Global Methane Tracker 2024 | Mitigating Methane Emissions
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
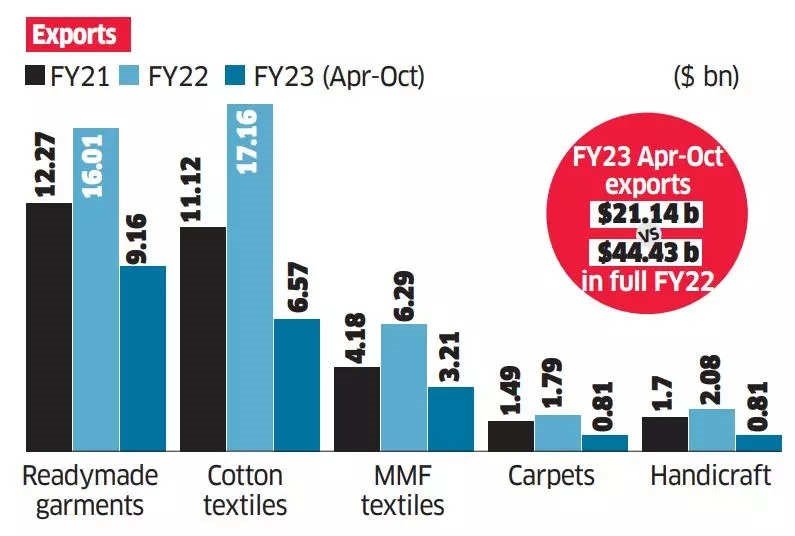
- Context (DTE): As per Global Methane Tracker 2024, Methane emissions from fossil fuels remain high despite progress with USA being on the top list of emitters.
- The Global Methane Tracker is released by the International Energy Agency (IEA) annually.
- It is based on the most recently available data on methane emissions from the energy sector and incorporates new scientific studies, measurement campaigns, & information collected from satellites.
Key Findings
- USA is the largest emitter of methane from oil and gas operations, closely followed by Russia.
- The energy sector — including oil, natural gas, coal and bioenergy — accounts for more than one third of total methane emissions attributable to human activity.
- Bioenergy — largely from biomass use — contributed a further 10 Mt emissions.
- Of the nearly 120 Mt of emissions, we estimate were tied to fossil fuels in 2023, around 80 Mt came from countries that are among the top 10 emitters of methane globally.
- More than 5 million tons of methane emissions were traced back to major fossil fuel leaks around the world.
- A major oil well blowout in Kazakhstan, which began in June 2023 and continued for more than 200 days.
- The world needs to slash methane emissions from fossil fuels by 75% by 2030 to achieve the Paris Agreement goal of limiting warming to 1.5°C.
Steps taken to mitigate Methane Emissions
Oil and Gas Decarbonisation Charter (OGDC)
- It is a global industry Charter dedicated to speeding up climate action and achieving high-scale impact across the oil and gas sectors.
- To date, 50 companies, representing more than 40 percent of global oil production have signed on to the OGDC, with National Oil Companies representing over 60 percent of signatories – the largest-ever number of NOCs to commit to a decarbonization initiative.
- The OGDC is a key initiative under the Global Decarbonization Accelerator (GDA).
Global Decarbonization Accelerator (GDA)
- It was launched at the World Climate Action Summit.
- It is focused on three key pillars:
- Rapidly scaling the energy system of tomorrow;
- Decarbonizing the energy system of today; and
- Targeting methane and other non-CO2 greenhouse gases.
- It is a comprehensive plan for system-wide change, addressing the demand and the supply of energy at the same time.
- Concern: It only focuses on upstream emissions from oil and gas production, leaving out the need for phasing out fossil fuels, where emissions are at least five times greater.
- It omits key countries and shows strong overlaps with Nationally Determined Contributions.
Oil and Gas Climate Initiative
- It is a CEO-led organization bringing together 12 of the largest oil and gas companies worldwide to lead the industry’s response to climate change.
