Current Affairs November 03, 2023: Kra Isthmus, Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, KAVACH System, UNESCO’s Creative Cities Network
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
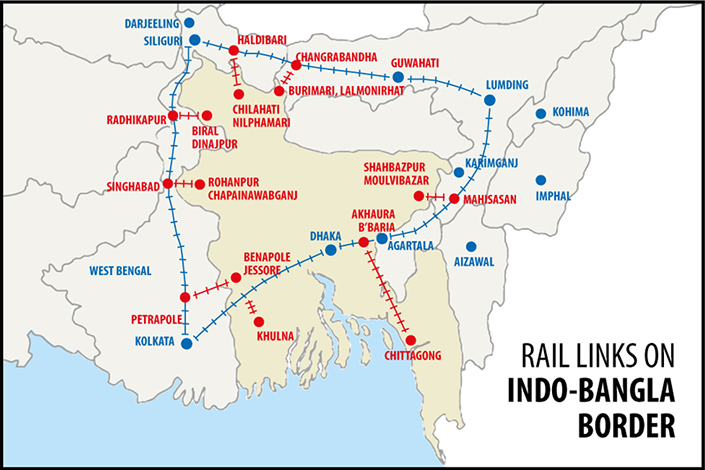
{GS2 – IR – India-Bangladesh} Indo-Bangla Railway Project
- Context (TH): The Agartala-Akhaura rail link project has been inaugurated.
Trains run between West Bengal and Bangladesh
- Three trains run between West Bengal and Bangladesh:
- Bandhan Express:
- The Bandhan Express has revived an old railway link between Kolkata and Khulna.
- Prior to the 1965 war between India and Pakistan, this route was served by the Barisal Express.
- In 2017, the government restarted the service.
- Maitree Express between Kolkata and Dhaka Cantonment started in April 2008.
- Mitali Express connects Siliguri in North Bengal with Dhaka, started in 2022.
- Bandhan Express:
{GS2 – IR – India-China} Thailand’s Kra Isthmus
- Context (IE): Thailand will build a land bridge across Kra Isthmus financed by China.
|
- This land bridge will give a direct access between the Andaman Sea and Gulf of Thailand.
- lt will have two large-capacity ports or shipping terminals on either side, joined by an east-west economic corridor including an oil pipeline.

Benefit of the Kra Isthmus Land Bridge
- It will reduce the sailing distance between the Indian Ocean Region and the waters of East Asia.
- It will be an alternative to the longer and congested shipping route through the Strait of Malacca.
|
Concern of the Kra Isthmus Land Bridge
- China increased surveillance in Indian Ocean region: A major concern for India.
- Viability: China-backed infrastructure projects such as the Pokhara airport in Nepal and Hambantota port in Sri Lanka have struggled with issues of viability.
- China’s debt trap: China’s alleged practice of providing loans to developing countries on unfavorable terms so that the countries are unable to repay and become dependent on China.
- Strain Thailand’s relations with the US, Japan, and India: Due to closeness with China.
Thailand
|
{GS2 – IR – India-Maldives} Strained Relations
- Context (TH): President-elect Mohamed Muizzu plans to remove Indian troops from the Maldives to ensure the country’s independence and sovereignty in his foreign policy.
- Currently, there are 75 Indian military personnel in the Maldives. They operate Dornier aircraft and two helicopters provided by India.
Reasons for Opposition
- Pro-China Tilt:
- Mr Muizzu and his political camp have been historically sensitive in their relations with India, which dates back to the administration of President Yameen.
- During his term, Yameen’s administration had a pro-China stance, which caused a strain in the relations with India.
- No Military Presence:
- Muizzu has pledged to keep the Maldives free from any foreign military presence, whether Indian, Chinese or from any other country.
India-Maldives Bilateral Relations
Bilateral Economic and Trade Relations
- India and Maldives signed a trade agreement in 1981, enabling the export of essential commodities.
- India emerged as Maldives’s 2nd largest trade partner in 2022.
- India-Maldives bilateral trade crossed USD 500 million for the first time in 2022.
