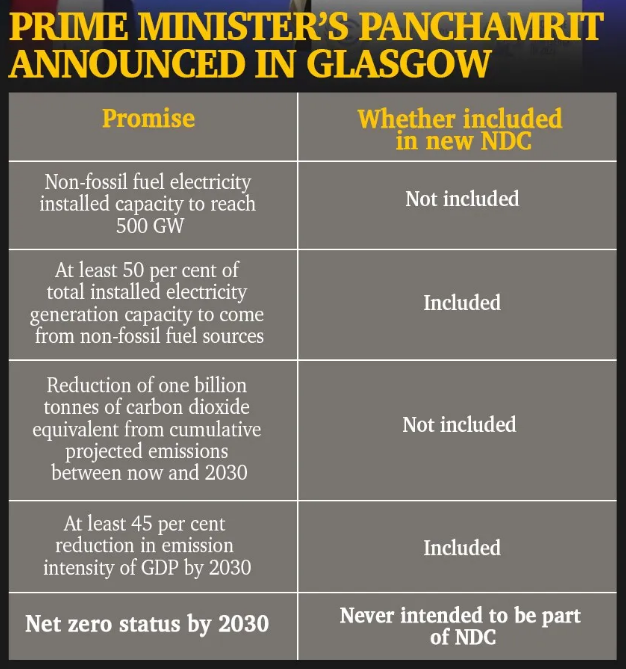
Cybercrime
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): A Chinese boy was ‘cyber kidnapped’ in Utah.
- Cybercrime refers to illegal activities on the internet using computer technology.
- It includes hacking, stealing personal information, spreading viruses, and online fraud.
- It falls under State subjects as per the 7th Schedule of the Constitution of India.
Types of Cybercrimes
- Phishing: Sending deceptive emails or messages to trick individuals into revealing personal information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Identity Theft: Stealing personal information, such as social security numbers or credit card details, to impersonate someone else.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Overloading a website or network with traffic to make it unavailable to users. This disrupts the targeted service, preventing legitimate users from accessing it.
- Cyber Espionage: Illegally accessing confidential information or trade secrets from governments, businesses, or individuals for economic, political, or military advantage.
- Cyberstalking: It involves online harassment of a user using digital communication tools aimed at causing fear, distress, or discomfort.
- Ransomware Attack: A type of malicious software (malware) that encrypts a victim’s files, making them inaccessible, and demands a ransom payment for their release.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Cyber-attacks conducted by highly skilled and organised threat actors, often with specific objectives such as espionage, data theft, or disruption. The attackers maintain a long-term presence within the targeted system while remaining undetected.
- For example, RedEcho (a cyber security firm) revealed that a China-linked APT group had targeted ten entities in India’s power sector.
- Cyber kidnapping: it refers to a crime where the kidnappers convince their victim to hide and then contact their loved ones for ransom. The kidnappers are not physically present but monitor the victim online through video-call platforms.

Challenges in India
- Increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks: Recent data from the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) highlights that in 2022, 13.91 lakh cybersecurity incidents were reported.
- The proliferation of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT): it is estimated that 14.4 billion IoT devices will be in use in India by the end of 2023.
- Weaknesses in IoT device security: Default passwords and lack of regular software updates create vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit.
- Rise of E-governance: Data breaches in government databases containing citizens’ personal information, such as Aadhaar details, have raised concerns about the security of sensitive data.
- Shortage of skilled professionals: India needs around 3 million cybersecurity professionals.
- Limited Cybersecurity Awareness: Individuals receiving phishing emails fall victim to Online/cyber frauds due to lack of awareness.
Steps taken
- National Cyber Security Policy (NCSP): it was introduced in 2013 to provide individuals, companies, and the Government with a secure and dependable cyberspace.
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): The national nodal agency for responding to cybersecurity incidents. It provides vulnerability management and coordination among stakeholders.
- National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC): CERT-In established it to provide real-time situational awareness and enable coordination among various agencies to respond effectively to cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre): Launched by CERT-In, it aims to detect and clean malware infections and botnets in citizens’ computers and systems.
- The Indian Cyber-Crime Coordination Center (I-4C) was established to tackle cybercrimes and develop effective coordination among law enforcement agencies and stakeholders.
- One of the most significant achievements of I4C is the launch of the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) in 2019.
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC): it was established to protect the CII of various sectors.
- Defence Cyber Agency (DCyA): The DCyA is a tri-service command of the Indian Armed Forces responsible for handling cyber security threats.
- Training: India has also created a massive open online courses platform called the ‘CyTrain‘ portal, which, perhaps, will be the world’s largest training program in the field of cyber security.
- Awareness programs: CERT-In, RBI and Digital India jointly carry out a cyber security awareness campaign on ‘beware and be aware of financial frauds’ through the Digital India Platform.
Way forward
- Invest in state-of-the-art cybersecurity technologies, including advanced threat detection systems, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Develop and implement regulatory frameworks for emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)