Nagara Style of Temple Architecture
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): The Ram temple in Ayodhya is constructed based on the Nagara style.
Nagara Style of Temple Architecture
- It began around the 5th century CE in northern India, during the late Gupta period.
- It developed alongside Dravida style, which originated in southern India during the same period.
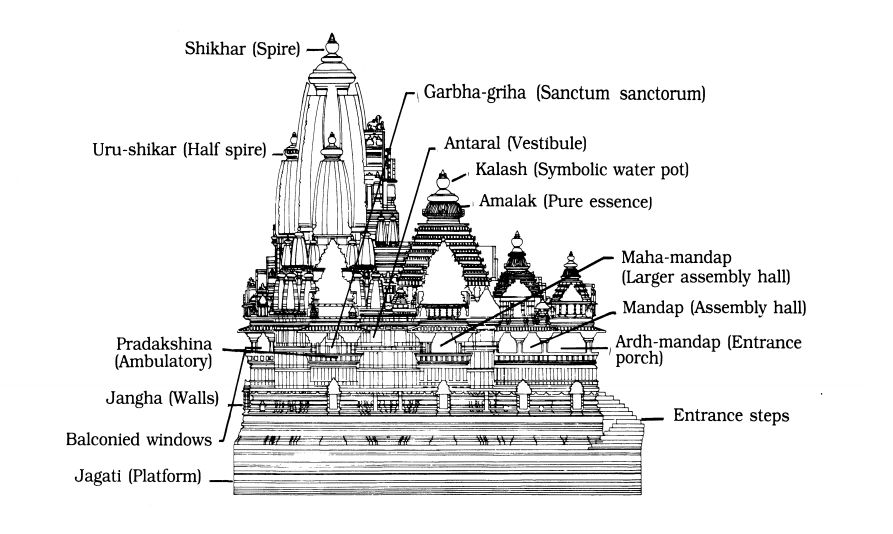
- Nagara-style temples are often built on a raised stone platform with steps leading up to them.
- Nagara temples typically lack elaborate boundary walls or gateways.
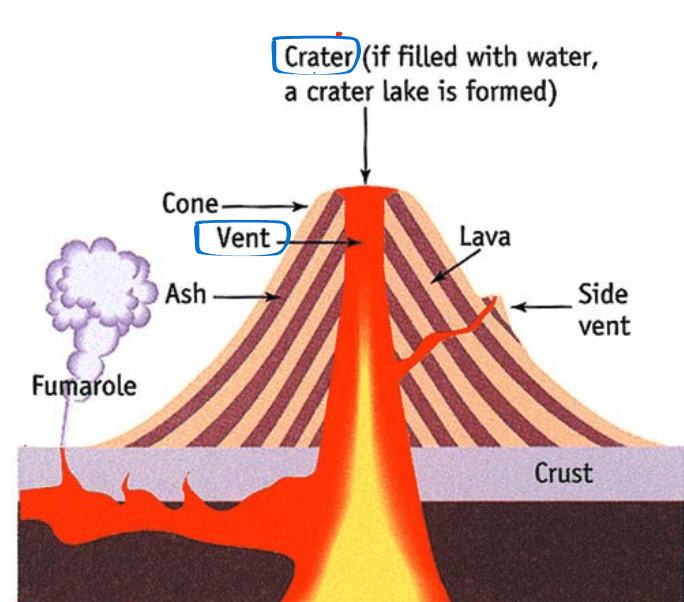
- The main tower always houses the garbhagriha.
- Towering over the garbha griha is the shikhara, the most distinguishable aspect of the Nagara style.
- The term “shikhara” refers to man-made representations of the natural and cosmological order.
- The Amalaka or Kalash on the Shikhara is a distinctive feature.
- Nagara temples have subdivisions based on the shape of the shikhara.
- A Nagara-style temple typically includes a circumambulatory passage around the garbha griha, along with one or more mandapas (halls) on the same axis.
- Elaborate murals and reliefs often decorate its walls.
- Examples: Kandariya Mahadev Temple in Madhya Pradesh, the Sun Temple in Konark, the Sun Temple in Modhera, Gujarat, and the Ossian Temple in Gujarat.
|
Classification of the Nagara Style of Temple Architecture
- Adam Hardy classifies the Nagara style of temple architecture based on the style of Shikhara.
Valabhi
- They have barrel-vaulted roofs and are rectangular in design.
- An example of this style is the Teli Ka Mandir, a 9th-century temple in Gwalior.

Teli ka Mandir
Phamsana
- These Nagara-style temples are shorter and broader structures.
- Multiple slabs rise upwards in a moderate slope on a straight incline like a pyramid, meeting at a single point above the building’s mid-point.
- An example of this style is the Jagmohan of Konark Temple.

Jagmohan temple
Rekha-Prasad or Latina
- It emerged from the previous styles (Valabhi,phamsana).
- These temples feature a basic Shikara, a slightly curved tower with four sides of equal length.
- It remained the most refereed style till the 10th century.
- E.g: Sun Temple at Markhera in Madhya Pradesh (MP) and the Sri Jagannath Temple in Odisha.