- Maldives Implemented visa-free entry for Indians for business purposes in Feb 2022.
Tourism
- The Maldivian economy heavily depends on its tourism sector, the primary source of foreign exchange earnings and government revenue.
- Tourism directly accounts for about a quarter of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Maldives.
- In 2023, India, with 147,527 tourist arrivals, is the 2nd leading source market for Maldives.
Security Concerns
- Maldives is strategically crucial to India due to its proximity to India’s west coast (70 nautical miles away from Minicoy and 300 nautical miles away from India’s West coast).
- India needs to maintain close ties with Maldives, considering the increasing influence of China in the Indian Ocean region.
- The Maldives is part of the ‘Colombo Security Conclave’ with India and other nations, emphasising collective security and regional cooperation.
|
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Elections} Electoral Literacy
- Context (TH | PIB): The MoU was signed between the ECI and the Ministry of Education (MoE) to introduce content on electoral literacy in the NCERT textbooks.
- Electoral Literacy is a process of transforming citizens into empowered voters by helping them understand the electoral process and the need to enrol as electors and participate in the elections in an ethical and informed manner.
Key Initiatives in the MoU
- Providing voter ID cards to students upon turning eighteen.
- Inclusion of electoral literacy in adult literacy and basic education curriculum.
- Establishment of Electoral Literacy Clubs (ELCs) in schools and colleges.
- Designating “democracy rooms” in senior secondary schools for voter education and activities.
Long-term Vision
- It aims to extend the Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation to schools/colleges.
- It also aims to instil electoral literacy in young people and addresses issues like voter apathy.
Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP)
Objectives
|
{GS3 – Envi – Laws} India’s Opposition to EU’s CBAM
- Context (TH | ET | IE | TH | TH): India has opposed Europeans Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) citing that carbon cannot be priced the same in India and Europe.
- GoI has declared that it is working on tax akin to CBAM to aid the local industries.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
- CBAM is a proposed EU carbon border tax on imports from countries with carbon-intensive production methods.
- CBAM, which will start in 2026, is a part of the “Fit for 55 in 2030 package”.
- Imports covered by CBAM: Initially, it will be imposed on the most carbon-intensive imports, i.e., iron and steel, cement, fertilisers, aluminium, hydrogen, and electricity.
|
Objectives of CBAM / Arguments in Favour of CBAM
Preventing Carbon leakage
- Carbon leakage refers to a situation where a company relocates production from strict carbon regulations to more lenient ones.
- CBAM as a carbon border tax will end this loophole of the carbon tax mechanism.
- It preserves the competitiveness of domestic industries subject to carbon pricing.
Level Playing Field
- CBAM ensures that domestic and imported goods are subject to similar carbon pricing.
- By doing so it protects the domestic industries from unfair competition.
Encouraging Global Emission Reductions
- CBAM raises costs for importing for companies from lax climate policy countries.
- This will pressurise these countries to bolster climate policies to remain competitive.
Penalise Free Riders in Fight against Climate Change
- A free-rider is one who is riding on the contribution of others, despite having means to do so. E.g., the US with its “sometimes in, sometimes out” response to climate action.
Criticism of CBAM
Unilateral Measure
- EU has decided on CBAM without agreement with other countries.
- This undermines the spirit of multilateralism and so, it can lead to trade disputes and hinder international climate cooperation.
Discriminatory Trade Barrier for Developing Countries
- Historically, developed economies have the primary responsibility for climate change.
- The contribution of the developing countries (the Global South) was negligible.
- That’s why, the Kyoto Protocol acknowledged “common but differentiated responsibilities” in the climate change fight.
- Although, the Paris Agreement asked countries to set voluntary emission targets but it mandated wealthier nations to make financial transfers to developing economies to combat climate change.
- Now, when the developing nations are earning from manufacturing industries, EU by imposing CBAM which considers only present emissions is restricting their development.
Beneficiary of CBAM
- The burning of carbon anywhere in the world affects climate change everywhere.
