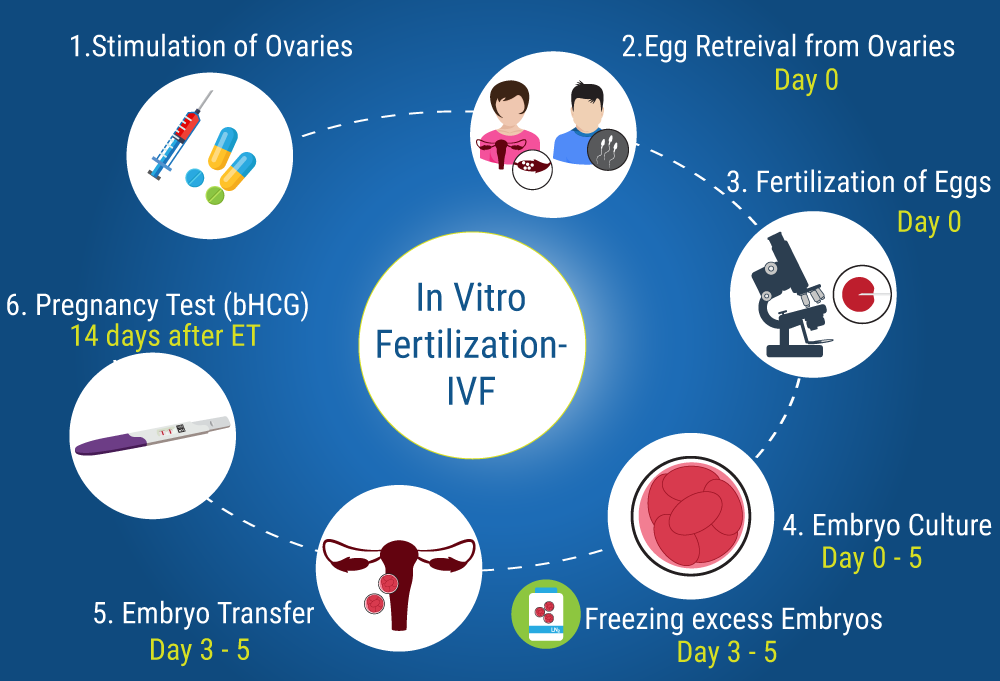
Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) Region
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): Scientists declare Hindu Kush Himalaya a biosphere on the brink of ‘collapse’.
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya region stretches 3,500 kilometres and spans eight countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- It is often referred to as the ‘Third Pole’, on Earth.
- The HKH is the world’s most important ‘water tower’, being the source of ten of Asia’s largest rivers as well as the largest volume of ice and snow outside the Arctic and Antarctica.

Significance

Threats to HKH
- HKHs are warming about three times faster than the global average.
- Glaciers lost ice 65% more quickly between 2010 and 2019 than they did between 2000 and 2009 and could lose up to 80% of their volume by 2100 if GHG emissions aren’t sharply reduced.
Impact of CC on HKH and associated hydrological consequences
- Increased drought-like situations due to an overall decrease in the number of rainy days.
- Increased flood events due to an overall increase in the rainy day intensity.
- Effect on groundwater quality in alluvial aquifers due to increased flood and drought events.
- Influence on groundwater recharge due to changes in precipitation and evaporation.
- Increased saline intrusion of coastal and island aquifers due to rising sea levels.
Steps Taken to Protect HKH Region
- International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): A regional intergovernmental organisation working to make the HKH region greener, more inclusive, and climate-resilient.
- Resilient Mountain Solutions (RMS): Initiative developed by ICIMOD to equip people in the region with simple and affordable technologies and knowledge required to build long-term resilience.
- Hindu Kush Himalayan Monitoring and Assessment Programme coordinated by ICIMOD.
- National Mission on Sustaining Himalayan Ecosystem (NMSHE): One of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
Way Forward
- Promote public–private–civil society partnerships: Incentives to be provided for green initiatives and other innovative financing ventures applying corporate social responsibility principles.
- Strengthen institutions: National and regional institutions to be strengthened to facilitate upstream-downstream knowledge exchange, transboundary cooperation, and capacity building.
- Evidence-based actions to reduce disaster risk, mitigate and adapt to climate change, and adopt good governance, are central to ensuring prosperity in the HKH region.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)