
March 27 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- These Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs) are based on PMF IAS Daily Current Affairs.
- The daily current affairs are uploaded every day by 8 PM. You can read the Daily Current Affairs from here.
- Subscribers of the “Current Affairs” course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC from here.
[Quiz] Daily Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs) – March 27 2024
0 of 10 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Information
These MCQs are based on PMF IAS Daily Current Affairs. The daily current affairs are uploaded every day by 8 PM. You can read the Daily Current Affairs from here. Subscribers of the “Current Affairs” course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC from here.
You have already completed the Test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the Test.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this Test:
Your results are here!! for" [Quiz] Daily Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs) – March 27 2024 "
0 of 10 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
Your Final Score is : 0
You have attempted : 0
Number of Correct Questions : 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions : 0 and Negative marks 0
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
-
Not categorized
You have attempted: 0
Number of Correct Questions: 0 and scored 0
Number of Incorrect Questions: 0 and Negative marks 0
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 10
1. Question
Q1. {Prelims – In News} The Moyar Valley recently seen in news is located in which of the following region?
Correct
Explanation
- Moyar valley is the home of critically endangered Gyps Vulture.
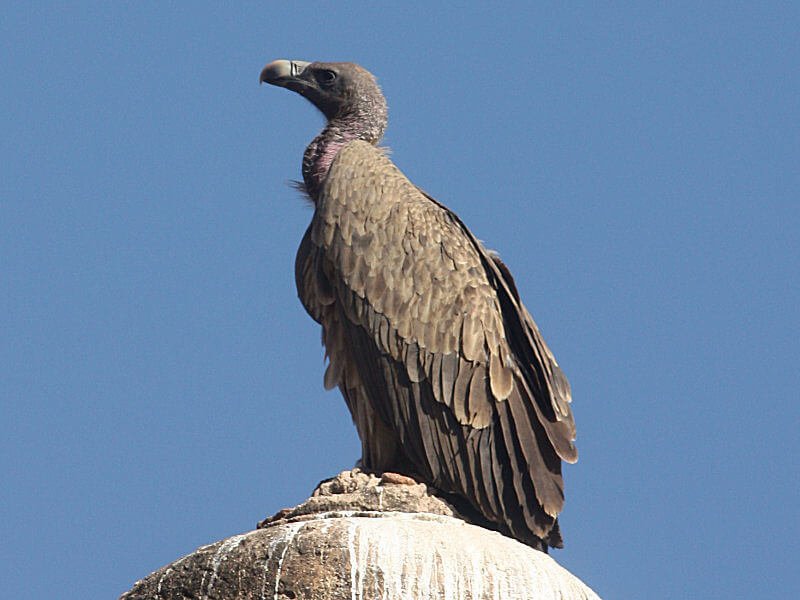

- It is also known by the name Maayar (Invisible River) valley.
- It extends from Gudalur through the core area of Mudumalai Tiger Reserve.
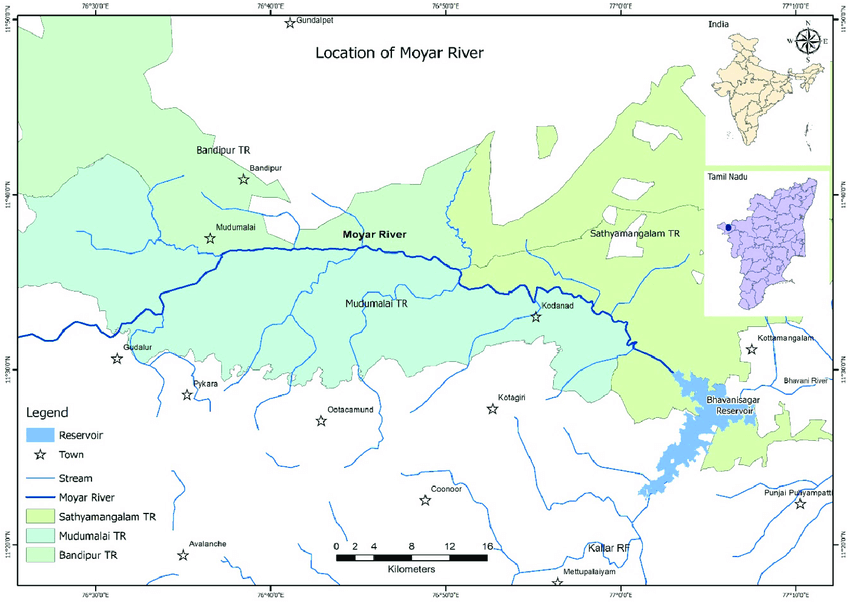
- The valley is an important biome in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, sheltering several vital species like tiger and elephant and the critically endangered Gyps vulture.
- A biome is an area classified according to the species that live in that location.
- It is the only region in peninsular India which has the biggest nesting colony of Gyps vultures in the wild.
- The region provides a stable food-chain to nature’s scavengers, simply because these carcasses are mostly free from Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other poisonous chemicals.
- Resident Vultures of Moyar Valley – White Rumped vultures, Long Billed vultures, Red Headed vultures, and Egyptian vultures.
Answer: (c) Karnataka-Kerala-Tamil Nadu; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
- Moyar valley is the home of critically endangered Gyps Vulture.

- It is also known by the name Maayar (Invisible River) valley.
- It extends from Gudalur through the core area of Mudumalai Tiger Reserve.

