Day of Zero Waste, observed on March 30.
- The Food Waste Index tracks the global and national generation of food and inedible parts wasted at the retail and consumer (household and food service) levels.
- The report defines food waste as food and the associated inedible parts removed from the human food supply chain.
- Food loss is defined as all the crop and livestock human-edible commodities that directly/indirectly, completely exit the post-harvest production, excluding, the retail level.
Statement 2 is correct
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is its custodian.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- The report pointed out that many low and middle income countries continue to lack adequate systems for tracking progress to meet Sustainable Development Goal 12.3.
- Sustainable Development Goal 12.3
- By 2020, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses.
- Hotter countries appear to generate more food waste per capita in households, potentially due to higher consumption of fresh foods with substantial inedible parts and a lack of robust cold chains.
- The report found that food loss and waste generated 8-10% of annual global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, almost 5 times that of the aviation sector.
- Food waste also contributes to significant biodiversity loss by taking up the equivalent of almost a third of the world’s agricultural land.
- It is estimated the roll of both food loss and waste on the global economy at $1 trillion.
- At present, only four G-20 countries (Australia, Japan, U.K., and U.S.) and the European Union have food waste estimates suitable for tracking progress to 2030.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- World wastes 1 billion meals a day, says UN’s Food Waste Index Report, 2024.
- The report is jointly authored by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and WRAP (Waste and Resources Action Programme), a U.K.-based non-profit.
- The report was released ahead of the International Day of Zero Waste, observed on March 30.
- The Food Waste Index tracks the global and national generation of food and inedible parts wasted at the retail and consumer (household and food service) levels.
- The report defines food waste as food and the associated inedible parts removed from the human food supply chain.
- Food loss is defined as all the crop and livestock human-edible commodities that directly/indirectly, completely exit the post-harvest production, excluding, the retail level.
Statement 2 is correct
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is its custodian.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- The report pointed out that many low and middle income countries continue to lack adequate systems for tracking progress to meet Sustainable Development Goal 12.3.
- Sustainable Development Goal 12.3
- By 2020, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses.
- Hotter countries appear to generate more food waste per capita in households, potentially due to higher consumption of fresh foods with substantial inedible parts and a lack of robust cold chains.
- The report found that food loss and waste generated 8-10% of annual global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, almost 5 times that of the aviation sector.
- Food waste also contributes to significant biodiversity loss by taking up the equivalent of almost a third of the world’s agricultural land.
- It is estimated the roll of both food loss and waste on the global economy at $1 trillion.
- At present, only four G-20 countries (Australia, Japan, U.K., and U.S.) and the European Union have food waste estimates suitable for tracking progress to 2030.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 9 of 11
9. Question
Q9. {Prelims – Envi – Pollution} Consider the following statements with respect to the Decision Support System (DSS):
- It is a numerical model-based framework to forecast Delhi’s air quality developed by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune.
- The system works only in winters.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are not correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- DSS is a numerical model-based framework to forecast Delhi’s air quality and sources of local and regional pollution which can impact the air.
- DSS was developed by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) Pune.
- The system gives forecasts the result of biomass burning activities in neighbouring states.
- DSS enhances Delhi’s air quality forecasting with updated 2023 emission inventory and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) satellite for PM2.5 predictions.
Statement 2 is correct
- The system works only in winter and is stopped from March to August, currently forecasts the contribution of emissions in Delhi’s air quality from 19 neighbouring districts.
- Now, the system will also forecast how Delhi’s emissions impact the air of eight surrounding districts in NCR.
- The emissions inventory currently being used was last updated in 2018, however DSS has now received an updated emission inventory of 2023.
- The two models, System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (Safar) and DSS, had temporarily stopped sharing data on air pollution for the country as there were differences between their forecasts and source contribution.
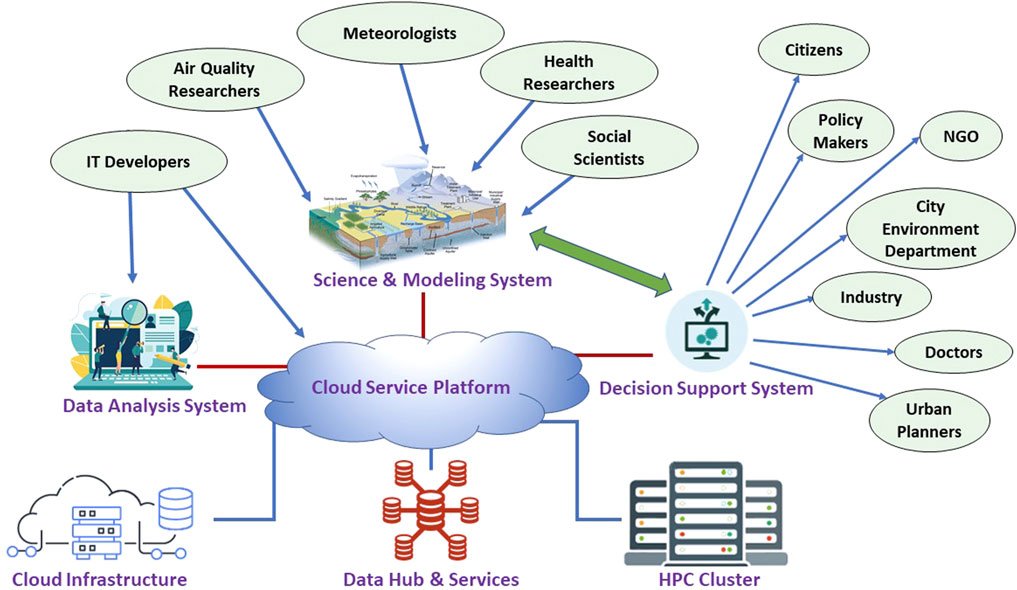
Answer: (d) Neither 1 nor 2; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- DSS is a numerical model-based framework to forecast Delhi’s air quality and sources of local and regional pollution which can impact the air.
- DSS was developed by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) Pune.
- The system gives forecasts the result of biomass burning activities in neighbouring states.
- DSS enhances Delhi’s air quality forecasting with updated 2023 emission inventory and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) satellite for PM2.5 predictions.
Statement 2 is correct
- The system works only in winter and is stopped from March to August, currently forecasts the contribution of emissions in Delhi’s air quality from 19 neighbouring districts.
- Now, the system will also forecast how Delhi’s emissions impact the air of eight surrounding districts in NCR.
- The emissions inventory currently being used was last updated in 2018, however DSS has now received an updated emission inventory of 2023.
- The two models, System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (Safar) and DSS, had temporarily stopped sharing data on air pollution for the country as there were differences between their forecasts and source contribution.

