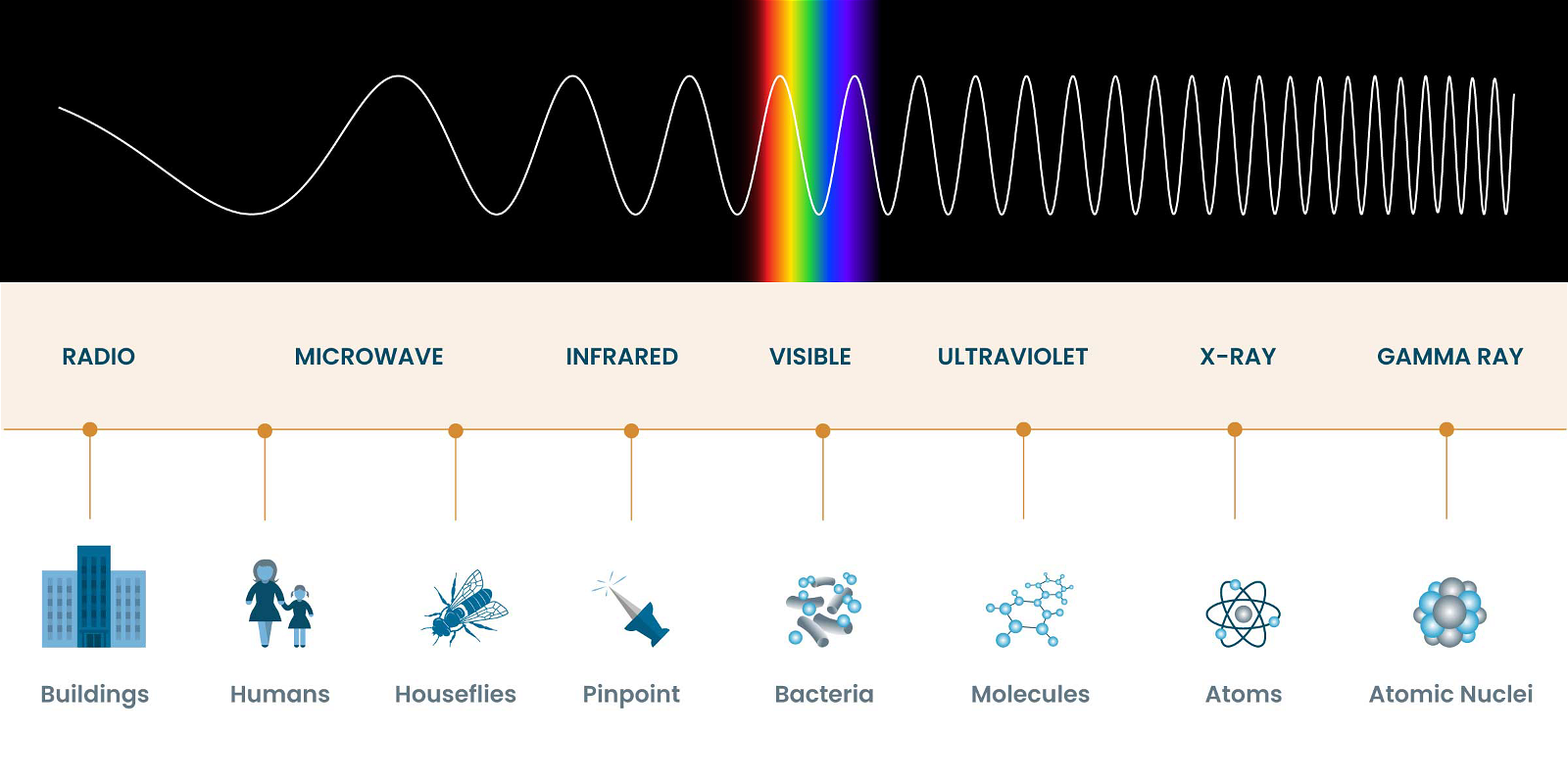
Pong Dam Draft ESZ Policy
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
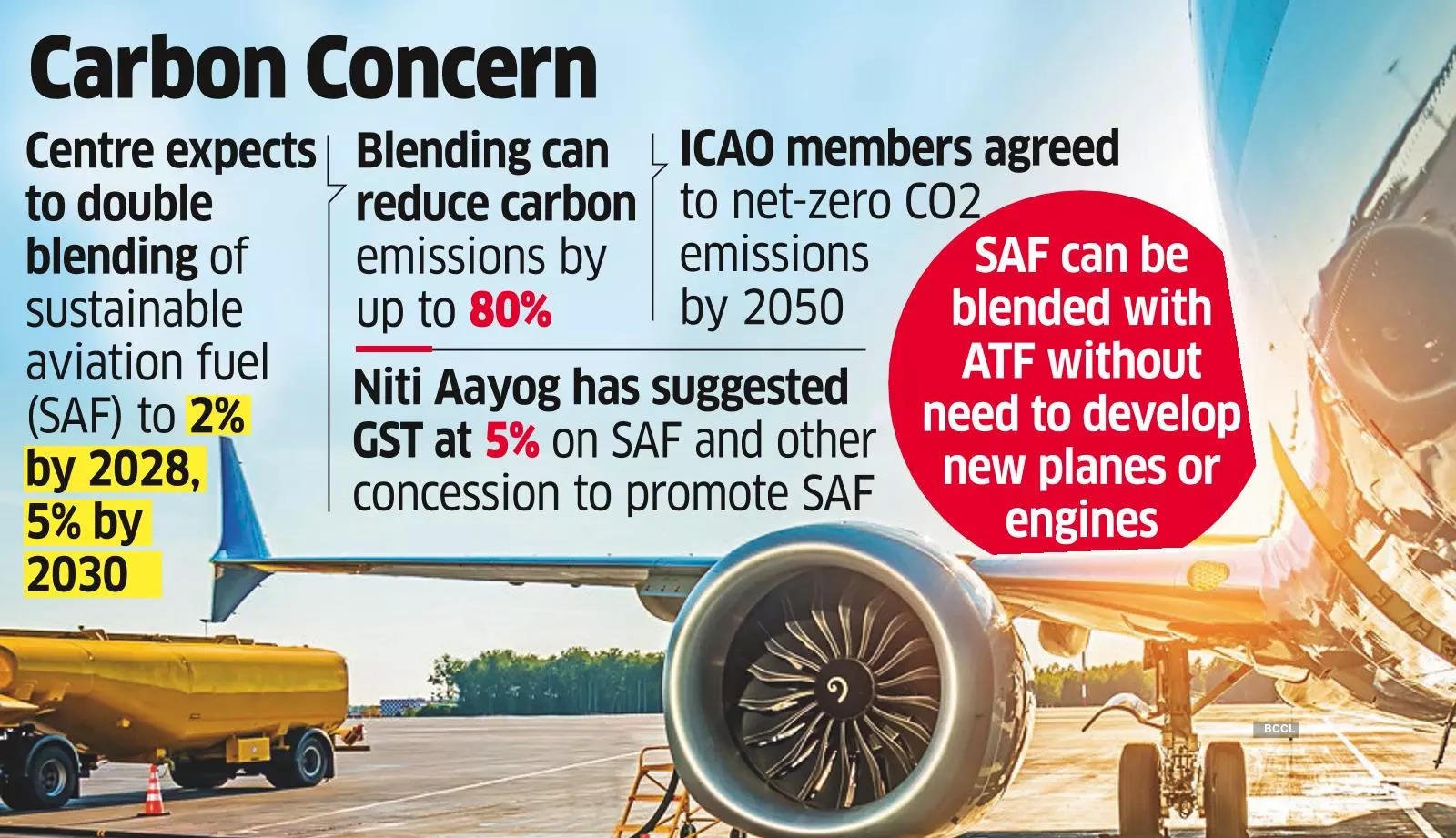
- Context (DTE): A draft eco-sensitive zone (ESZ) policy for the Pong dam was prepared.
- Locals are against the declaration due to the impact on their livelihood & incomplete rehabilitation.
