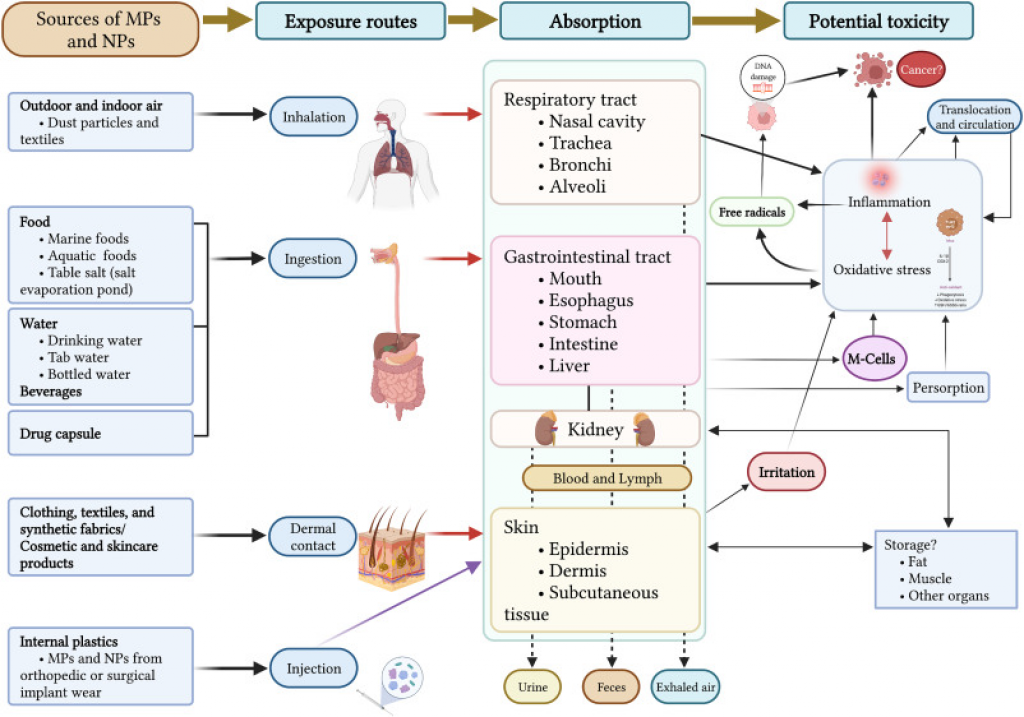
Forest Fires
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (DTE | HT | TOI): A state of emergency has been declared in Chile, with many having died due to wildfires along the coastal towns of the country.
Forest Fires
- Forest fires or wildfires are spontaneously occurring forest, bush and plain fires and can occasionally be controlled.
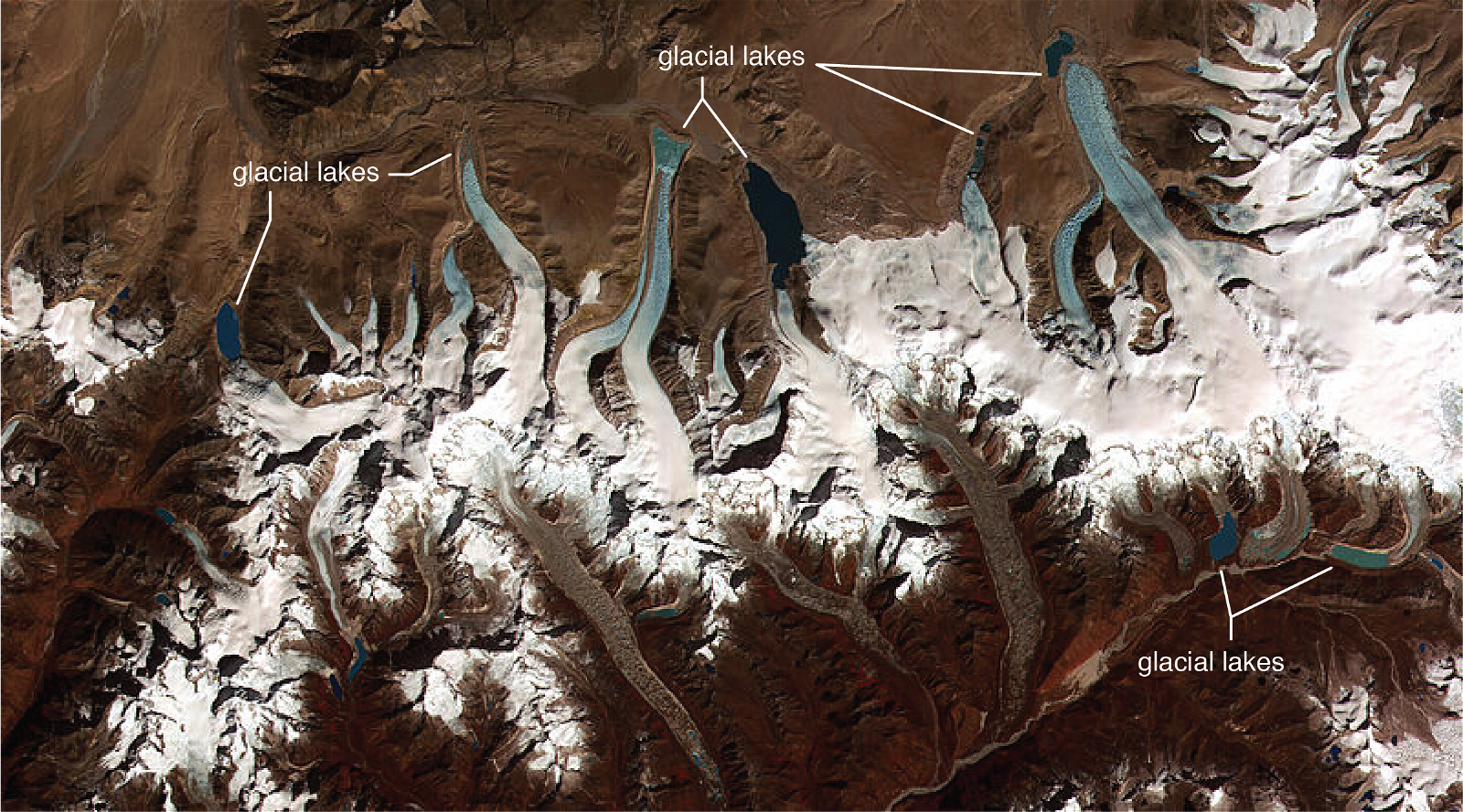
- Over 6.6 million hectares of tree cover was lost to forest fires in 2022.