Answer: (d) Neither 1 nor 2; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- DSS is a numerical model-based framework to forecast Delhi’s air quality and sources of local and regional pollution which can impact the air.
- DSS was developed by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) Pune.
- The system gives forecasts the result of biomass burning activities in neighbouring states.
- DSS enhances Delhi’s air quality forecasting with updated 2023 emission inventory and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) satellite for PM2.5 predictions.
Statement 2 is correct
- The system works only in winter and is stopped from March to August, currently forecasts the contribution of emissions in Delhi’s air quality from 19 neighbouring districts.
- Now, the system will also forecast how Delhi’s emissions impact the air of eight surrounding districts in NCR.
- The emissions inventory currently being used was last updated in 2018, however DSS has now received an updated emission inventory of 2023.
- The two models, System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research (Safar) and DSS, had temporarily stopped sharing data on air pollution for the country as there were differences between their forecasts and source contribution.

Answer: (d) Neither 1 nor 2; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 10 of 11
10. Question
Q10. {A&C – Art – Puppetry} Consider the following pairs:
Puppet Form States - Kathputli
Gujarat - Gombeyatta
Andhra Pradesh - Ravanachhaya
Karnataka How many of the pairs are correctly matched?
Correct
Explanation
- Ravanachhaya
- Ravanachhaya is a Puppetry form of Odisha.
- The puppets are in one piece and have no joints.
- They are not coloured, hence throw opaque shadows on the screen.
- The puppets are made of deer skin and are conceived in bold dramatic poses.
- Apart from human and animal characters, many props such as trees, mountains, chariots, etc. are also used.

- Gombeyatta
- Gombeyatta is a puppetry form of Karnataka.
- The Gombeyatta puppet figures are highly stylized and have joints at the legs, shoulders, elbows, hips and knees.
- These puppets are manipulated by five to seven strings tied to a prop.
- Episodes enacted in Gombeyatta are usually based on Prasangas of the Yakshagana plays.

- Kathputli
- Kathputli is a famous puppetry form of Rajasthan.
- Carved from a single piece of wood, these puppets are like large dolls that are colorfully dressed.
- Puppeteers manipulate them with two to five strings which are normally tied to their fingers and not to a prop or a support.

Answer: (d) None; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
- Ravanachhaya
- Ravanachhaya is a Puppetry form of Odisha.
- The puppets are in one piece and have no joints.
- They are not coloured, hence throw opaque shadows on the screen.
- The puppets are made of deer skin and are conceived in bold dramatic poses.
- Apart from human and animal characters, many props such as trees, mountains, chariots, etc. are also used.

- Gombeyatta
- Gombeyatta is a puppetry form of Karnataka.
- The Gombeyatta puppet figures are highly stylized and have joints at the legs, shoulders, elbows, hips and knees.
- These puppets are manipulated by five to seven strings tied to a prop.
- Episodes enacted in Gombeyatta are usually based on Prasangas of the Yakshagana plays.

