Odisha National Parks, Tiger Reserves, Wildlife Sanctuaries & Ramsar Sites
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 25, 2024 2:22 AM
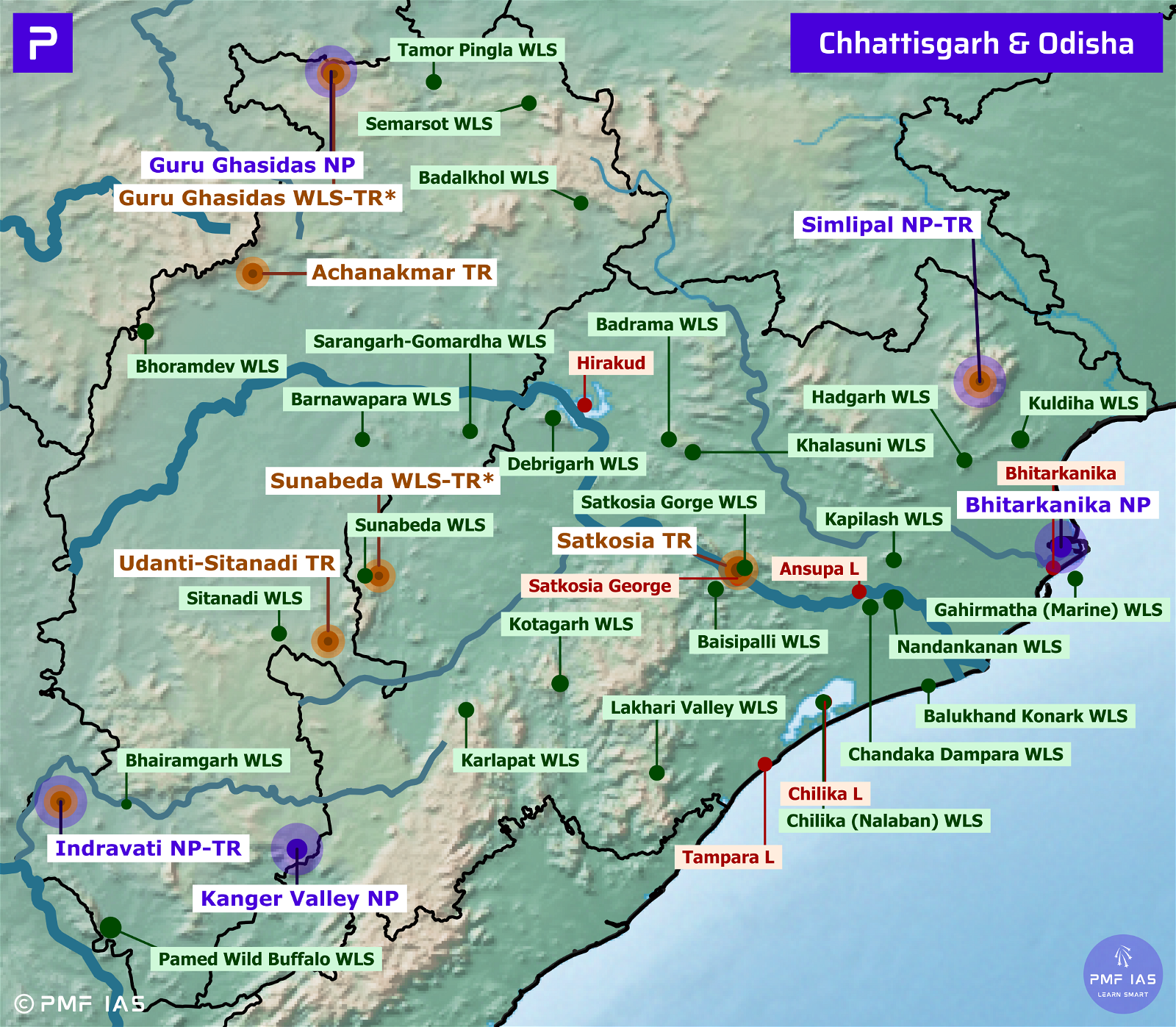
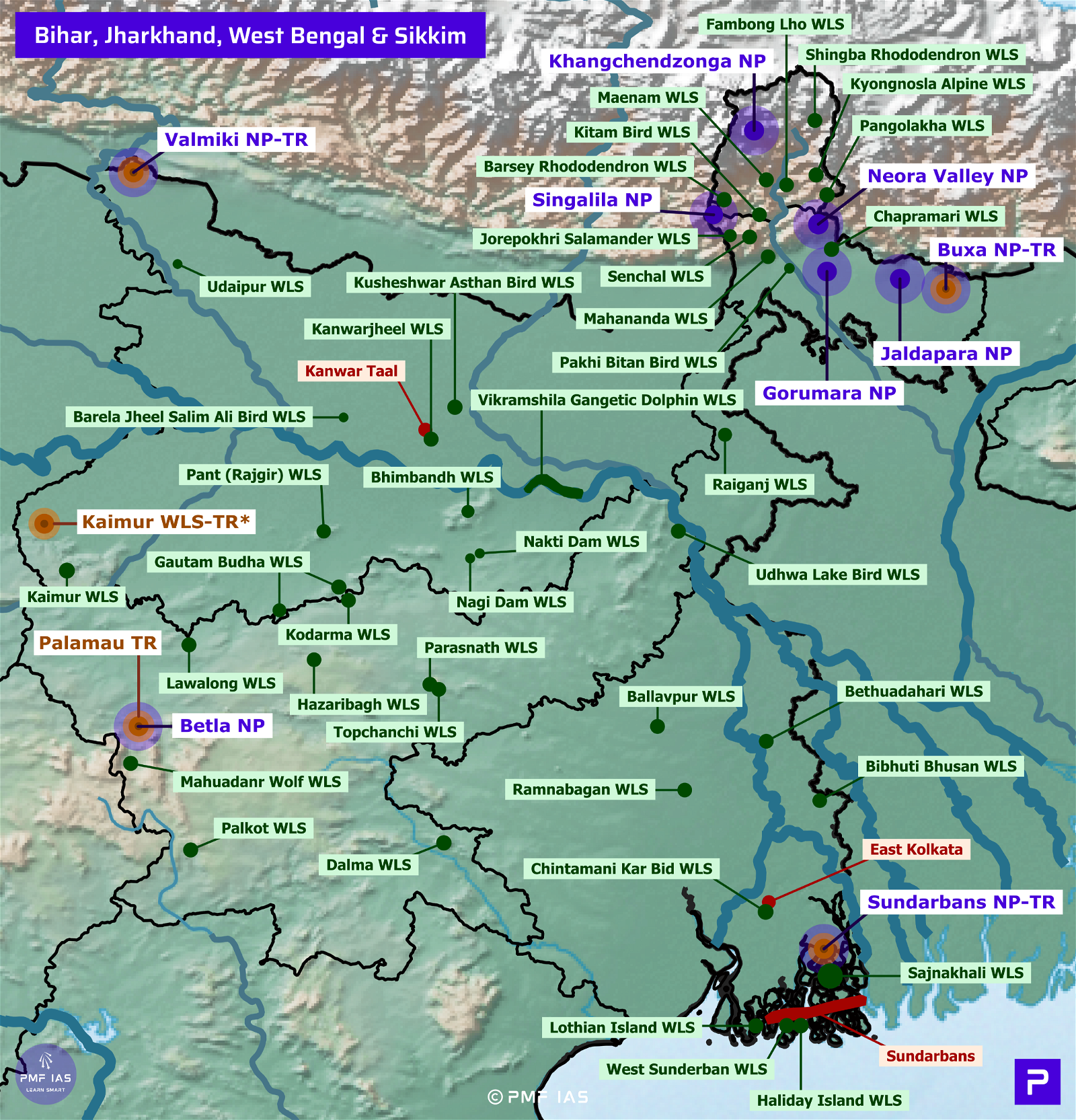
Bhitarkanika National Park, Wildlife Sanctuary, Ramsar Site
- It is the second Ramsar Site of Odisha after Chilika Lake. It is surrounded by Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary. Gahirmatha Marine Sanctuary separates the National Park from the Bay of Bengal. It is inundated by the rivers Brahmani, Baitarani & Dhamra.