- The valley is an important biome in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, sheltering several vital species like tiger and elephant and the critically endangered Gyps vulture.
- A biome is an area classified according to the species that live in that location.
- It is the only region in peninsular India which has the biggest nesting colony of Gyps vultures in the wild.
- The region provides a stable food-chain to nature’s scavengers, simply because these carcasses are mostly free from Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other poisonous chemicals.
- Resident Vultures of Moyar Valley – White Rumped vultures, Long Billed vultures, Red Headed vultures, and Egyptian vultures.
Answer: (c) Karnataka-Kerala-Tamil Nadu; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
- Moyar valley is the home of critically endangered Gyps Vulture.

- It is also known by the name Maayar (Invisible River) valley.
- It extends from Gudalur through the core area of Mudumalai Tiger Reserve.

- The valley is an important biome in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, sheltering several vital species like tiger and elephant and the critically endangered Gyps vulture.
- A biome is an area classified according to the species that live in that location.
- It is the only region in peninsular India which has the biggest nesting colony of Gyps vultures in the wild.
- The region provides a stable food-chain to nature’s scavengers, simply because these carcasses are mostly free from Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other poisonous chemicals.
- Resident Vultures of Moyar Valley – White Rumped vultures, Long Billed vultures, Red Headed vultures, and Egyptian vultures.
Answer: (c) Karnataka-Kerala-Tamil Nadu; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 2 of 10
2. Question
Q2. {Internal Security – Money Laundering} Consider the following statements:
- Proceeds of crime is any property derived directly or indirectly, by any person as a result of criminal activity.
- A Person who is not even shown as an accused in any scheduled or predicate offence can still be prosecuted under Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) criminalises money laundering.
- According to PMLA, money laundering is defined as:
- Whosoever directly or indirectly attempts to indulge in any process connected with the proceeds of crime, including its concealment, possession, acquisition shall be guilty of offence of money laundering.
- Proceeds of crime is any property derived directly or indirectly, by any person as a result of criminal activity relating to a scheduled offence.
- The law also defines scheduled offences, which are listed in two schedules attached to the PMLA.
- These acts in the schedules (scheduled acts) are also called predicate offences.
- Predicate offenses in money laundering refers to a crime component of a larger crime.
- In a financial context, the predicate offense would be any crime that generates monetary proceeds.
- The larger crime would be money laundering or financing of terrorism.
Statement 2 is correct
- In a judgement in the Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors v Union of India case, the Supreme Court upheld key provisions of the PMLA.
- The court had said that if an accused in the predicate offence is acquitted or discharged, he cannot be prosecuted for the offence punishable under the PMLA.
- The Supreme Court in Pavana Dibbur v Enforcement Directorate verdict, answered the question of, what if an accused is not even shown as an accused in any scheduled or predicate offence.
- The verdict said that an accused in the PMLA case who comes into the picture after the scheduled offence is committed, by assisting in the concealment or use of proceeds of crime, need not be an accused in the scheduled offence.
- Here, the proceeds of crime that the accused has allegedly concealed or possessed must simply be linked to the scheduled offence.
- Such an accused can still be prosecuted under PMLA so long as the scheduled offence exists, the court had said.
Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) criminalises money laundering.
- According to PMLA, money laundering is defined as:
- Whosoever directly or indirectly attempts to indulge in any process connected with the proceeds of crime, including its concealment, possession, acquisition shall be guilty of offence of money laundering.
- Proceeds of crime is any property derived directly or indirectly, by any person as a result of criminal activity relating to a scheduled offence.
- The law also defines scheduled offences, which are listed in two schedules attached to the PMLA.
- These acts in the schedules (scheduled acts) are also called predicate offences.
- Predicate offenses in money laundering refers to a crime component of a larger crime.
- In a financial context, the predicate offense would be any crime that generates monetary proceeds.
- The larger crime would be money laundering or financing of terrorism.
Statement 2 is correct
- In a judgement in the Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors v Union of India case, the Supreme Court upheld key provisions of the PMLA.
- The court had said that if an accused in the predicate offence is acquitted or discharged, he cannot be prosecuted for the offence punishable under the PMLA.
- The Supreme Court in Pavana Dibbur v Enforcement Directorate verdict, answered the question of, what if an accused is not even shown as an accused in any scheduled or predicate offence.
- The verdict said that an accused in the PMLA case who comes into the picture after the scheduled offence is committed, by assisting in the concealment or use of proceeds of crime, need not be an accused in the scheduled offence.
- Here, the proceeds of crime that the accused has allegedly concealed or possessed must simply be linked to the scheduled offence.
- Such an accused can still be prosecuted under PMLA so long as the scheduled offence exists, the court had said.
Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) criminalises money laundering.
- According to PMLA, money laundering is defined as:
- Whosoever directly or indirectly attempts to indulge in any process connected with the proceeds of crime, including its concealment, possession, acquisition shall be guilty of offence of money laundering.
- Proceeds of crime is any property derived directly or indirectly, by any person as a result of criminal activity relating to a scheduled offence.
- The law also defines scheduled offences, which are listed in two schedules attached to the PMLA.
- These acts in the schedules (scheduled acts) are also called predicate offences.
- Predicate offenses in money laundering refers to a crime component of a larger crime.
- In a financial context, the predicate offense would be any crime that generates monetary proceeds.
- The larger crime would be money laundering or financing of terrorism.
Statement 2 is correct
- In a judgement in the Vijay Madanlal Choudhary & Ors v Union of India case, the Supreme Court upheld key provisions of the PMLA.
- The court had said that if an accused in the predicate offence is acquitted or discharged, he cannot be prosecuted for the offence punishable under the PMLA.
- The Supreme Court in Pavana Dibbur v Enforcement Directorate verdict, answered the question of, what if an accused is not even shown as an accused in any scheduled or predicate offence.
- The verdict said that an accused in the PMLA case who comes into the picture after the scheduled offence is committed, by assisting in the concealment or use of proceeds of crime, need not be an accused in the scheduled offence.
- Here, the proceeds of crime that the accused has allegedly concealed or possessed must simply be linked to the scheduled offence.
- Such an accused can still be prosecuted under PMLA so long as the scheduled offence exists, the court had said.