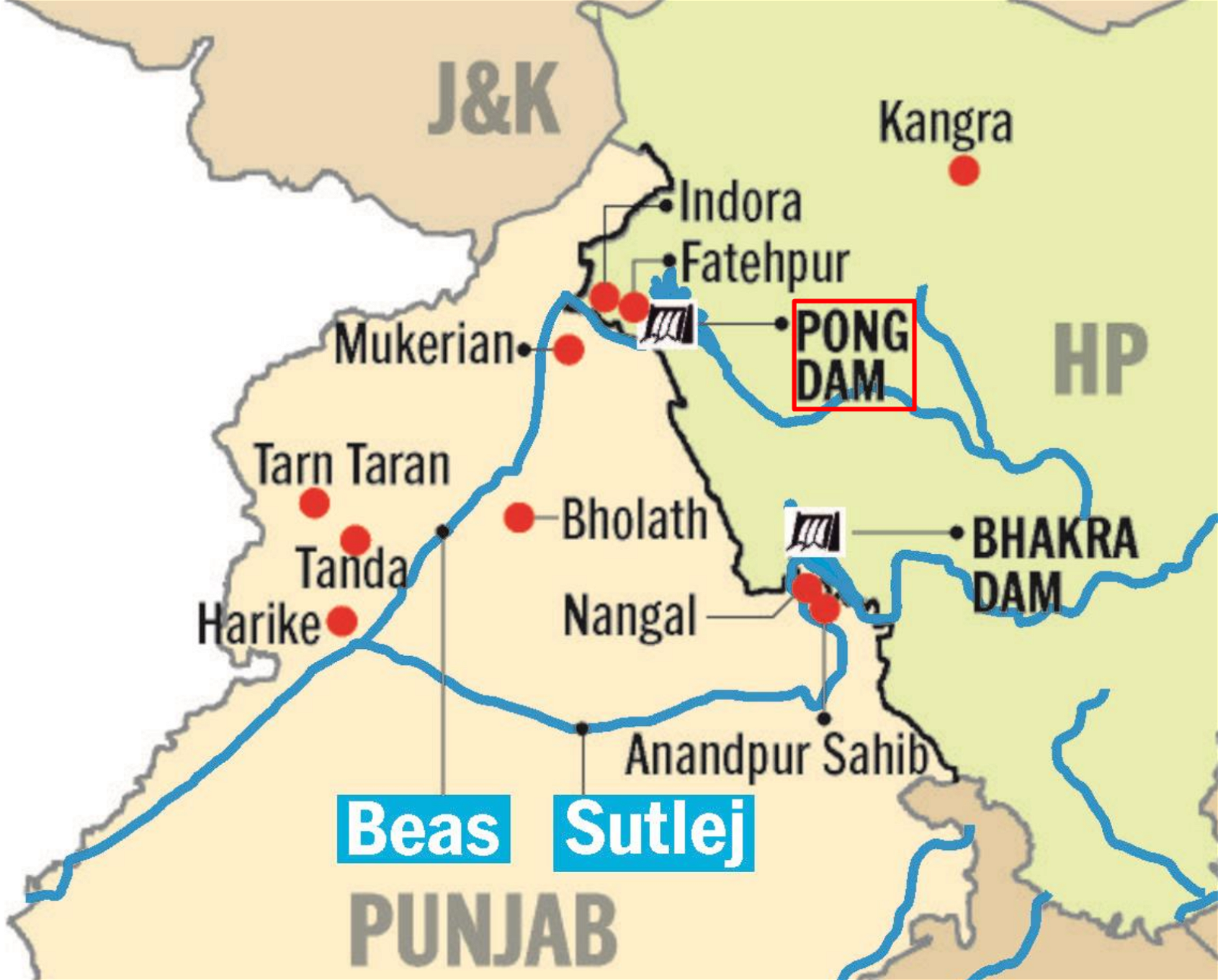
About Pong Dam
- Location: Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh
- It is an artificial reservoir on the Beas River, also known as Maharana Pratap Sagar Dam.
- The Pong Dam is the highest earth-fill dam in India.
- It is a “Ramsar site“, “a wetland of national importance”, and a “wildlife sanctuary”.
- Pong Dam is significant as a resting place for migratory birds.
Beas River
|
ESZ Policy
- It was first suggested in the National Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- State governments were advised to designate areas within 10 km of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries as Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs).
- The 10 km limit is general and can vary according to specific cases.
- ESZ is declared under the Environmental (Protection) Act of 1986.
Restrictions in ESZs
- Permitted Activities: Ongoing agricultural or horticultural practices, rainwater harvesting, organic farming, use of renewable energy sources, and adoption of green technology.
- Regulated Activities: Felling of trees, establishing hotels and resorts, commercial use of natural water, erecting electrical cables, drastic change of agriculture system, e.g., adoption of heavy technology, pesticides, widening roads.
- Prohibited Activities: Commercial mining, sawmills, industries causing pollution, establishing major hydroelectric projects (HEP), commercial use of wood, hot-air balloons, discharge of effluents or any solid waste or production of hazardous substances.
Ecological Significance of ESZs
- ESZs rule out harmful interference by construction and industrial activities.
- It promotes in-situ conservation of endangered species and landscapes.
- ESZs act as “shock absorbers” around the ecologically fragile area.
Reasons behind opposition
- This is typical of the development v/s environment debate.
- ESZs restrict the scope of land use for the construction of developmental structures.
- Limits on tourism, agriculture and other livelihood practices impact the locals.
- Mining and other exploration projects are not allowed to impact the state economy.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)