
Karst Landforms & Cycle of Erosion | Stalactite & Stalagmite
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 26, 2024 11:37 PM
Karst Landforms – Cavern, Arch/Natural Bridge, Sink Hole/Swallow Hole, Karst Window, Sinking Creeks/Bogas, Stalactite and Stalagmite.
Landforms and Cycle of Erosion
- Fluvial Erosional Landforms [Done]
- Fluvial Depositional Landforms [Done]
- Glacial landforms and Cycle of Erosion [Done]
- Marine landforms and Cycle of Erosion [Done]
- Arid landforms and Cycle of Erosion [Previous Post]
- Karst landforms and Cycle of Erosion [This Post]
Karst Landforms and Cycle of Erosion
- Karst is a landscape which is underlain by limestone which has been eroded by dissolution, producing towers, fissures, sinkholes, etc.
- It is so named after a province of Yugoslavia on the Adriatic sea coast where such formations are most noticeable.
- Karst topography is a landscape formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum.
- It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes, caves etc..
Conditions Essential for Full Development of Karst Topography
- Presence of soluble rocks, preferably limestone at the surface or sub-surface level.
- These rocks should be dense, highly jointed and thinly bedded.
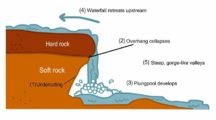
Cavern
- This is an underground cave formed by water action by various methods in a limestone or chalk area.

Arch/Natural Bridge
- When a part of the cavern collapses the portion which keeps standing forms an arch.
Sink Hole/Swallow Hole
- Sink holes are funnel-shaped depressions having an average depth of three to nine metres.
- These holes are developed by enlargement of the cracks found in such rocks, as a result of continuous solvent action of the rainwater.
- The surface streams which sink disappear underground through swallow holes.

Karst Window
- When a number of adjoining sink holes collapse, they form an open, broad area called a karst window.

Sinking Creeks/Bogas
- In a valley, the water often gets lost through cracks and fissures in the bed. These are called sinking creeks, and if their tops are open, they are called bogas.

Stalactite and Stalagmite
- The water containing limestone in solution, seeps through the roof in the form of a continuous chain of drops.
- A portion of the roof hangs on the roof and on evaporation of water, a small deposit of limestone is left behind contributing to the formation of a stalactite, growing downwards from the roof.
- The remaining portion of the drop falls to the floor. This also evaporates, leaving behind a small deposit of limestone aiding the formation of a stalagmite, thicker and flatter, rising upwards from the floor.
- Sometimes, stalactite and stalagmite join together to form a complete pillar known as the column.

Last updated on April 26, 2024 11:37 PM




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)







SIR PLEASE EXPLAIN STALACTITE FORMATION. I AM UNABLE TO UNDERSTAND FROM THE TEXT. PLEASE EXPLAIN IN SOME DETAIL.
In a Karst Cavern (let us simply call it karst cave), when water seeps through the ceiling (upper part of the cave) it trickles drop by drop . Small amount of water drop evaporates even before falling down from the ceiling leaving behind very minute limestone particles (Take a look at these images: https://goo.gl/m0TKU0 & https://goo.gl/ZqaoVy). Over a period of time (few years) the process of evaporation continues as the limestone particles keep accumulating at to the ceiling forming a inverted cone like structure).
This a common phenomenon that we observe in our daily lives. A leaky ceiling is the simple example (See image: https://goo.gl/O1JsM8)
THANKYOU SIR, UNDERSTOOD.
Sir, these geography notes are very helpful, appreciate your efforts. Please provide notes for history and polity also.
Sir, these geography notes are very helpful, appreciate your efforts. Please provide notes for history and polity also.
Sir,
What is the arrangement of karst topography (erosional) according to their size?