Answer: (c) Both 1 and 2; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 3 of 10
3. Question
Q3. {S&T – Space} Consider the following statements about the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module 3 (POEM 3) Mission:
- POEM performs in-orbit scientific experiments during the 3rd stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) launch vehicle.
- PSLV is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
Which of the above statement is/are not correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- PSLV Orbital Experimental Module 3 (POEM 3):
- The fourth stage of PSLV (PS4), also called the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM) will perform orbital experiments.
- Since this is the 3rd time ISRO has used PS4 to exhibit orbital experiments, XPoSAT’s PS4 is called POEM-3.
- The spent PS4 stage will be used to conduct in-orbit scientific experiments in microgravity conditions for an extended duration of 4-6 months.
- It derives power from the solar panels mounted around the PS4 tank and a Lithium-ion battery.
- POEM-3 is equipped with 10 payloads.
- Following the successful placement of all satellites into their designated orbits, the final stage of the PSLV was converted into a 3-axis stabilized platform known as POEM-3.
- This stage was then deorbited from an altitude of 650 km to 350 km, enabling an expedited re-entry process.
- The mission objectives of these payloads were met in a month.
Statement 2 is correct
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- After its first successful launch in October 1994, PSLV emerged as a reliable and versatile workhorse launch vehicle of India.
- The vehicle has launched numerous Indian and foreign customer satellites.
- Besides, the vehicle successfully launched two spacecraft “Chandrayaan-1 in 2008 and Mars Orbiter Spacecraft in 2013“that later travelled to Moon and Mars respectively.
- Chandrayaan-1 and MOM are feathers in the hat of PSLV.
- In POEM 3 Mission, PSLV-C58 rocket was used.
Answer: (a) 1 Only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- PSLV Orbital Experimental Module 3 (POEM 3):
- The fourth stage of PSLV (PS4), also called the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM) will perform orbital experiments.
- Since this is the 3rd time ISRO has used PS4 to exhibit orbital experiments, XPoSAT’s PS4 is called POEM-3.
- The spent PS4 stage will be used to conduct in-orbit scientific experiments in microgravity conditions for an extended duration of 4-6 months.
- It derives power from the solar panels mounted around the PS4 tank and a Lithium-ion battery.
- POEM-3 is equipped with 10 payloads.
- Following the successful placement of all satellites into their designated orbits, the final stage of the PSLV was converted into a 3-axis stabilized platform known as POEM-3.
- This stage was then deorbited from an altitude of 650 km to 350 km, enabling an expedited re-entry process.
- The mission objectives of these payloads were met in a month.
Statement 2 is correct
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- After its first successful launch in October 1994, PSLV emerged as a reliable and versatile workhorse launch vehicle of India.
- The vehicle has launched numerous Indian and foreign customer satellites.
- Besides, the vehicle successfully launched two spacecraft “Chandrayaan-1 in 2008 and Mars Orbiter Spacecraft in 2013“that later travelled to Moon and Mars respectively.
- Chandrayaan-1 and MOM are feathers in the hat of PSLV.
- In POEM 3 Mission, PSLV-C58 rocket was used.
Answer: (a) 1 Only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- PSLV Orbital Experimental Module 3 (POEM 3):
- The fourth stage of PSLV (PS4), also called the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM) will perform orbital experiments.
- Since this is the 3rd time ISRO has used PS4 to exhibit orbital experiments, XPoSAT’s PS4 is called POEM-3.
- The spent PS4 stage will be used to conduct in-orbit scientific experiments in microgravity conditions for an extended duration of 4-6 months.
- It derives power from the solar panels mounted around the PS4 tank and a Lithium-ion battery.
- POEM-3 is equipped with 10 payloads.
- Following the successful placement of all satellites into their designated orbits, the final stage of the PSLV was converted into a 3-axis stabilized platform known as POEM-3.
- This stage was then deorbited from an altitude of 650 km to 350 km, enabling an expedited re-entry process.
- The mission objectives of these payloads were met in a month.
Statement 2 is correct
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India.
- It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- After its first successful launch in October 1994, PSLV emerged as a reliable and versatile workhorse launch vehicle of India.
- The vehicle has launched numerous Indian and foreign customer satellites.
- Besides, the vehicle successfully launched two spacecraft “Chandrayaan-1 in 2008 and Mars Orbiter Spacecraft in 2013“that later travelled to Moon and Mars respectively.
- Chandrayaan-1 and MOM are feathers in the hat of PSLV.
- In POEM 3 Mission, PSLV-C58 rocket was used.
Answer: (a) 1 Only; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 4 of 10
4. Question
Q4. {IE – Employment} Which one of the following organisation prepared the India Employment Report 2024?
Correct
Explanation
- The recently released India Employment Report 2024 has highlighted the issue of high unemployment amongst India’s educated youth.
- The report is prepared by the Institute for Human Development (IHD) and International Labour Organisation (ILO).
- India’s youth account for almost 83% of the unemployed workforce.
- The Labour Force Participation Rate, Worker Population Ratio and the Unemployment Rate showed a long-term deterioration between 2000 and 2018, but witnessed an improvement after 2019.
- The youth unemployment rate increased with the level of education, with the highest among graduates and higher among women than men.
- Most of the workers remain engaged in informal work and the share of regular work declined after 2018.
- India’s large young workforce don’t appear to have the necessary skills with 75% of youth unable to send emails with attachments.
- India remains ready to reap a demographic dividend for at least another decade due to the youth population remaining at 23% of the total in 2036 from 27% in 2021.
Answer: (d) International Labour Organisation; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
- The recently released India Employment Report 2024 has highlighted the issue of high unemployment amongst India’s educated youth.
- The report is prepared by the Institute for Human Development (IHD) and International Labour Organisation (ILO).
- India’s youth account for almost 83% of the unemployed workforce.
- The Labour Force Participation Rate, Worker Population Ratio and the Unemployment Rate showed a long-term deterioration between 2000 and 2018, but witnessed an improvement after 2019.
- The youth unemployment rate increased with the level of education, with the highest among graduates and higher among women than men.
- Most of the workers remain engaged in informal work and the share of regular work declined after 2018.
- India’s large young workforce don’t appear to have the necessary skills with 75% of youth unable to send emails with attachments.
- India remains ready to reap a demographic dividend for at least another decade due to the youth population remaining at 23% of the total in 2036 from 27% in 2021.
Answer: (d) International Labour Organisation; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
- The recently released India Employment Report 2024 has highlighted the issue of high unemployment amongst India’s educated youth.
- The report is prepared by the Institute for Human Development (IHD) and International Labour Organisation (ILO).
- India’s youth account for almost 83% of the unemployed workforce.
