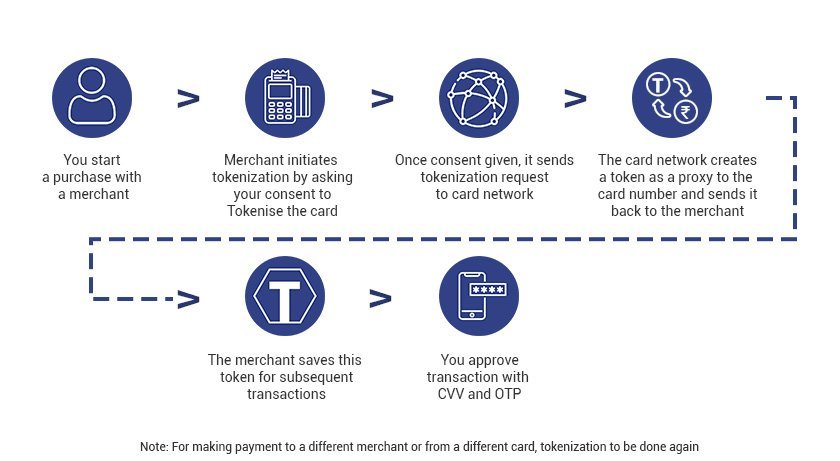
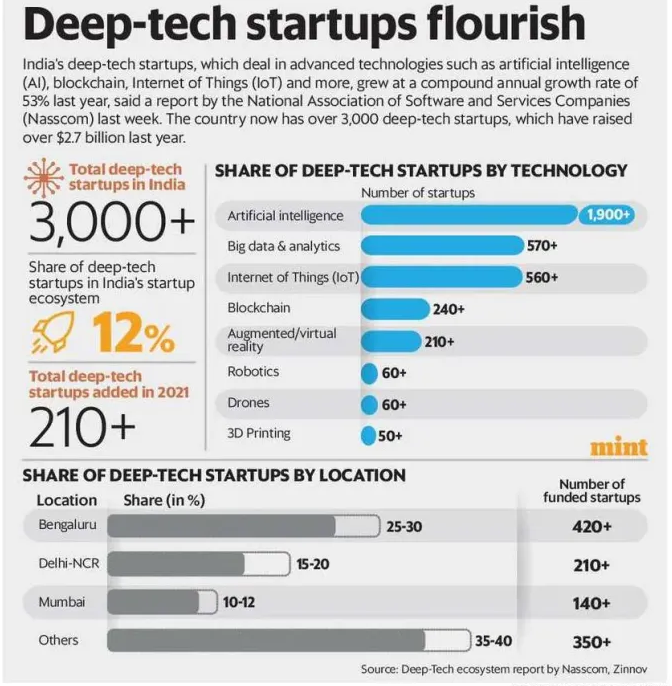
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): India is likely to lower tariffs on a range of goods and services for the first time under the free trade agreements (FTAs) with developed economies.
- India is currently negotiating FTAs with the UK, the European Union (EU), Australia and Oman.
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) are agreements between two or more countries or economic blocs. It is aimed to facilitate trade and eliminate or reduce barriers to the exchange of goods and services.
- Example, The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
Key features of Free Trade Agreements
- Tariff Reduction or Elimination
- Greater market Access
- Trade in Services
- Investment Protection
- Agreements on intellectual property rights
- Rules of origin
- It defines the criteria for determining the country of origin of a product. It helps to prevent third-party goods from taking advantage of the agreement.
- Address non-tariff barriers to trade.
- Such as quotas, licensing requirements, and technical standards
- Provisions for customs cooperation
India & FTA’s
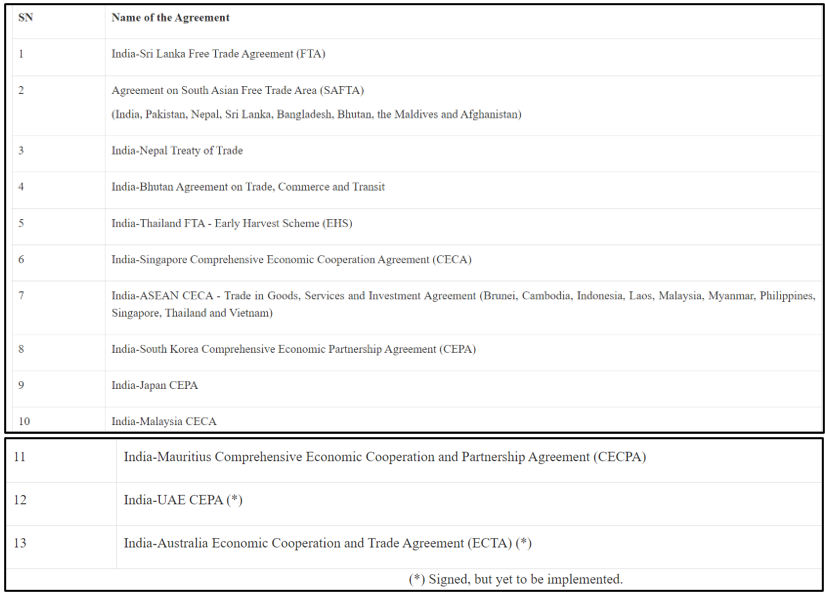 India has signed 13 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with its trading partners.
India has signed 13 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with its trading partners.
Factors Affecting India’s FTA
Tariffs/Customs duties
- High tariffs are among the key concerns raised by trade partners India is negotiating FTA.
- India has the highest import duty compared to most major economies with an average Most Favored Nation. It is twice the global average (WTO).
- The most-favored-nation clause requires WTO members to offer the same trade terms to all trading partners.
|
Other factors affecting India’s Trade
- Technical barriers to trade (TBT)
- Sanitary and Phyto-sanitary (SPS) measures
- Deviation from internationally agreed standards
- Discrimination based on legislative or administrative measures by India.
Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
Various Forms of Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)