Types of Wildfires

Causes of Forest Fires
Natural Causes
- Thunderstorms and lightening: Lightning-caused forest fires are caused by thunderstorms where the lightning strikes combustible materials on ground under conditions that support combustion.
- In Canada’s British Columbia province, lightening has been the cause of 60% of regions wildfires.
- Climate change impacts: Hotter temperatures dry out the landscape creating a perfect environment for larger, more frequent forest fires leading to higher emissions from forest fires, further exacerbating climate change & contributing to more fires as part of a “fire-climate feedback loop.”
- E.g. During the 2015-2016 El Niño season tree cover loss due to fires increased 10-fold in the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia and Latin America.
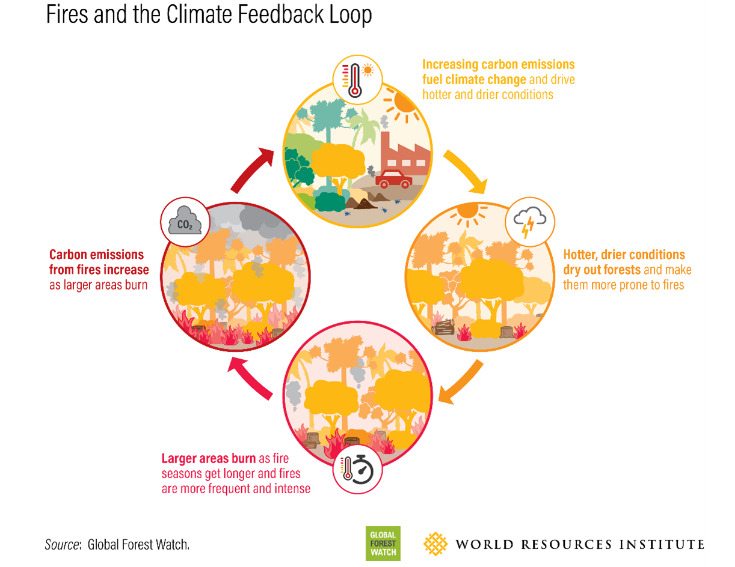
- High temperatures: The large majority, roughly 70%, of all fire-related tree cover loss occurred in boreal regions since northern high-latitude regions are warming at a faster rate contributing to longer fire seasons, greater fire frequency and severity, and larger burned areas.
- Vegetation: Dry deciduous forests, which receive low rainfall, and have nutrient poor soil are more vulnerable to fire compared to others (dry vegetation has been a major cause of fires in Australia).
Anthropogenic Causes
- Carelessness while smoking or using mosquito coil or candles or camp-fires,
- Arson or intentional,
- Tribal ritual/tradition,
- To ward off wild animals,
- Poor land & forest management,
- Conceal illegal timber cutting,
- Collection of minor forest produce by tribals,
- Burning of debris etc.
Impact of Forest Fires
Loss of natural resources
- Loss of natural vegetation & forest cover, degradation of water catchment areas by decreasing soil moisture, soil degradation due to repeated burnings etc.
- E.g. Forest fires now cause 3 million more hectares of tree cover loss each year than they did in 2001.
Impact on biodiversity
- Proliferation of exotic species: Fires create gaps in a forest, making the area vulnerable to invasions by exotic species. E.g. Cogon grass recovers quickly after fire, elbowing out biodiversity.
- Loss of Indigenous Vegetation: E.g. In the Himalayas, uncontrolled fires have made the situation less favourable for oaks to grow and more favourable for fire prone chir to grow.
- Loss of wildlife habitat and depletion of wildlife: E.g. Australia fires (2019-20) have displaced an estimated 3 billion animals.
Socio-economic impact
- Forest fires decimate plants & animals, destroy source of fodder, fuel, human settlements, and livelihood of local residents, threatening both human life and property.
Impact on Agriculture
- Frequent fire kills regeneration ability of the soil, thereby delaying the establishment of a new crop and extending the rotation.
Impact on Climate change
- Forest fires reverse carbon sequestration process, exacerbating global warming & climate change.
- Climate change alters forest boundaries and types, impact productivity, species population and migration, the occurrence of pests and diseases and the capacity for forests to regenerate.
Adverse Impact on Health System
- Forest fires are source of polluting smoke and noxious gases that may result in serious respiratory problems for humans.
Way Forward
- Prevention by breaking the ‘fire triangle’ composed of fuel, air/oxygen and ignition source.
- Improving forest resilience by halting deforestation and forest degradation.
- Advocate large-scale incentives and programmes to collect inflammable pines for use as fuel, or preparation of fire bricks.
- Capacity building of forest departments and other stakeholders
- Encourage local participation of tribal people/farmers. E.g. Van Panchayats.
- Use of corporate social responsibility funds for creating awareness campaigns on forest fires.
- Increased R&D in fire detection, suppression and fire ecology for better management of wildfires.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)