- The Labour Force Participation Rate, Worker Population Ratio and the Unemployment Rate showed a long-term deterioration between 2000 and 2018, but witnessed an improvement after 2019.
- The youth unemployment rate increased with the level of education, with the highest among graduates and higher among women than men.
- Most of the workers remain engaged in informal work and the share of regular work declined after 2018.
- India’s large young workforce don’t appear to have the necessary skills with 75% of youth unable to send emails with attachments.
- India remains ready to reap a demographic dividend for at least another decade due to the youth population remaining at 23% of the total in 2036 from 27% in 2021.
Answer: (d) International Labour Organisation; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 5 of 10
5. Question
Q5. {Agri – Tech} Consider the following statements about Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC):
- ICCC will enable monitoring of the farm sector by making available at one place geospatial information received from multiple sources.
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmer’s Welfare and Ministry of Earth Sciences, with IMD providing the technical assistance.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- The ICCC is a tech-based solution involving multiple IT applications and platforms, which is designed to help in making informed decisions.
- The ICCC uses state of the art technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process large amounts of granular data.
- The ICCC uses platforms including the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) to collect micro-level data, process it, and present the macro picture.
- How will the Krishi ICCC Work?
- The AI machine learning-based system will identify a farmer through his/ her mobile number or Aadhaar.
- Then, the system will match it with the farmer’s field information obtained through land records, historical crop sowing information from the crop registry, weather data from IMD, etc.
- It will then generate a customised advisory in the local language of the farmer. For this, the system will use the Bhashini platform that allows translation into several Indian languages.
- What Information will the Krishi ICCC Provide?
- On 8 large, 55-inch LED screens installed at the ICCC, one can see information on –
- Temperatures, rainfall, wind speed, crop yields, production, drought situation, cropping patterns (geographic region-wise and year-wise) and production estimations.
- In graphical/ map, timeline, and drill-down format.
- One can also see –
- The relevant trends (periodic and non-periodic), outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and
- Receive insights, alerts, and feedback on agriculture schemes, programmes, projects, and initiatives.
- If needed, farmer beneficiaries can interact directly with officials or the Minister through video conferencing facilities.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW) inaugurated a Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) set up at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi.
- The centre is housed in the MoA&FW, which is responsible for legislation, policy formation, and implementation of initiatives in the agriculture sector.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- The ICCC is a tech-based solution involving multiple IT applications and platforms, which is designed to help in making informed decisions.
- The ICCC uses state of the art technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process large amounts of granular data.
- The ICCC uses platforms including the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) to collect micro-level data, process it, and present the macro picture.
- How will the Krishi ICCC Work?
- The AI machine learning-based system will identify a farmer through his/ her mobile number or Aadhaar.
- Then, the system will match it with the farmer’s field information obtained through land records, historical crop sowing information from the crop registry, weather data from IMD, etc.
- It will then generate a customised advisory in the local language of the farmer. For this, the system will use the Bhashini platform that allows translation into several Indian languages.
- What Information will the Krishi ICCC Provide?
- On 8 large, 55-inch LED screens installed at the ICCC, one can see information on –
- Temperatures, rainfall, wind speed, crop yields, production, drought situation, cropping patterns (geographic region-wise and year-wise) and production estimations.
- In graphical/ map, timeline, and drill-down format.
- One can also see –
- The relevant trends (periodic and non-periodic), outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and
- Receive insights, alerts, and feedback on agriculture schemes, programmes, projects, and initiatives.
- If needed, farmer beneficiaries can interact directly with officials or the Minister through video conferencing facilities.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW) inaugurated a Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) set up at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi.
- The centre is housed in the MoA&FW, which is responsible for legislation, policy formation, and implementation of initiatives in the agriculture sector.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- The ICCC is a tech-based solution involving multiple IT applications and platforms, which is designed to help in making informed decisions.
- The ICCC uses state of the art technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to collect and process large amounts of granular data.
- The ICCC uses platforms including the Krishi Decision Support System (DSS) to collect micro-level data, process it, and present the macro picture.
- How will the Krishi ICCC Work?
- The AI machine learning-based system will identify a farmer through his/ her mobile number or Aadhaar.
- Then, the system will match it with the farmer’s field information obtained through land records, historical crop sowing information from the crop registry, weather data from IMD, etc.
- It will then generate a customised advisory in the local language of the farmer. For this, the system will use the Bhashini platform that allows translation into several Indian languages.
- What Information will the Krishi ICCC Provide?
- On 8 large, 55-inch LED screens installed at the ICCC, one can see information on –
- Temperatures, rainfall, wind speed, crop yields, production, drought situation, cropping patterns (geographic region-wise and year-wise) and production estimations.
- In graphical/ map, timeline, and drill-down format.
- One can also see –
- The relevant trends (periodic and non-periodic), outliers, and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and
- Receive insights, alerts, and feedback on agriculture schemes, programmes, projects, and initiatives.
- If needed, farmer beneficiaries can interact directly with officials or the Minister through video conferencing facilities.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare (MoA&FW) inaugurated a Krishi Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) set up at Krishi Bhavan in New Delhi.
- The centre is housed in the MoA&FW, which is responsible for legislation, policy formation, and implementation of initiatives in the agriculture sector.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 6 of 10
6. Question
Q6. {IC – Parliament – Elections} Consider the following statements about District Election Management Plan (DEMP):
- As per the Election Commission of India, the DEMP is to be prepared at least 90 days before the tentative poll day.
- It is a comprehensive document that uses statistics and analysis to ensure the smooth conduct of elections.
- Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) plan along with Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) management is a crucial component of the DEMP.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are not correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- As per the Election Commission of India (ECI), the District Election Management Plan (DEMP) is to be prepared at least six months before the tentative poll day.
- However, many things become clearer as the election is notified, so it becomes necessary to revise/update the plan occasionally.
- Executing the DEMP requires a collaborative effort involving election officials, administrative authorities, law enforcement agencies etc.
- Regular interactions with political parties and media are also planned to brief them on electoral rules.
Statement 2 is correct
- The plan starts with a district profile that serves as the foundation of the electoral strategy.
- This includes a political map outlining constituencies, key demographic and infrastructure statistics, a brief on the district’s administrative setup and socio-economic features.
- The plan encompasses detailed strategies for improving the availability and accessibility of polling stations, ensuring that all stations have essential facilities.
Statement 3 is correct
- A critical component of the DEMP is the Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) plan, which focuses on increasing electoral participation.
- Activities under the SVEEP plan include the use of social media, engagement with various community and youth organisations, and organising events leading up to the poll day to increase awareness and participation.
- The plan also includes training district-level teams to enforce the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) and providing a training program for all election personnel to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Material management is a crucial component of the DEMP involving procuring 61 essential items, including indelible ink, seals, stamps, stationary and statutory forms.
- These items are categorised based on the level at which they are to be procured (State/U.T. or district level), with timelines ranging from two-to-three weeks to four months before the election.
- EVMs management is crucial with plans necessary for secure storage and availability of EVMs and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs), including plans for their transportation and maintenance.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- As per the Election Commission of India (ECI), the District Election Management Plan (DEMP) is to be prepared at least six months before the tentative poll day.
- However, many things become clearer as the election is notified, so it becomes necessary to revise/update the plan occasionally.
- Executing the DEMP requires a collaborative effort involving election officials, administrative authorities, law enforcement agencies etc.
- Regular interactions with political parties and media are also planned to brief them on electoral rules.
Statement 2 is correct
- The plan starts with a district profile that serves as the foundation of the electoral strategy.
- This includes a political map outlining constituencies, key demographic and infrastructure statistics, a brief on the district’s administrative setup and socio-economic features.
- The plan encompasses detailed strategies for improving the availability and accessibility of polling stations, ensuring that all stations have essential facilities.
Statement 3 is correct
- A critical component of the DEMP is the Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) plan, which focuses on increasing electoral participation.
- Activities under the SVEEP plan include the use of social media, engagement with various community and youth organisations, and organising events leading up to the poll day to increase awareness and participation.
- The plan also includes training district-level teams to enforce the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) and providing a training program for all election personnel to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Material management is a crucial component of the DEMP involving procuring 61 essential items, including indelible ink, seals, stamps, stationary and statutory forms.
- These items are categorised based on the level at which they are to be procured (State/U.T. or district level), with timelines ranging from two-to-three weeks to four months before the election.
- EVMs management is crucial with plans necessary for secure storage and availability of EVMs and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs), including plans for their transportation and maintenance.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is incorrect
- As per the Election Commission of India (ECI), the District Election Management Plan (DEMP) is to be prepared at least six months before the tentative poll day.
- However, many things become clearer as the election is notified, so it becomes necessary to revise/update the plan occasionally.
- Executing the DEMP requires a collaborative effort involving election officials, administrative authorities, law enforcement agencies etc.
- Regular interactions with political parties and media are also planned to brief them on electoral rules.
Statement 2 is correct
- The plan starts with a district profile that serves as the foundation of the electoral strategy.
- This includes a political map outlining constituencies, key demographic and infrastructure statistics, a brief on the district’s administrative setup and socio-economic features.
- The plan encompasses detailed strategies for improving the availability and accessibility of polling stations, ensuring that all stations have essential facilities.
Statement 3 is correct
- A critical component of the DEMP is the Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) plan, which focuses on increasing electoral participation.
- Activities under the SVEEP plan include the use of social media, engagement with various community and youth organisations, and organising events leading up to the poll day to increase awareness and participation.
- The plan also includes training district-level teams to enforce the Model Code of Conduct (MCC) and providing a training program for all election personnel to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Material management is a crucial component of the DEMP involving procuring 61 essential items, including indelible ink, seals, stamps, stationary and statutory forms.
- These items are categorised based on the level at which they are to be procured (State/U.T. or district level), with timelines ranging from two-to-three weeks to four months before the election.
- EVMs management is crucial with plans necessary for secure storage and availability of EVMs and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trails (VVPATs), including plans for their transportation and maintenance.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 7 of 10
7. Question
Q7. {IC – Parliament – Elections} Consider the following statements with respect to Postal Ballot Voting in India:
- Individuals detained under preventive custody orders during the election period are eligible for opting to vote through postal ballots.
- Postal ballots are counted alongside votes cast at polling stations.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- Postal voting also known as mail-in ballots, allow voters to cast their votes by mail instead of physically going to a polling station.
- Eligible electors who can opt to vote through postal ballots include:
- Service voters – Members of the armed forces, paramilitary forces, and government employees deployed on election duty far from their home constituencies.
- Absentee voters – Individuals unable to vote in person due to reasons like work commitments, illness, or disability.