- It aims to accelerate action towards a net zero emissions future consistent with the Paris Agreement.
- Together, OGCI member companies represent about 30% of global oil and gas production.
- Achievement: Since 2017, OGCI’s member companies have collectively reduced their upstream methane emissions by 50% and upstream carbon intensity by 21%.
- Concern: Several companies focus solely on methane intensity targets, that do not consider absolute emission levels, which can increase even with declining methane intensity if production volumes rise.
Oil and Gas Methane Partnership 2.0 (OGMP 2.0)
- It is the flagship oil and gas reporting and mitigation programme of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It is the only comprehensive, measurement-based reporting framework for the oil and gas industry that improves the accuracy and transparency of methane emissions reporting.
- Over 130 companies with assets in more than 70 countries, representing nearly 40% of the world’s oil and gas production, over 80% of LNG flows, nearly 25% of global natural gas transmission and distribution pipelines and over 10% of global gas storage capacity, have joined OGMP 2.0.
- OGMP 2.0’s data is one of the key components of UNEP’s International Methane Emissions Observatory’s solution to the methane data problem.
International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO)
- It was launched at the G20 Summit, on the eve of the COP26 UN climate conference in Glasgow.
- It will initially focus on methane emissions from the fossil fuel sector, and then expand to other major emitting sectors like agriculture and waste.
- IMEO is a core implementing partner of the Global Methane Pledge.
Global Methane Pledge
- It was launched at COP26 by the European Union and the United States.
- Participants joining the Pledge agree to take voluntary actions to contribute to a collective effort to reduce global methane emissions at least 30 percent from 2020 levels by 2030.
- The Climate and Clean Air Coalition provides secretariat services to the GMP.
- Significance: Meeting the GMP would reduce methane emissions to a level consistent with 1.5°C pathways, reduce warming by at least 0.2 °C by 2050 and prevent annually 26 million tons of crop losses, 255,000 premature deaths, 775 thousand asthma-related hospitalizations and 73 billion hours of lost labour due to extreme heat.
Global Methane Initiative
- It is a voluntary, international public-private initiative that aims to reduce global methane emissions and to advance the abatement, recovery, and use of methane as a valuable clean energy source.
- It focusses on four sectors: agriculture, coal mines, municipal solid waste, oil and gas systems, and wastewater.
Methane Alert and Response System (MARS)
- It was launched at COP27 by UNEP’s International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO).
- It is the first-ever global system that uses satellite data to monitor major emission events and notify governments and companies who can address them.
- It works in partnership with the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- It brings together four critical components to drive transparency and enable emission reductions:
- Detection of large sources of human-caused methane emissions.
- Notification of relevant countries and companies about these detected emissions.
- Response from notified stakeholders to address the emissions.
- Tracking progress of actions taken to reduce emissions and collaboration to prevent future methane.
Lowering Organic Waste Methane Initiative (LOW-Methane)
- It is a coalition of international partners launched at COP 28.
- Objective: To deliver at least 1 million metric tons of annual waste sector methane reductions well before 2030 and to unlock over $10 billion in public and private investment.
- It will support action across the waste value chain, from reducing food loss and waste to diverting and treating organics in the waste stream to cutting emissions from disposal sites, in line with waste management hierarchies.
MethaneSAT
- It is a satellite project led by the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), a US nonprofit organisation.
- EDF collaborated with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency for its development.
- The satellite will orbit the Earth 15 times daily, focusing on monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- Objective: To collect data revealing methane emissions’ sources, intensity, and changes over time.
Methane
- While methane has a much shorter lifetime than carbon dioxide (CO2), it is much more efficient at trapping radiation.
- Per unit of mass, methane has a warming effect about 80 times more potent than CO2 over 20 years.
- Methane has been responsible for 30% of total warming since the Industrial Revolution and is the second largest contributor to global warming after carbon dioxide (CO2).





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)