- It hosts many mangrove species and is the second-largest mangrove ecosystem in India.
- Major Fauna: Saltwater (Estuarine) Crocodile (LC).
- Major Flora: Mangrove species.
Gahirmatha Marine Wildlife Sanctuary
- Gahirmatha Marine Wildlife Sanctuary is the world’s largest nesting beach for Olive Ridley Sea Turtles (VU).
- It extends from Dhamra River mouth in the north to Brahmani River mouth in the south.
Chilika Lake Ramsar Site & Nalbana Bird Sanctuary
- Chilika Lake is a ephemeral (not permanent) brackish water lagoon. It is a shallow bar-built estuary (partially enclosed coastal area of brackish water).
- The western and southern margins of the lake are fringed by the Eastern Ghats. It is located at the mouth of the Daya River (that flows into the Bay of Bengal).
- It is the largest coastal lagoon in India and the largest brackish water lagoon in Asia. In 1981, Chilika Lake was designated the India’s first Ramsar Site.
- It sustains the livelihood for many fishermen who live in and near the lagoon.
- Major Fauna: Green sea turtle (EN), dugong (VU), Irrawaddy dolphin (EN), Chilika limbless skink or Madras Spotted Skink (CR).
- The Irrawaddy dolphin (EN) is the flagship species of Chilika lake. Chilika is home to the only known population of Irrawaddy dolphins in India.
- Major Avifauna: White bellied sea eagles, flamingos, egrets, grey herons, storks, spoonbills.
- Chilika is the largest wintering ground for migratory birds on the Indian sub-continent. Birds from as far as the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea come here.
- Threats: Siltation due to littoral drift and sediments from the inland river systems, decrease in salinity and fishery resources, proliferation of freshwater invasive species.
Nalbana Bird Sanctuary
- It is the core area of Ramsar wetlands of Chilika Lake.
- It hosts thousands of migratory birds.
- The island disappears during monsoon due to inundation, only to emerge again in post-monsoon.
Chilika Development Authority (CDA)
- In 1992, Government of Odisha set up the Chilika Development Authority (CDA). It was set up for the restoration and overall development of the lake.
- The governing body of the Authority is headed by the Chief Minister of Odisha State.
Satkosia Tiger Reserve
- Satkosia Tiger Reserve = Satkosia Gorge Wildlife Sanctuary + Baisipalli Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The Tiger Reserve is located where the Mahanadi River passes through a long gorge in the Eastern Ghats.
- The area is also a part of the Mahanadi ER.
- Vegetation: Moist deciduous forests and riverine forest.
- Major Fauna: Leopard, indian wild dog (dhole), sloth bear, Asian elephant, Bengal tiger.
Simlipal Biosphere Reserve, National Park, Tiger Reserve
- It is located Eastern Ghats and is listed in UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- Mayurbhanj ER = Similipal Tiger Reserve + Hadgarh + Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Vegetation: moist and dry deciduous forests, grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Bengal tigers, wild elephants, gaurs (Indian bison), chausingha.
- Major Avifauna: Hill myna and crested serpent eagle.
Wildlife Sanctuaries of Odisha
Badrama (Ushakothi) Wildlife Sanctuary
- To the west of the Sanctuary lies Hirakud Dam (Ib river joins Mahanadi River in Hirakud Reservoir), and to the east lies Rengali Reservoir (on Brahmani River).
Baisipalli Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located where the Mahanadi River passes through a gorge in the Eastern Ghats.
Balukhand Konark Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located along the Bay of Bengal coast, between the Puri and Konark.
