Decline in China’s Population
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): Since 2016, the Total Fertility Rate (TFR) has been falling in China.
- India overtook it as the most populous country in the world in 2023.
|
Evolution of Birth Control Policy in China

- For the First Chinese President, Mao Zedong, birth control was a concern but not of great importance.
- Failure of the Great Leap Forward (1958-62) programme led to starvation and death of millions.
- With the rolling back of the Great Leap Forward, the population bounced back.
|
- Five-Year Plans after the 1970s encouraged birth control and even coerced.
- The One-child policy, introduced in 1980, restricted couples to having only one child.
- The “Later, longer, and fewer” slogan encouraged delayed marriage, longer gaps in children and fewer children.
- The One-child policy was questioned later not just over issues of privacy and the state’s overreach but also the need.
Reasons for the decline
- China’s TFR (2020 Census) was 1.3 births per woman, way below the replacement rate of 2.1.
|
- “One Child policy” claims to have reduced the TFR from 2.75 (1979) to 1.3 (2020) in China.
- In 2016, the “One Child Policy” officially ended, and couples were allowed to have up to two children, which was later increased to three children in 2021.
- Women’s education and employment allow them to make choices about their reproductive health.
- Dejection from family life and customs is also one of the reasons.
- High pressures of modern society, with increasing competition for jobs, are also factors leading to delayed marriage and no child.
- COVID-19 pandemic deaths have also caused a decrease in the population.
Impact of declining population on China
- The Working-age population has now fallen to 61% of the total population.
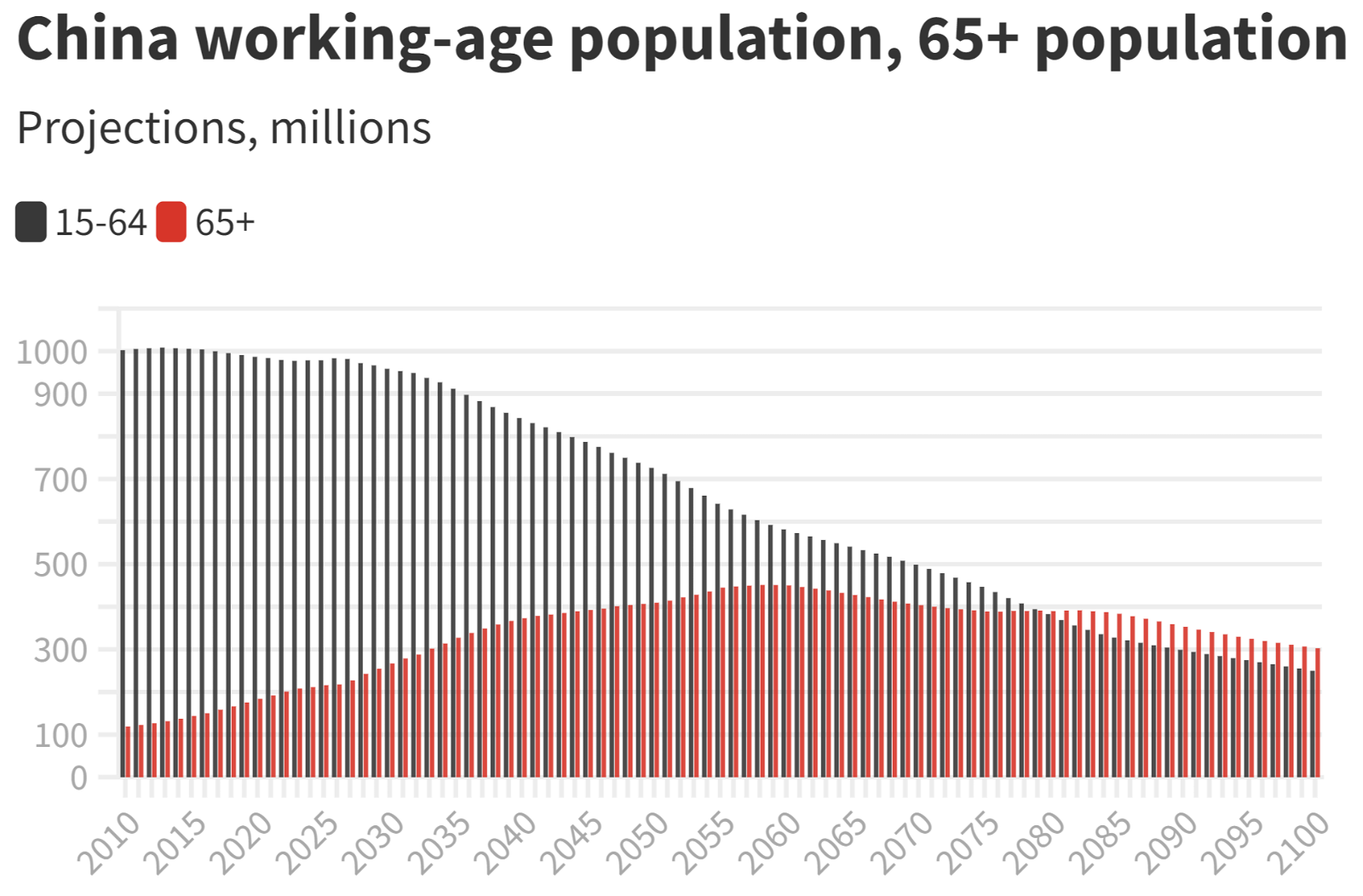
- Greater investments in elderly care, including palliative care, are needed.
- Pressure on the young population to support ‘dependents’ (Aged less than 15 or more than 59).
- Vicious cycle of slowdown: An economic slowdown should mean young couples delay having children. The resulting decline in fertility rates eventually pushes the economy’s productivity rates lower.
|







![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)