Lithium Battery
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): With Electric Vehicles (EV) recording a 50% growth in 2023, compared to 2022, the heart of it, i.e. Lithium Battery is a topic of discussion.
- A Lithium-ion or Li-Ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium compounds as one of the electrodes.
- In 1985, Akira Yoshino developed the first prototype.
Lithium battery Cell
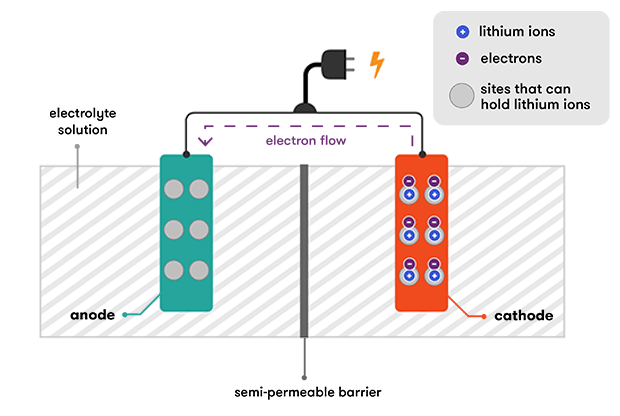
- Each Lithium battery cell has essentially three components.
- A Positive electrode – (Lithium cobalt oxide, or LiCoO2).
- A Negative electrode – (Carbon).
- A Separator – Electrolyte – most commonly used (lithium salt, such as LiPF6) in an organic solution.
- In addition, lithium-ion batteries incorporate other elements that improve their performance and safety: a temperature sensor, a voltage regulator circuit and a state-of-charge monitor.
- When the battery is charged, lithium ions flow from the positive electrode to the negative electrode through the electrolyte and attach to the carbon.
- During discharge, the lithium ions return from the carbon to the LiCoO2.
Why Lithium for EV Batteries?
- High power density.
- Easy maintenance.
- Variety of models available.
- Higher Battery Life.
- Much lighter than other types of rechargeable batteries of the same size.
- High specific energy and high load capabilities with Power Cells.
- High capacity, low internal resistance.
- Simple charge algorithm and reasonably short charge times.
- Low self-discharge. A lithium-ion battery pack loses only about 5 percent of its charge per month.
|
Applications
- Emergency power systems – server farms, the batteries of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply).
- Solar energy storage: Solar energy storage is intermittent, and these batteries are best suited to solar panels because they charge fast.
- Consumer electronics and mobile devices: Allows for ever-increasing miniaturisation.
- Disability assistance: electric wheelchairs, stairlifts or motorised prostheses.
Problems with Lithium-ion Batteries
- Energy density is still lower compared to petrol.
- Requires higher protection circuit to prevent thermal runaway if stressed.
- Performance declines with time.
- At freezing temperatures (zero degrees Celsius), quick charging is not possible.
- Lithium-ion battery packs degrade significantly more quickly when exposed to heat.
- Environmental concerns are primarily related to the mining of lithium.
- The liquid electrolyte used in EV batteries is highly flammable.
Other Types of EV batteries
- Lead Acid Battery: They are heavier and have a low energy density.
- Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Battery: They had a low cycle life. Banned because of their toxicity.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NIMH) Battery: Sufficient for smaller battery applications. It does not require an external source for charging. It is charged only by the regenerative braking mechanism.
- Sodium-ion batteries: Sodium ions are physically larger than lithium, which translates to lower energy density resulting in lower range for EV’s.
- Solid-state batteries (SSB): Lower risk of ignition, can also hold more energy compared to their Li-on counterparts. (Potential viable alternative so far).
- Potential benefits of SSB: reduced weight, improved charging speed, and enhanced safety.
- Hydrogen fuel cells
- They are a clean, reliable, quiet, and efficient source of high-quality electric power.
- It produces electricity, with water and heat as the only by-products.
- Hydrogen is one of the most abundant elements on earth.
- Disadvantages: quite expensive, need to build a network of hydrogen filling stations.
Approaches to improve Lithium batteries
- Retaining basic lithium-ion battery structure with tweaks to electrodes (e.g., Tesla’s use of Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP).
- Deployment of sensing and control infrastructure (Battery Management System) for safety and faster charging.
- Exploration of Solid-State Lithium Battery (SSB) for significant improvements in performance.
India’s EV Battery Ecosystem
- Last year saw 50% growth in EV sales in India.
- EV market expected to reach $100 billion by 2030.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)