Sri Jagannath Temple
Shekhari
- From the tenth century onwards, composite Latinas began to emerge, giving rise to Shekhari and Bhumija styles.
- It has a primary Rekha-Prasad Shikara and one or more rows of lesser steeples (a tower with a pointed top) on both sides of the centre spire.
- Mini Shikaras can also be found at the base and on the corners.
- The Kandariya Mahadev Temple in Khajuraho is a notable example of this style.
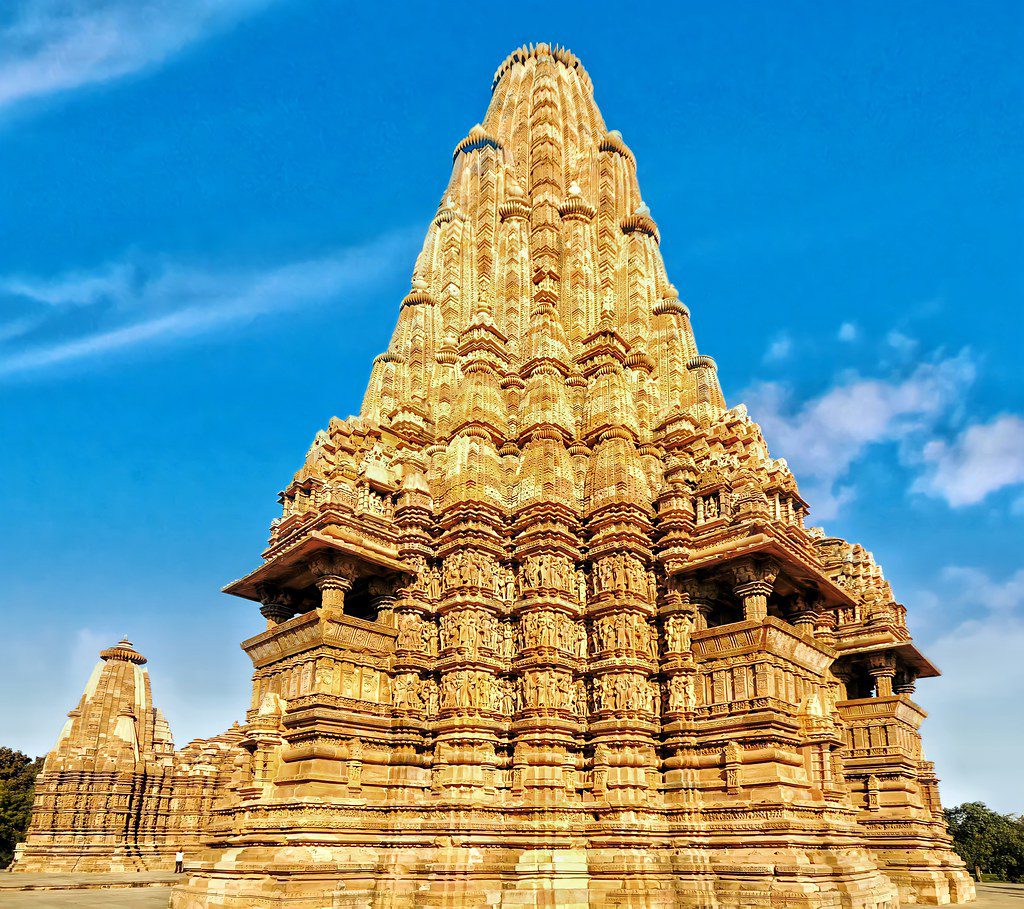

Kandariya Mahadev Temple
Bhumija
- It was developed in Malwa under the Paramara dynasty.
- It has miniature spires in horizontal and vertical rows all the way to the top, creating a grid-like effect on each face. The actual shikhara often approaches a pyramidal shape.
- The Udayeshwar Temple in Madhya Pradesh is an example of this architectural style.

The Udayeshwar Temple
Comparison to Dravida style

| Features |
Nagara Style |
Dravida Style |
| Geographic Distribution | Northern India | Southern India |
| Vimana Shape | Curvilinear (Bulbous or Pyramid) | Pyramidal (Step-like) |
| Boundary walls | it does not usually have elaborate boundary walls or gateways. | It is enclosed within a compound wall. The front wall has an entrance gateway, which is known as a gopuram. |
| Towers | Multiple towers | Always a single tower. |
| Entrance Deities | Ganga and Yamuna rivers are depicted in personified form. | The entrance has Dwarapalas. |
| Pedestals | Are higher than the ground | Are at ground level |
| Crowing element | It is referred as Shikara. | It is referred as Kalash and Amalaka. |
| Presence of a water tank | Temple tanks or large water reservoir are generally not enclosed with in the temple complex | It is common to find a large water reservoir, or a temple tank, enclosed within the complex. |
| Examples | Kandariya Mahadeva (Khajuraho), Jagannath Temple (Puri), Dashavatara temple (Deogarh). | Shore temple (Mahabalipuram), Brihadesvara temple (Thanjavur), Meenakshi Temple (Madurai) |







![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)