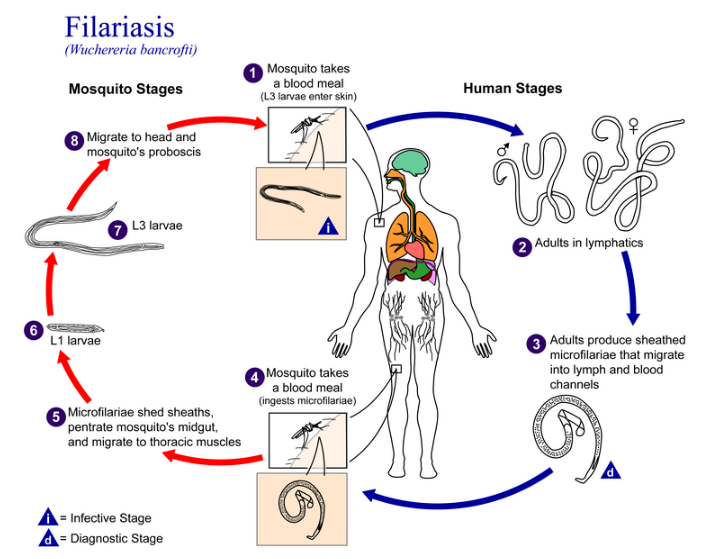
Down Syndrome | Edwards Syndrome
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): Researchers have reported chromosomal disorders in prehistoric skeletal remains dating back up to 5,500 years.
- The research marks the 1st identification of Edwards syndrome from historic or prehistoric remains.
- The findings date back to the Bronze Age (around 2,700 BCE) and the Neolithic period (around 3,500 BCE).
Down syndrome
- Down syndrome is named after the physician Langdon Down, who first observed this condition.
- It is due to the presence of an extra chromosome 21, also known as trisomy of chromosome 21.
- This extra copy changes how a baby’s body and brain develop. It can cause both abnormal mental and physical development during their lifetime.
- Down syndrome is also due to the translocation of a part of a chromosome to another chromosome.
- It is one of the leading causes of genetic disorders around the world. It is mostly not inherited.
- It is a chromosomal disorder caused by abnormal cell division.
- It is due to aneuploidy of the autosome (any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome).
|
- There is no cure; only the quality of life can be improved by taking extra care.

- The occurrence of Down syndrome is 1:800 live births.
- The primary risk factor is the age of the mother. Most trisomy cases occur in mothers aged more than 35.
Edwards syndrome
- It is named after Dr. John H. Edwards, who first described the condition in 1960.
- Also known as Trisomy 18, it is a chromosomal disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 18.

- Edwards syndrome is a rare congenital disorder that affects approximately 1 in every 5,000 live births.
- There is no cure for Edwards syndrome, and treatment focuses on managing the individual symptoms and providing supportive care.
- Symptoms: Low birth weight, small head, intellectual disability and developmental delays, Facial abnormalities, etc.
Types of Trisomy 18
- Full/Complete Trisomy 18: This is the most common form of Edwards syndrome, where every cell in the body contains three copies of chromosome 18.
- Mosaic Trisomy 18: In this form, some cells have the extra chromosome 18, while others have the normal pair.
- Mosaic Trisomy 18 often leads to milder symptoms compared to full Trisomy 18.
- Partial Trisomy 18: This occurs when only a portion of chromosome 18 is duplicated instead of the entire chromosome.
- Partial Trisomy 18 is the least common form and often results from specific genetic abnormalities.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)