- Kathputli
- Kathputli is a famous puppetry form of Rajasthan.
- Carved from a single piece of wood, these puppets are like large dolls that are colorfully dressed.
- Puppeteers manipulate them with two to five strings which are normally tied to their fingers and not to a prop or a support.

Answer: (d) None; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
- Ravanachhaya
- Ravanachhaya is a Puppetry form of Odisha.
- The puppets are in one piece and have no joints.
- They are not coloured, hence throw opaque shadows on the screen.
- The puppets are made of deer skin and are conceived in bold dramatic poses.
- Apart from human and animal characters, many props such as trees, mountains, chariots, etc. are also used.

- Gombeyatta
- Gombeyatta is a puppetry form of Karnataka.
- The Gombeyatta puppet figures are highly stylized and have joints at the legs, shoulders, elbows, hips and knees.
- These puppets are manipulated by five to seven strings tied to a prop.
- Episodes enacted in Gombeyatta are usually based on Prasangas of the Yakshagana plays.

- Kathputli
- Kathputli is a famous puppetry form of Rajasthan.
- Carved from a single piece of wood, these puppets are like large dolls that are colorfully dressed.
- Puppeteers manipulate them with two to five strings which are normally tied to their fingers and not to a prop or a support.

Answer: (d) None; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 11 of 11
11. Question
Q11. {Internal Security – Law} Consider the following statements about Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA):
- Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru originally brought the act into force as an ordinance and then notified it as an Act in 1958 to curb the violence in the Northeastern States.
- AFSPA is completely withdrawn in Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- Both the State and Central governments can issue notification regarding the AFSPA.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Origin of AFSPA:
- The Act in its original form was promulgated by the British in response to the Quit India movement in 1942.
- After Independence, Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru decided to retain the Act, which was first brought in as an ordinance and then notified as an Act in 1958.
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, enacted in the year 1958, grants extraordinary powers and immunity to the armed forces to bring back order in the “disturbed areas”.
- The Act came into force in the context of increasing violence in the Northeastern States decades ago, which the State governments found difficult to control.
Statement 2 is correct
- States under AFSPA – Nagaland, Manipur, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir.
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA), 1958, was completely withdrawn in Meghalaya in 2018, Tripura in 2015 and Mizoram in the 1980s.
Statement 3 is correct
- Both the State and Central governments can issue notification regarding the AFSPA.
- The MHA issues periodic “disturbed area” notification to extend the AFSPA only for Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The notification for Manipur and Assam is issued by the State governments.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Origin of AFSPA:
- The Act in its original form was promulgated by the British in response to the Quit India movement in 1942.
- After Independence, Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru decided to retain the Act, which was first brought in as an ordinance and then notified as an Act in 1958.
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, enacted in the year 1958, grants extraordinary powers and immunity to the armed forces to bring back order in the “disturbed areas”.
- The Act came into force in the context of increasing violence in the Northeastern States decades ago, which the State governments found difficult to control.
Statement 2 is correct
- States under AFSPA – Nagaland, Manipur, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir.
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA), 1958, was completely withdrawn in Meghalaya in 2018, Tripura in 2015 and Mizoram in the 1980s.
Statement 3 is correct
- Both the State and Central governments can issue notification regarding the AFSPA.
- The MHA issues periodic “disturbed area” notification to extend the AFSPA only for Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The notification for Manipur and Assam is issued by the State governments.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- Origin of AFSPA:
- The Act in its original form was promulgated by the British in response to the Quit India movement in 1942.
- After Independence, Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru decided to retain the Act, which was first brought in as an ordinance and then notified as an Act in 1958.
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, enacted in the year 1958, grants extraordinary powers and immunity to the armed forces to bring back order in the “disturbed areas”.
- The Act came into force in the context of increasing violence in the Northeastern States decades ago, which the State governments found difficult to control.
Statement 2 is correct
- States under AFSPA – Nagaland, Manipur, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir.
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA), 1958, was completely withdrawn in Meghalaya in 2018, Tripura in 2015 and Mizoram in the 1980s.
Statement 3 is correct
- Both the State and Central governments can issue notification regarding the AFSPA.
- The MHA issues periodic “disturbed area” notification to extend the AFSPA only for Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The notification for Manipur and Assam is issued by the State governments.
Answer: (b) Only two; Difficulty Level: Medium
Newsletter Updates
Subscribe to our newsletter and never miss an important update!
Assured Discounts on our New Products!
Related Posts

Daily Prelims Practise Questions (PPQs) – October 29-30 2023

January 23 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

April 04 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

December 15 2023 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

March 19 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

December 20 2023 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

December 10-11 2023 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)






![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)