- It includes sandy beaches, coastal dunes, groves of introduced Casuarina plantations.
- Major Fauna: Blackbuck, spotted deer.
Chandaka Dampara Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is an Elephant Sanctuary located in Khurdha and Cuttack districts. It is bounded on the north by Mahanadi River. The Mahanadi River separates it from Kapilash Wildlife Sanctuary.
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is bound on the north and east by the Hirakud Dam.
Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated to the south of Similipal National Park and west of Kuladiha Wildlife Sanctuary. It lies in the catchment of Salandi River (a tributary of Baitarani River).
Kapilash Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated near Cuttack between Mahanadi and Brahmani Rivers. It is an elephant corridor.
Kothagarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is an ER situated in Eastern Ghats. It is contiguous with Karlapat Wildlife Sanctuary and Satkosia Tiger Reserve.
Lakhari Valley Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is located in Eastern Ghats and Rushikulya River flows through the region.
Nandankanan Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is a zoological park and botanical garden in Bhubaneswar. It is located in the environs of the Chandaka forest and Kanjia lake. It is known for the captive breeding of Asiatic lions, tigers and crocodiles.
Satkosia Gorge Wildlife Sanctuary
- Saktosia Tiger Reserve = Satkosia Gorge Wildlife Sanctuary + Baisipalli Wildlife Sanctuary.
Sunabeda Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is a proposed Tiger Reserve. It forms catchment area of Jonk River. It is contiguous with Udanti-Sitanadi Tiger Reserve of Chhattisgarh.
- Major Fauna: Tiger, swamp deer, wild water buffalo (EN).
Others
- Karlapat Wildlife Sanctuary: Eastern Ghats of Kalahandi district.
- Khalasuni Wildlife Sanctuary: adjacent to Badrama Wildlife Sanctuary in Sambalpur district.
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary: Linked with Simlipal National Park via small hill ranges.
Ramsar Sites of Odisha (6)
Ansupa Lake
- It is a freshwater oxbow lake formed by the Mahanadi River. It is the largest freshwater lake in Odisha.
- Endangered species: Indian Skimmer (EN), Black-Bellied Tern (EN), Wagur (EN), Indian River Tern (VU), Helicopter Catfish (Wallago attu – VU)
Bhitarkanika Mangroves
- It is part of the Bhitarkanika WLS. The core area was declared Bhitarkanika NP. Gahirmatha Marine WLS is adjacent to the Bhitarkanika WLS. It is famous for Olive Ridley Turtle (VU) & Saltwater Crocodile (LC)
Chilika Lake
- In 1981, Chilika Lake was designated the first Indian wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention. Nalbana BS is the core area of Chilika Lake.
- It is located at the mouth of the Daya River. It is a brackish water lagoon separated from the Bay of Bengal by a long sandy ridge. It is the largest coastal lagoon in India.
- Birds from as far as the Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal, Aral Sea and other parts of Asia, Ladakh and Himalayas come here.
- Chilka has the only population of Irrawaddy dolphin (EN – flagship species of the lake) in India.
- It was placed on the Montreux Record in 1993 due to siltation and removed from the Record in 2002 following rehabilitation efforts of the Chilika Development Authority.
Hirakud Reservoir
- Hirakud Reservoir is the largest earthen dam in Odisha. It provides important hydrological services by moderating floods in the Mahanadi delta.
Satkosia Gorge
- It is a gorge over the Mahanadi. It is a mosaic of rivers, marshes & evergreen forests at the meeting point of the Deccan Peninsula & Eastern Ghats biogeographic regions.
- Major Fauna: Red-Crowned Roofed Turtle (CR), Indian Narrowheaded Softshell Turtle (EN), Tiger (EN), Black-Bellied Tern (EN)
Tampara Lake
- The use of explosives during a battle in the Ganjam district between the British East India Company and French colonists in 1766 created this large depression. The lake is now connected to the Rushikulya river and helps in flood control.
Last updated on April 25, 2024 2:22 AM