Card-on-File Tokenisation
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (TH): The RBI has enabled Card-on-File-Tokenisation at the issuer bank level.
- Tokenisation is a service where a unique alternate code is generated to facilitate transactions through cards. It involves substituting a 16-digit customer card number with a token.
- Tokens are unique for a combination of cards, token requestors, and devices.
- The tokenized data is stored to bill the cardholders’ accounts for future purchases.
- The customer need not pay any charges for availing of this service.
- Tokenisation is not mandatory for a customer, and those who choose not to let their card be tokenized can continue to transact as before by entering card details manually.
- A customer can request for tokenization of his/her card on any number of devices.
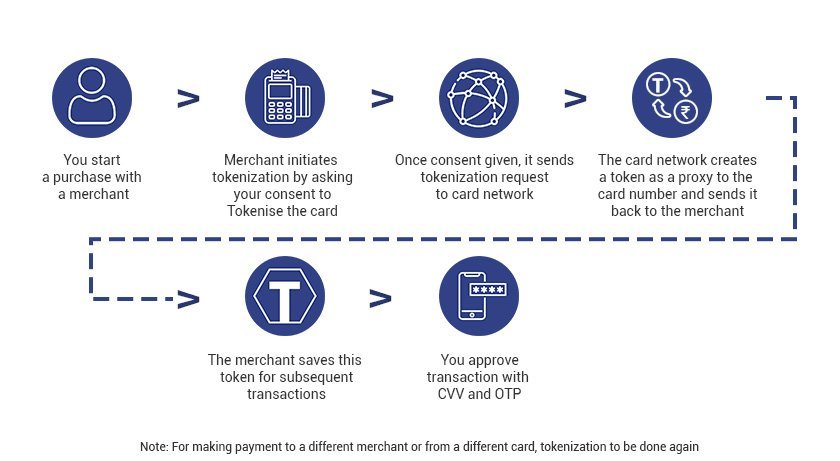 Tokenisation and de-tokenization can be performed by the authorised card network or by the card issuer.
Tokenisation and de-tokenization can be performed by the authorised card network or by the card issuer.
- Benefits of tokenization: Token contains no personal information that can be directly accessed and keeps changing, making it the most secure method to complete payments.
- Applications: Tokens can be used for online transactions, mobile point-of-sale transactions or in-app transactions.
|
RBI Guidelines on Tokenisation
- Online payment aggregators are not allowed to store card number, CVV and expiry date for processing online transactions.
- Single-use provision: Tokens registered on one merchant cannot be used on another merchant.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)