- Electors on election duty – Government officials and polling staff assigned duties at polling stations other than their own.
- Electors under preventive detention – Individuals detained under preventive custody orders during the election period.
- Essential services covering polling day activities – Media persons with authorization letters from the EC and those involved in essential services such as metros, railways, and healthcare have the option to vote using postal ballots in Lok Sabha and four state Assembly polls.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Postal ballots are counted separately from votes cast at polling stations.
- On the designated counting day, postal ballots are collected by postal authorities and brought to the counting centre.
- Counting of postal ballot paper starts half an hour before counting of votes on EVMs.
- The Returning Officer and election officials scrutinise postal ballots for validity and integrity, adding valid ballots to the respective candidate’s vote count.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- Postal voting also known as mail-in ballots, allow voters to cast their votes by mail instead of physically going to a polling station.
- Eligible electors who can opt to vote through postal ballots include:
- Service voters – Members of the armed forces, paramilitary forces, and government employees deployed on election duty far from their home constituencies.
- Absentee voters – Individuals unable to vote in person due to reasons like work commitments, illness, or disability.
- Electors on election duty – Government officials and polling staff assigned duties at polling stations other than their own.
- Electors under preventive detention – Individuals detained under preventive custody orders during the election period.
- Essential services covering polling day activities – Media persons with authorization letters from the EC and those involved in essential services such as metros, railways, and healthcare have the option to vote using postal ballots in Lok Sabha and four state Assembly polls.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Postal ballots are counted separately from votes cast at polling stations.
- On the designated counting day, postal ballots are collected by postal authorities and brought to the counting centre.
- Counting of postal ballot paper starts half an hour before counting of votes on EVMs.
- The Returning Officer and election officials scrutinise postal ballots for validity and integrity, adding valid ballots to the respective candidate’s vote count.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- Postal voting also known as mail-in ballots, allow voters to cast their votes by mail instead of physically going to a polling station.
- Eligible electors who can opt to vote through postal ballots include:
- Service voters – Members of the armed forces, paramilitary forces, and government employees deployed on election duty far from their home constituencies.
- Absentee voters – Individuals unable to vote in person due to reasons like work commitments, illness, or disability.
- Electors on election duty – Government officials and polling staff assigned duties at polling stations other than their own.
- Electors under preventive detention – Individuals detained under preventive custody orders during the election period.
- Essential services covering polling day activities – Media persons with authorization letters from the EC and those involved in essential services such as metros, railways, and healthcare have the option to vote using postal ballots in Lok Sabha and four state Assembly polls.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- Postal ballots are counted separately from votes cast at polling stations.
- On the designated counting day, postal ballots are collected by postal authorities and brought to the counting centre.
- Counting of postal ballot paper starts half an hour before counting of votes on EVMs.
- The Returning Officer and election officials scrutinise postal ballots for validity and integrity, adding valid ballots to the respective candidate’s vote count.
Answer: (a) 1 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 8 of 10
8. Question
Q8. {Disaster Management – NDRF} Consider the following statements about National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF):
- NDRF is placed in the Public Account, thus the government does not require parliamentary approval to take money out of this fund.
- NDRF does not cover man-made disasters such as terrorist attacks and nuclear disaster.
- NDRF is not audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India but by an independent auditor.
How many of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- NDRF is a fund managed by the Central Government to meet the expenses for emergency response, relief, and rehabilitation due to any threatening disaster situation or disaster.
- NDRF is constituted to supplement the funds of the State Disaster Response Funds (SDRF) in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in SDRF.
- It is placed in the “Public Account” of the GOI under “reserve funds not bearing interest”. Since it is placed in the public accounts, the government does not require parliamentary approval to take money out of this fund.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- NDRF guidelines state that natural calamities of cyclones, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslide, avalanche, cloud burst, pest attack, and cold wave and frost considered to be of severe nature by the Government of India (GoI) and requiring expenditures by a state government in excess of the balances available in its own SDRF will qualify for immediate relief assistance from NDRF.
- The NDRF also covers man-made disasters such as terrorist attacks, chemical or biological disasters, or nuclear disasters as notified by the Central Government.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- NDRF is financed through the levy of a cess on certain items, chargeable to excise and customs duty, and approved annually through the Finance Bill.
- The requirement for funds beyond what is available under the NDRF is met through general budgetary resources.
- The National Executive Committee (NEC) of the National Disaster Management Authority takes decisions on the expenses from NDRF.
- The NDRF accounts are audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) every year.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- NDRF is a fund managed by the Central Government to meet the expenses for emergency response, relief, and rehabilitation due to any threatening disaster situation or disaster.
- NDRF is constituted to supplement the funds of the State Disaster Response Funds (SDRF) in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in SDRF.
- It is placed in the “Public Account” of the GOI under “reserve funds not bearing interest”. Since it is placed in the public accounts, the government does not require parliamentary approval to take money out of this fund.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- NDRF guidelines state that natural calamities of cyclones, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslide, avalanche, cloud burst, pest attack, and cold wave and frost considered to be of severe nature by the Government of India (GoI) and requiring expenditures by a state government in excess of the balances available in its own SDRF will qualify for immediate relief assistance from NDRF.
- The NDRF also covers man-made disasters such as terrorist attacks, chemical or biological disasters, or nuclear disasters as notified by the Central Government.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- NDRF is financed through the levy of a cess on certain items, chargeable to excise and customs duty, and approved annually through the Finance Bill.
- The requirement for funds beyond what is available under the NDRF is met through general budgetary resources.