- CBAM like tax regime can only be meaningful if they are utilised for the whole world.
- Otherwise it will simply become a revenue earning mechanism of the EU.
Other Criticisms of CBAM
- Double taxation: Products being subject to carbon pricing of the exporting country and CBAM.
- Market distortions: CBAM can inflate the cost of products from specific countries or industries.
- Complexity and administrative burden
- Higher consumer prices
Countries that will be Most Affected by CBAM
- According to United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), countries most affected by CBAM are Russia, China, Turkey, India, Brazil, South Africa, and Mozambique.
India’s Trade with the European Union
- The EU is India’s third largest trading partner, accounting for 10.8% of total Indian trade.
- India is the EU’s 10th largest trading partner, accounting for 2.1% of EU total trade in goods.
- Trade in services between the EU and India reached €30.4 billion in 2020.
{GS3 – IE – NITI Aayog} Vision India@ 2047
- Context (TH | IE): The Vision India@2047 document by Niti Aayog will provide the roadmap for India to become a developed economy with an estimated $30 trillion GDP by 2047.
- It will provide a roadmap for India’s progress in 2030 and the ultimate vision for 2047.
Progress Towards 2047
- The Union FM outlined key objectives for India’s development in the FY23 budget:
- Focus on macro-economic growth and micro-economic welfare.
- Promotion of digital economy, fintech, technology, energy transition, and climate action.
- Encourage private investment with public capital investment.
- The FY24 budget reiterated Jan Bhagidari (people’s participation) through Sabka Saath, Sabka Prayas (Collective Efforts for Everyone’s Success) & introduced the Saptarishi principles:
- Inclusive Development
- Reaching the Last Mile
- Infrastructure and Investment
- Unleashing the Potential
- Green Growth
- Youth Power
- Financial Sector
Current State of the Indian Economy
- In 2022, India’s GDP surpassed that of the UK & France, making it the world’s fifth-largest economy.
- India’s GDP is estimated at $3.7 trillion, and it is expected to overtake Japan and Germany by 2030, with a projected nominal GDP of $7.3 trillion by that year.
Vision India@2047 Contents
- The document will outline structural changes and reforms necessary to:
- Transform India into a $30 trillion developed economy by 2047.
- Achieve per-capita income of $18,000-20,000.
- The vision document will emphasise the development of:
- Human capital
- Leveraging India’s market size
- Addressing regional disparities
- It will include government process re-engineering and reducing duplication in ministries and departments.
Preliminary Results
- To achieve the Vision India@2047 goals, India needs annual economic growth rates of:
- 9.2% (2030-2040)
- 8.8% (2040-2047)
- 9% (2030-2047)
- Exports are projected to reach $8.67 trillion by 2047, while imports are estimated at $12.12 trillion.
- India’s average life expectancy is expected to increase to 71.8 years, up from 67.2 in 2021, and the literacy rate is predicted to rise to 89.8%, compared to 77.8% in 2021.

Challenges
- Aligning state vision documents
- Avoiding middle-income trap
- Strategy to prevent the economy from getting stuck in the middle-income trap.
- Ensures competitiveness amid rising costs to reach high-income status.
