Neanderthals and Denisovans
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
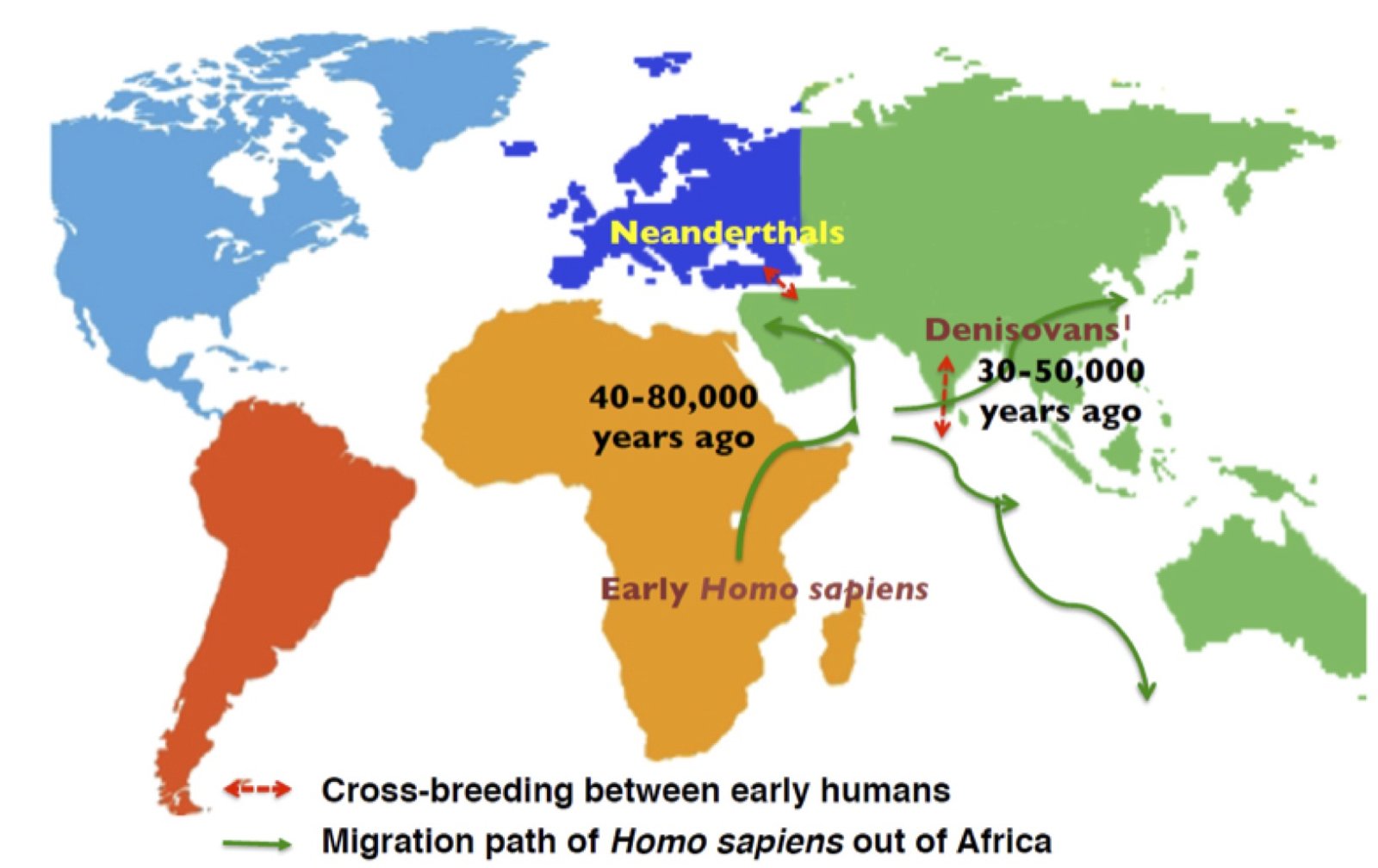
- Context (DTE): As per Scientists, Indians derive 1-2% of their ancestry from gene flow from Neanderthals and Denisovans.
Neanderthals
- The Neanderthals were likely our closest human relatives. Members of this now-extinct group were hominins — a lineage that includes living humans (Homo sapiens) and our extinct relatives.
- The first fossils to be called Neanderthals were found in 1856 in Germany, at a site in the Neander Valley (where Neanderthals get their name from).
- The German word for valley is ‘Tal’ although in the 1800s it was spelt ‘Thal’. Homo neanderthalensis therefore means ‘Human from the Neander Valley’.
- Neanderthals diverged from modern humans around 500,000 years ago, likely evolving outside of Africa.
Distribution
- Remains of this species have been found scattered across Europe and the Middle East.
- The eastern-most occurrence of a Neanderthal may be represented by a fossil skull from China known as ‘Maba’.
Physical Features
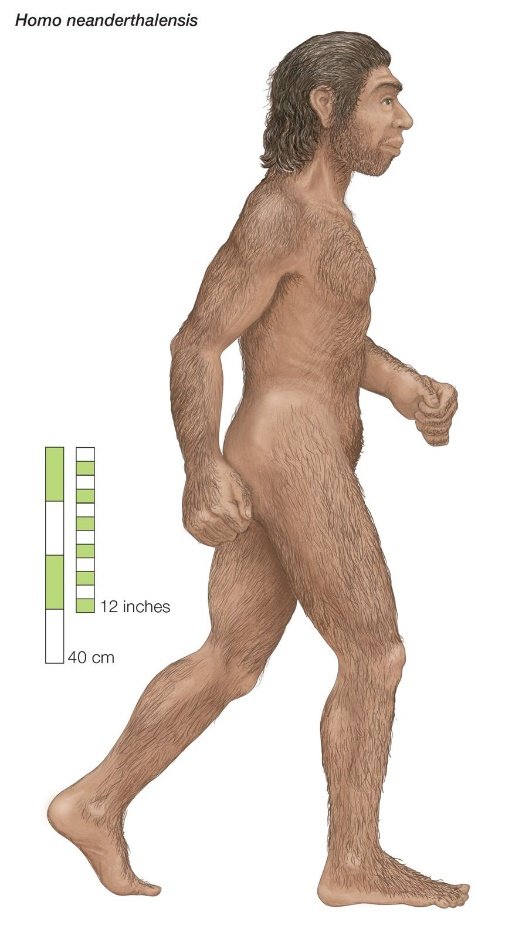
- Neanderthals were generally shorter and had more robust skeletons and muscular bodies than modern humans.
- Males averaged about 168 centimetres in height while females were slightly shorter at 156 centimetres.
- Neanderthals had a long, low skull (compared to the more globular skull of modern humans) with a characteristic prominent brow ridge above their eyes.
- Their heads were long rather than globe-shaped and had lower foreheads and crowns.
Tools
- Like early humas, Neanderthals, made an assortment of sophisticated tools from stone and bones. These included small blades, hand axe and scrapers used to remove flesh and fat from animal skin.
Denisovan
- The Denisovans, together with the Neanderthals, are the closest extinct relatives of modern humans.
- The Denisovans are named for the location where the first fossils were found, Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains of Siberia, Russia.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)