- The National Executive Committee (NEC) of the National Disaster Management Authority takes decisions on the expenses from NDRF.
- The NDRF accounts are audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) every year.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- NDRF is a fund managed by the Central Government to meet the expenses for emergency response, relief, and rehabilitation due to any threatening disaster situation or disaster.
- NDRF is constituted to supplement the funds of the State Disaster Response Funds (SDRF) in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in SDRF.
- It is placed in the “Public Account” of the GOI under “reserve funds not bearing interest”. Since it is placed in the public accounts, the government does not require parliamentary approval to take money out of this fund.
Statement 2 is incorrect
- NDRF guidelines state that natural calamities of cyclones, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslide, avalanche, cloud burst, pest attack, and cold wave and frost considered to be of severe nature by the Government of India (GoI) and requiring expenditures by a state government in excess of the balances available in its own SDRF will qualify for immediate relief assistance from NDRF.
- The NDRF also covers man-made disasters such as terrorist attacks, chemical or biological disasters, or nuclear disasters as notified by the Central Government.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- NDRF is financed through the levy of a cess on certain items, chargeable to excise and customs duty, and approved annually through the Finance Bill.
- The requirement for funds beyond what is available under the NDRF is met through general budgetary resources.
- The National Executive Committee (NEC) of the National Disaster Management Authority takes decisions on the expenses from NDRF.
- The NDRF accounts are audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) every year.
Answer: (a) Only one; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 9 of 10
9. Question
Q9. {Prelims – S&T – Defence} Consider the following statements about Samudra Paheredar:
- It is a specialised Pollution Control Vessel (PCV) of the Indian Coast Guard.
- It is the second PCV of India after ICGS Samudra Prahari.
- It has been built by Cochin Shipyard Ltd.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Correct
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- Samudra Paheredar is a specialised Pollution Control Vessel (PCV) of the Indian Coast Guard.
- It was commissioned in 2012.
- The ship’s primary role is pollution response at sea.
- It is equipped with the most advanced and sophisticated pollution response and control equipment for mitigating oil spills.
- It includes containment equipment like hi-sprint booms and river booms, recovery devices like skimmers and side sweeping arms.
- The ship is capable of unhindered oil-recovery operations.
- The special features include an integrated platform management system, a power management system and a high-powered external firefighting system.
Statement 2 is correct
- It is the second PCV of India after ICGS Samudra Prahari.
- The Indian Coast Guard Ship Samudra Prahari boasts state-of-the-art pollution response.
- It was commissioned at Mumbai on October 9, 2010.
- Samudra Prahari is outfitted with advanced pollution control gear, including containment tools like Hi-Sprint Booms and river booms to contain oil spills, as well as oil recovery devices like skimmers and side sweeping arms, along with storage facilities within the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- It has been built by ABG Shipyard, Surat.
- It is stationed on the East Coast of India in Vishakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- Samudra Paheredar is a specialised Pollution Control Vessel (PCV) of the Indian Coast Guard.
- It was commissioned in 2012.
- The ship’s primary role is pollution response at sea.
- It is equipped with the most advanced and sophisticated pollution response and control equipment for mitigating oil spills.
- It includes containment equipment like hi-sprint booms and river booms, recovery devices like skimmers and side sweeping arms.
- The ship is capable of unhindered oil-recovery operations.
- The special features include an integrated platform management system, a power management system and a high-powered external firefighting system.
Statement 2 is correct
- It is the second PCV of India after ICGS Samudra Prahari.
- The Indian Coast Guard Ship Samudra Prahari boasts state-of-the-art pollution response.
- It was commissioned at Mumbai on October 9, 2010.
- Samudra Prahari is outfitted with advanced pollution control gear, including containment tools like Hi-Sprint Booms and river booms to contain oil spills, as well as oil recovery devices like skimmers and side sweeping arms, along with storage facilities within the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- It has been built by ABG Shipyard, Surat.
- It is stationed on the East Coast of India in Vishakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
Statement 1 is correct
- Samudra Paheredar is a specialised Pollution Control Vessel (PCV) of the Indian Coast Guard.
- It was commissioned in 2012.
- The ship’s primary role is pollution response at sea.
- It is equipped with the most advanced and sophisticated pollution response and control equipment for mitigating oil spills.
- It includes containment equipment like hi-sprint booms and river booms, recovery devices like skimmers and side sweeping arms.
- The ship is capable of unhindered oil-recovery operations.
- The special features include an integrated platform management system, a power management system and a high-powered external firefighting system.
Statement 2 is correct
- It is the second PCV of India after ICGS Samudra Prahari.
- The Indian Coast Guard Ship Samudra Prahari boasts state-of-the-art pollution response.
- It was commissioned at Mumbai on October 9, 2010.
- Samudra Prahari is outfitted with advanced pollution control gear, including containment tools like Hi-Sprint Booms and river booms to contain oil spills, as well as oil recovery devices like skimmers and side sweeping arms, along with storage facilities within the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone.
Statement 3 is incorrect
- It has been built by ABG Shipyard, Surat.
- It is stationed on the East Coast of India in Vishakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only; Difficulty Level: Medium
-
Question 10 of 10
10. Question
Q10. {Geo – EG – Mineral Resources} Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (AN Seamount), recently seen in news is located in which of the following ocean body?
Correct
Explanation
- Afanasy Nikitin Seamount is a major seamount in the central Indian Ocean Basin.
- It is located about 3,000 km away from India’s coast.
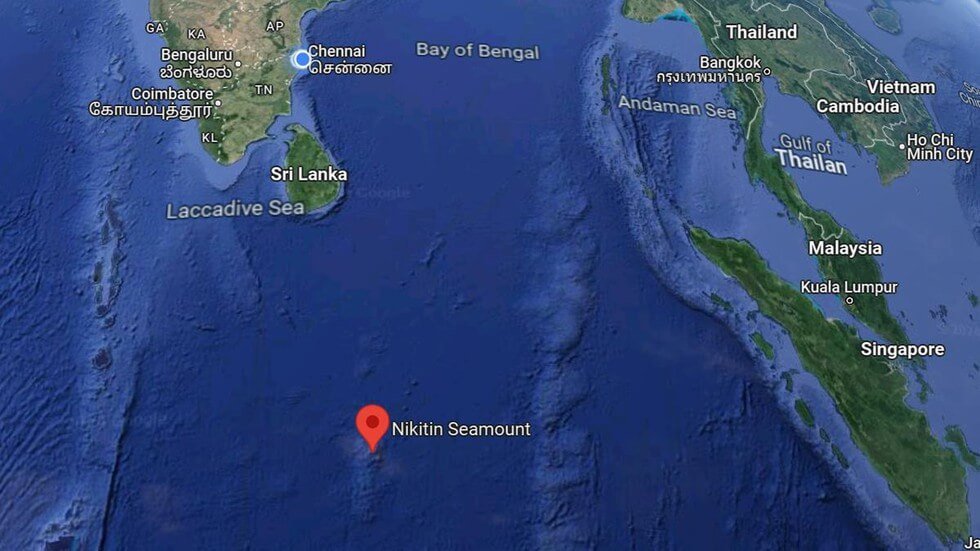
- It is rich in deposits of cobalt, nickel, manganese and copper.
- Seamounts are underwater mountains formed through volcanic activity and are recognized as hotspots for marine life.
- India has applied to the International Seabed Authority (ISBA) for rights to explore the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (AN Seamount), a cobalt-rich region in the Indian Ocean.
- This move, motivated partly by Chinese activity in the area, aims to secure strategic resources.
- The application faces challenges due to overlapping claims by Sri Lanka and international regulations governing seabed exploration. Also, the cost of exploration and extraction is very high.
- India is also seeking permission to explore the Carlsberg Ridge for polymetallic sulphide.
Answer: (d) Indian Ocean; Difficulty Level: Medium
Incorrect
Explanation
- Afanasy Nikitin Seamount is a major seamount in the central Indian Ocean Basin.
- It is located about 3,000 km away from India’s coast.