Indian Economy by Nominal Exchange Rate
Indian Economy by PPP Exchange Rate
|
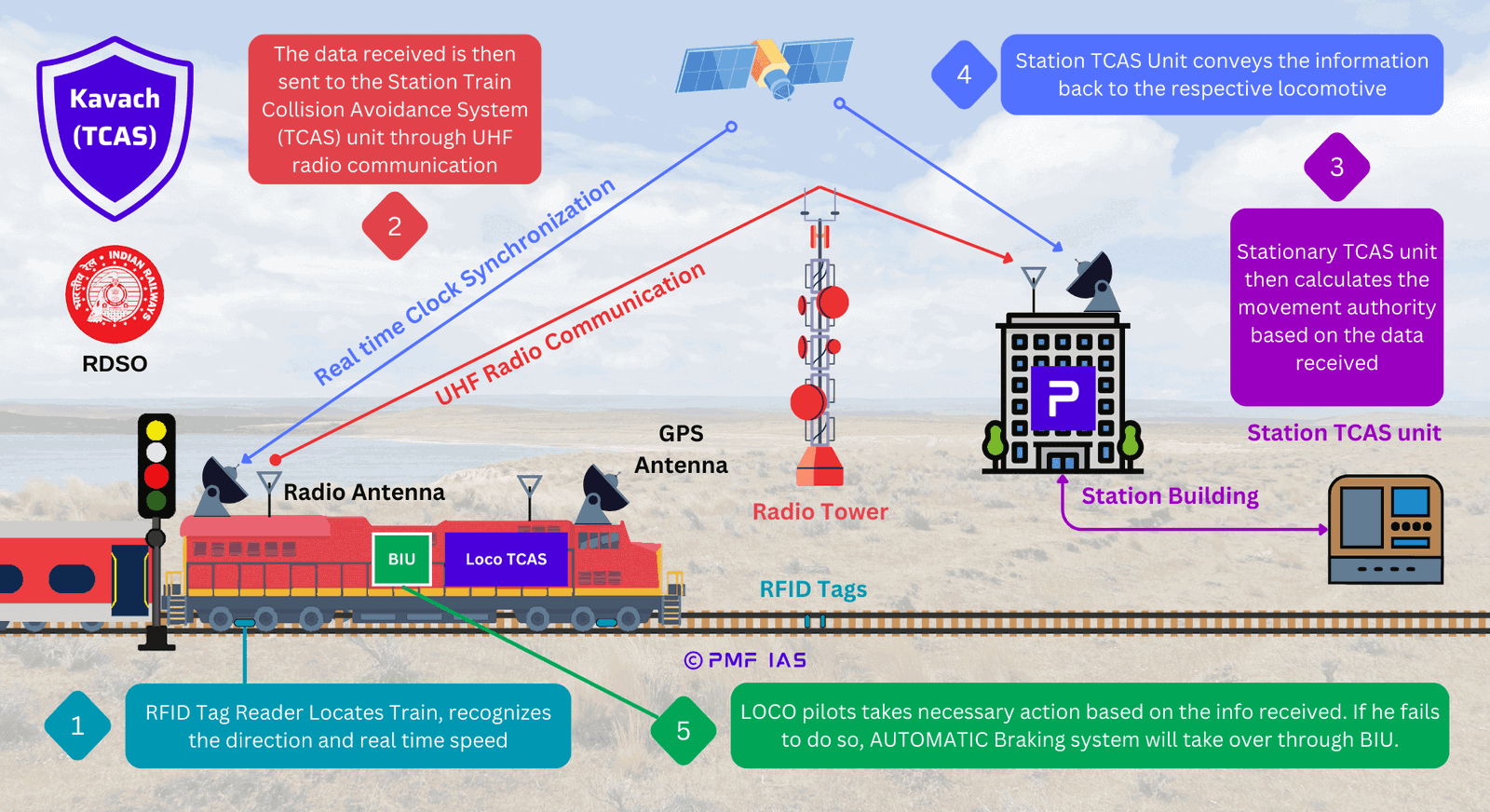
{GS3 – Infra – Railways} Overshoot and Importance of KAVACH System
- Context (TH | TH | IE): The Vizianagaram train accident may have occurred due to overshot.
- The anti-collision KAVACH system is not available on either of these trains.
Overshot
- Overshot is technically called Signal Passing at Danger (SPAD).
- It occurs when a train doesn’t stop at a red signal and keeps moving forward.
- It is a serious safety hazard that can lead to train collisions and other accidents.
Reasons of Overshot
- Human error: Due to fatigue, distraction, or signal misinterpretation.
- Technical failure: It includes problems with the train’s brakes, signalling system, or track.
- External factors: Such as bad weather or obstructions on the track.
KAVACH System: Solution to Overshot
- The KAVACH is an indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system.
- It was developed by the Research Design & Standards Organisation (RDSO) of the Indian Railways.
