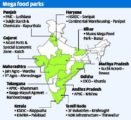
Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)
- APEDA is a statutory body under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It was established under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act of 1985.
- It is the apex body for agricultural export promotion in India.
- Objective: To develop and promote the export of scheduled products.
- The products specified under the APEDA ACT are called scheduled products, and exporters of such scheduled products are required to register under APEDA.
- Scheduled products include fruits, vegetables, meat, dairy products, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages, etc.
- It provides financial assistance, information, and guidelines for the development of scheduled products.
- In addition, APEDA has been entrusted with monitoring sugar imports.
- APEDA serves as the Secretariat to the National Accreditation Board (NAB).
- It plays a crucial role in accrediting Certification Bodies for the National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP).
- Organic Products for export are to be certified only if Produced, Processed and Packed as per the standards laid down in the document of NPOP.
- Headquarters: New Delhi.
Functions of APEDA
- Development of industries relating to the scheduled products for export.
- Registration of persons as exporters of the scheduled products.
- Fixing standards and specifications for the scheduled products for exports.
- Carrying out inspection of meat and meat products in slaughterhouses, processing plants, storage premises, conveyances, or other places where such products are kept or handled.
- Improving packaging of the Scheduled products.
- Improving marketing of the Scheduled products outside India.
Banana
- Banana is a tropical crop & a major horticultural produce.
- Favourable climatic conditions:
- Temperature range: 15ºC – 35ºC
- Relative humidity: 75-85%.
- Altitude: prefers tropical humid lowlands (but grown from the sea level to 2000m).
- Rainfall: Four months of monsoon (June to September) with an average of 650-750 mm.
- Threats:
- Chilling injury occurs at a temperature below 12ºC.
- High-velocity winds that exceed 80 km /hr. damages the crop.
- Soil requirement:
- Deep, rich, loamy soil with a pH between 6.5 – and 7.5 is most preferred for banana cultivation.
- A soil that is neither too acidic nor too alkaline, rich in organic material with high nitrogen content, adequate phosphorus level and plenty of potash is good for bananas.
- Saline solid, calcareous soils are not suitable for banana cultivation.
- Varieties grown:
- Dwarf Cavendish, Robusta, Monthan, Poovan, Nendran, Red banana, Nyali, Safed Velchi, Basrai, Ardhapuri, Rasthali, Karpurvalli, Karthali and Grand Naine etc.
- Grand Naine, an imported variety from Israel, is gaining popularity due to its tolerance to abiotic stresses and good quality bunches.
- Andhra Pradesh is the largest banana-producing state in India, followed by Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh.
- These 5 states contribute around 67 percent to India’s banana production in FY 2022-23.
- Despite being the largest global producer of bananas, India’s exports do not reflect this.
- India’s export share in the global market is only 1% even though the country accounts for 26.45 per cent of the world’s banana production (35.36 Million Metric Tons).
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)