- It is rich in deposits of cobalt, nickel, manganese and copper.
- Seamounts are underwater mountains formed through volcanic activity and are recognized as hotspots for marine life.
- India has applied to the International Seabed Authority (ISBA) for rights to explore the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (AN Seamount), a cobalt-rich region in the Indian Ocean.
- This move, motivated partly by Chinese activity in the area, aims to secure strategic resources.
- The application faces challenges due to overlapping claims by Sri Lanka and international regulations governing seabed exploration. Also, the cost of exploration and extraction is very high.
- India is also seeking permission to explore the Carlsberg Ridge for polymetallic sulphide.
Answer: (d) Indian Ocean; Difficulty Level: Medium
Unattempted
Explanation
- Afanasy Nikitin Seamount is a major seamount in the central Indian Ocean Basin.
- It is located about 3,000 km away from India’s coast.

- It is rich in deposits of cobalt, nickel, manganese and copper.
- Seamounts are underwater mountains formed through volcanic activity and are recognized as hotspots for marine life.
- India has applied to the International Seabed Authority (ISBA) for rights to explore the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount (AN Seamount), a cobalt-rich region in the Indian Ocean.
- This move, motivated partly by Chinese activity in the area, aims to secure strategic resources.
- The application faces challenges due to overlapping claims by Sri Lanka and international regulations governing seabed exploration. Also, the cost of exploration and extraction is very high.
- India is also seeking permission to explore the Carlsberg Ridge for polymetallic sulphide.
Answer: (d) Indian Ocean; Difficulty Level: Medium
Newsletter Updates
Subscribe to our newsletter and never miss an important update!
Assured Discounts on our New Products!
Related Posts

April 10 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

December 14 2023 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

January 17 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

April 12 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

April 06-07-08 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

December 17-18 2023 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)

May 01 2024 Prelims Practice Questions (PPQs)





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)