- It has been adopted as the National ATP System for Indian Railways.
- It is a state-of-the-art electronic system developed under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- It is one of the cheapest systems with Safety Integrity Level-4 (SIL-4) certification.
|
Key Features/Advantages of the KAVACH System
- Avoid SPAD: When a red signal is ignored, and two trains approach each other on the same track, the system applies sudden brakes.
- Overspeed protection: It will automatically apply the brakes if the train exceeds the speed limit.
- Collision avoidance: Through direct loco-to-loco communication.
- Signal information: The system offers the driver real-time signal information. It provides a line-side signal display in the cabin for better visibility in fog and at high speeds.
- Automatic whistling at level crossings: A big boon during fog conditions.
- SOS feature: To control trains in emergency situations.
Where has KAVACH been Implemented?
- The South Central Railway (SCR) Zone pioneered implementing the KAVACH.
- Trials of Kavach were conducted on the Lingampally–Vikarabad–Wadi and Vikarabad–Bidar sections of the South Central Railway, covering a distance of 250 km.
{GS3 – Infra – Tourism} Domestic Sailing of the First International Cruise Liner
- Context (PIB): Domestic sailing of the first International Cruise Liner ‘COSTA SERENA’ in India is set to be launched at Mumbai.
- Costa Cruises, a prominent European cruise company, operates under an Italian flag.
- This cruise initiative is part of ‘Dekho Apna Desh’, launched to appeal the middle class to prefer domestic tourism over international.
|
{GS3 – S&T – Discovery} Haemoglobin in Cartiledge
- Context (TH): Haemologlobin is found in chondrocytes, cells that make cartilage.
- Cartilage is the connecting tissue between bones.
- Significance: Earlier, it was believed that haemoglogin is found only in red blood cells (RBCs).
Haemoglobin
- Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein in that carries oxygen in our body.
- Without it, oxygen could not be transported to the body’s tissues, and the cells would die.
Haemoglobin in Blood
- The fluid part of blood is called plasma.
- Cells in blood are:
- Red blood cells (RBC) carries oxygen with the help of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin binds with oxygen and transports it to all the parts of the body and, ultimately, to all the cells.
- White blood cells (WBC), which fight against germs that may enter our body.
- Platelets help in the clotting of blood.
{Prelims – In News} UNESCO’s Creative Cities Network
- Context (TH | HT): UNESCO added 55 cities to its Creative Cities Network for their commitment to culture and creativity in urban planning.
- Now, the UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) has 350 cities in seven creative fields.
- Kozhikode is designated as a “City of Literature,” known for hosting literary festivals.
- Gwalior is recognized as a “City of Music” for its rich musical heritage and prestigious music institutes.
- Other cities added to the list are:
- Bukhara (Uzbekistan)
- Casablanca (Morocco)
- Kathmandu (Nepal)
- Rio de Janeiro (Brazil)
- UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) was established in 2004 to promote cooperation among cities valuing creativity for sustainable urban development.
- Cities in the network aim to prioritize creativity and cultural industries in their local development plans and collaborate internationally.
- The Network spans seven creative fields: Crafts and Folk Art, Media Arts, Film, Design, Gastronomy, Literature and Music.
- UCCN partners with UNESCO, serving as a platform for sustainable development discussions and implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Indian Cities on UCCN
- Kozhikode: City of Literature (2023)
- Gwalior: City of Music (2023)
- Srinagar: Crafts and Folk Arts (2021)
- Mumbai: Film (2019)
- Hyderabad: Gastronomy (2019)
- Chennai: City of Music (2017)
- Jaipur: Crafts and Folk Arts (2015)
- Varanasi: City of Music (2015)
Kozhikode’s Literary Tradition
- Kozhikode (in Kerala) is known for its rich literary and cultural heritage.
- The city is a hub for various media houses & boasts numerous publishing companies and libraries.
- The first Malayalam novel, “Kundalatha,” was authored by Appu Nedungadi in Kozhikode in 1887.
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
Major Initiatives of UNESCO
Reports
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)