Leptospirosis: Risks, Symptoms and Treatment
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH | TH): Leptospirosis has emerged as an important infectious disease in the world today.
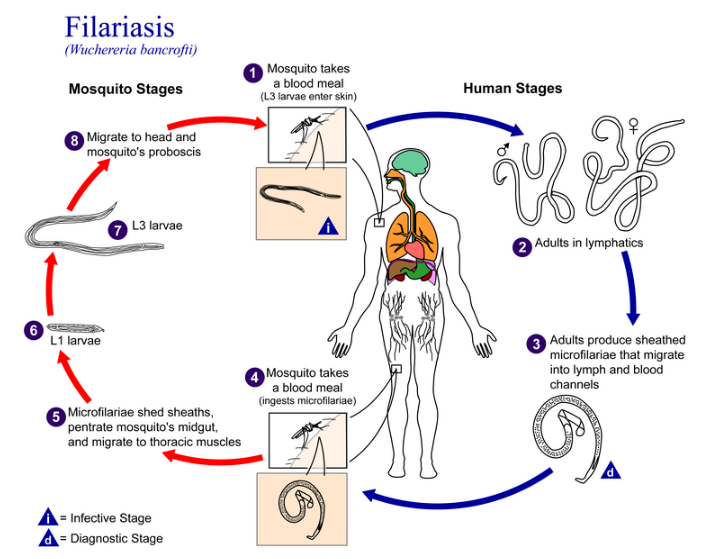
- It is a potentially fatal zoonotic bacterial disease caused by a bacterium Leptospira interrogans.
- Host: It has a spectrum of reservoir hosts which includes rodents, wild and domestic animals.
- Misconception: It is called “ili jwara” in Kannada and “eli pani” in Malayalam, both meaning rat fever. It is named so because of the belief that rats are the sole cause of the disease, which is not true.
- Transmission: Direct or indirect contact with urine or reproductive fluids of infected animals.
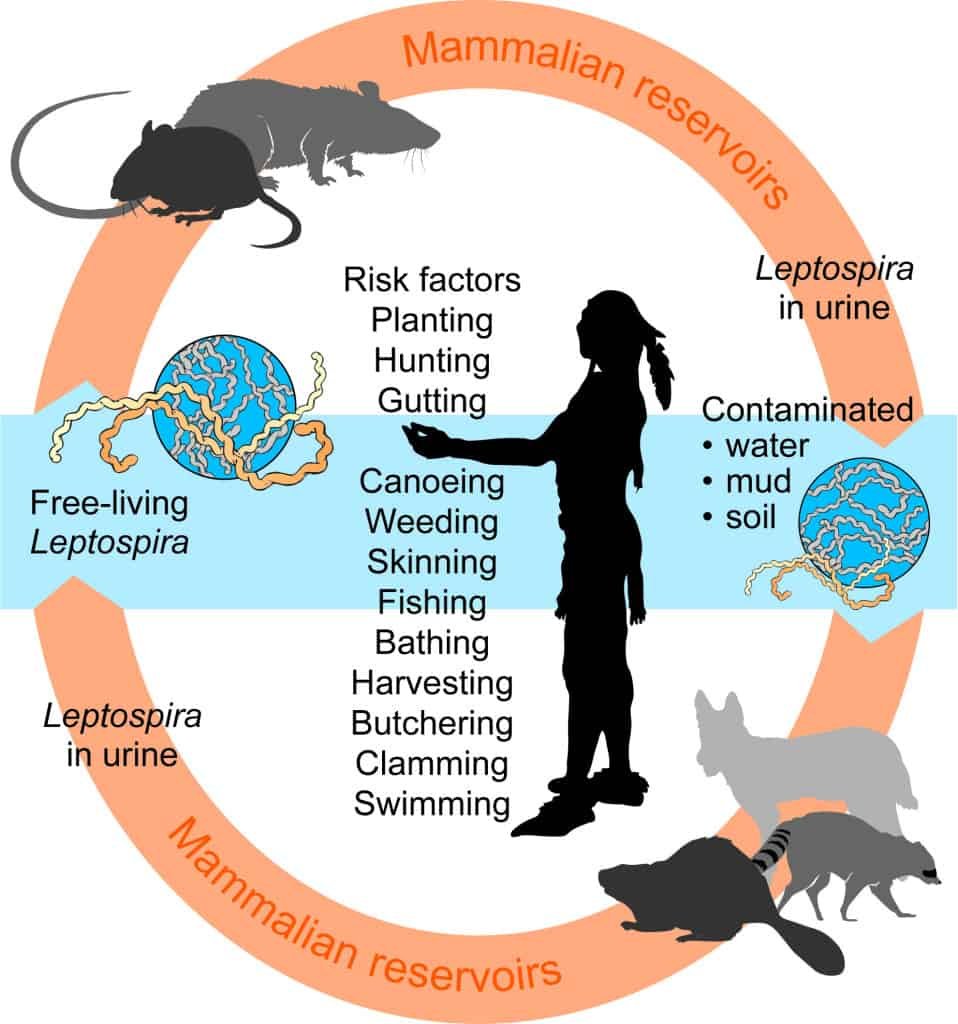
- Incubation period: 2 to 14 days.
- Symptoms: fever, diarrhea, jaundice, etc. Severe ones include coughing of blood and blood in urine.
- Severity: Ranges from a mild flu-like illness to being life-threatening.
- Effect on Animals: Reproductive failure, stillbirths, and weak offsprings, and even death.
- Risk Climatic Region: Warm and humid air helps the pathogen survive longer.
- Risk Season: Monsoon rains or flooding exposes the people to contaminated water.
- Treatment: Antibiotics and Plasmapheresis (or plasma exchange).
- Problems in Treatment: Misdiagnosis (its symptoms mimic those of dengue, malaria, and hepatitis).
- Way Forward: ‘One Health’ approach — an interdisciplinary approach that recognises the interconnections between the health of humans, animals, plants, and their shared environment.
Suggested Reading: One Health Joint Plan of Action (OH JPA) > PMF IAS S&T Current Affairs 10/2022




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)