Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – May 04, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – Governance – Issues} World Press Freedom Index *
- Context (TH): Reporters sans Frontieres (RSF) (Reporters Without Borders) has observed that India’s press freedom score has fallen in the World Press Freedom Index.
- It was released on 3 May (World Freedom Day).
- Total countries assessed: 180.
- Best performers: Norway and Denmark
- Worst performer: Eritrea, even worse than Syria.
- The press freedom questionnaire covers five categories — political context, legal framework, economic context, sociocultural context and security.
- The U.S. press freedom score fell from 71.22 to 66.59, and its rank deteriorated from 45 to 55.
India’s Performance
- India’s rank improved from 161 in 2023 to 159 in 2024, but this was because other countries had slipped in their rankings.
- India’s score on the World Press Freedom Index fell over the last year from 36.62 to 31.28.
- Scores for India dropped (worsened) in all categories except the security indicator.
- The government has dismissed international rankings as misinformed and propaganda-driven.
Observations in RSF reports
- India’s media has fallen into an ‘unofficial state of emergency’ since 2014.
- Indian journalists who are very critical of the government are subjected to harassment campaigns.
- It alleges the perceived role of authorities in mass disinformation and propaganda campaigns.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Citizenship} Diplomatic Passports *
Diplomatic passport (‘Type D’ passports)

Credits: Bankbazaar
- Diplomatic passports have maroon covers and are valid for five years or less.
- Entitlements: Certain privileges and immunities as per international law, including immunity from arrest, detention, and certain legal proceedings in the host country.
- Issuing authority: Consular, Passport & Visa Division of Ministry of External Affairs.
- Eligible categories: Diplomatic status holders; government-appointed individuals travelling abroad for official business; branches A and B of Indian Foreign Service (IFS) officials (normally at the rank of Joint Secretary and above); and relatives and immediate family of officers employed in IFS and MEA.
- Lastly, diplomatic passports are also issued to “select individuals who are authorised to undertake official travel on behalf of the government”. This includes union ministers and MPs who often travel abroad to represent the government with validity concurrent with their term.
- Typically, MEA issues visa notes to government officials going abroad for an official assignment or visit.
Operational visa exemption agreements
- Germany is among the 34 countries with whom India has operational visa exemption agreements for holders of diplomatic passports.
- India has similar agreements with countries such as France, Austria, Afghanistan, Czech Republic, Italy, Greece, Iran, and Switzerland.
- India has agreements with 99 other countries, wherein diplomatic passport holders, service & official passports can avail of operational visa exemption for stays up to 90 days.
- According to the Rajya Sabha Secretariat, “Members, when using a diplomatic passport, are required to apply for prior political clearance directly to MEA at least three weeks in advance.”
Revocation of diplomatic passport
- It is done as per the Passport Act 1967. It can be done in case of:
- Wrongful possession,
- Or if it is obtained by the suppression of material information;
- Or if deemed necessary in the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India,
- Or friendly relations of India with any foreign country.
- It can also be revoked if the holder is convicted by a court in India and sentenced to imprisonment for not less than two years after the passport is issued.
- Finally, it can be revoked upon orders from a court during proceedings of criminal cases.
To know more, visit > Passports: Evolution and Features.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Judiciary} 33% Seats for Women in Bar Association Committee
- Context (IE I TOI): The SC reserved one-third of the seats in the executive committee of the SC Bar Association (SCBA) for women.
SC Directions
- A minimum of 3 out of 9 positions in the Executive Committee and 2 of 6 Senior Executive Member posts will be reserved for women.
- At least one post of the office bearer shall be reserved exclusively for women candidates, by turn and on a rotation basis.
- In the ensuing election for 2024-2025, the post of Treasurer of the Executive Committee is reserved for women.
- The reservation is only to guarantee a minimum, and women members of the SCBA, subject to their eligibility, shall be entitled to contest the election for all the posts in the Executive Committee.
|
Bar Council of India
- The Bar Council of India is a statutory body created by Parliament under the Advocates Act, 1961 to regulate and represent the Indian Bar.
- It performs the regulatory function by prescribing standards of professional conduct and etiquette and by exercising disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar.
- It also sets standards for legal education and grants recognition to Universities whose degree in law will serve as qualification for enrolment as an advocate.
- It also protects the rights and interests of advocates and establishes funds to support welfare schemes for them.
- Each state’s State Bar Council is affiliated with the Bar Council of India.
{GS2 – Social Sector – Health – Diseases} Surge in dengue cases
Extant of dengue upsurge
- Some countries are witnessing a surge in dengue; others are recording severe outbreaks for the first time.
- Brazil is the worst affected country in the region, with 1.8% of the population affected.
- Several of Brazil’s states have declared a state of emergency.
- Peru & Puerto Rico have also declared states of emergency in response to a spike in dengue fever cases.
- Central American countries and Mexico, which usually see a rise in dengue cases towards the end of the year, are already witnessing a spread.
Reasons for upsurge
Global warming and dengue
- According to the State of the Climate in Latin America and the Caribbean 2022 report, the region has warmed an average of 0.2 degrees Celsius per decade in the past 30 years.
- Soaring global temperatures have created ideal conditions for mosquitoes.
- This leads to frequent and intense extreme weather events and an increase in the mosquitoes.
- Higher temperatures have also extended the length of the breeding season for mosquitoes.
- The situation was exacerbated by the onset of the 2023 El Niño.
- Untimely rainfall, storms, flooding, and rising sea levels create shallow, stagnant pools of water in which the bugs thrive. On the other hand, droughts lead people to collect and save water in containers that provide breeding places for mosquitoes.
- Rapid urbanisation in Latin America is leading to an abundance of standing water, where the insects lay their eggs.
Absence of a high-efficacy dengue vaccine
- Although scientists have created vaccines that protect against the four strains, they are either expensive or have serious limitations.
- Qdenga — a Japanese-made vaccine — costs about $115 per dose in Europe and $40 in Indonesia.
- Dengvaxia vaccine, which can be given only to people who have already had a dengue infection.
To know more, visit > Dengue.
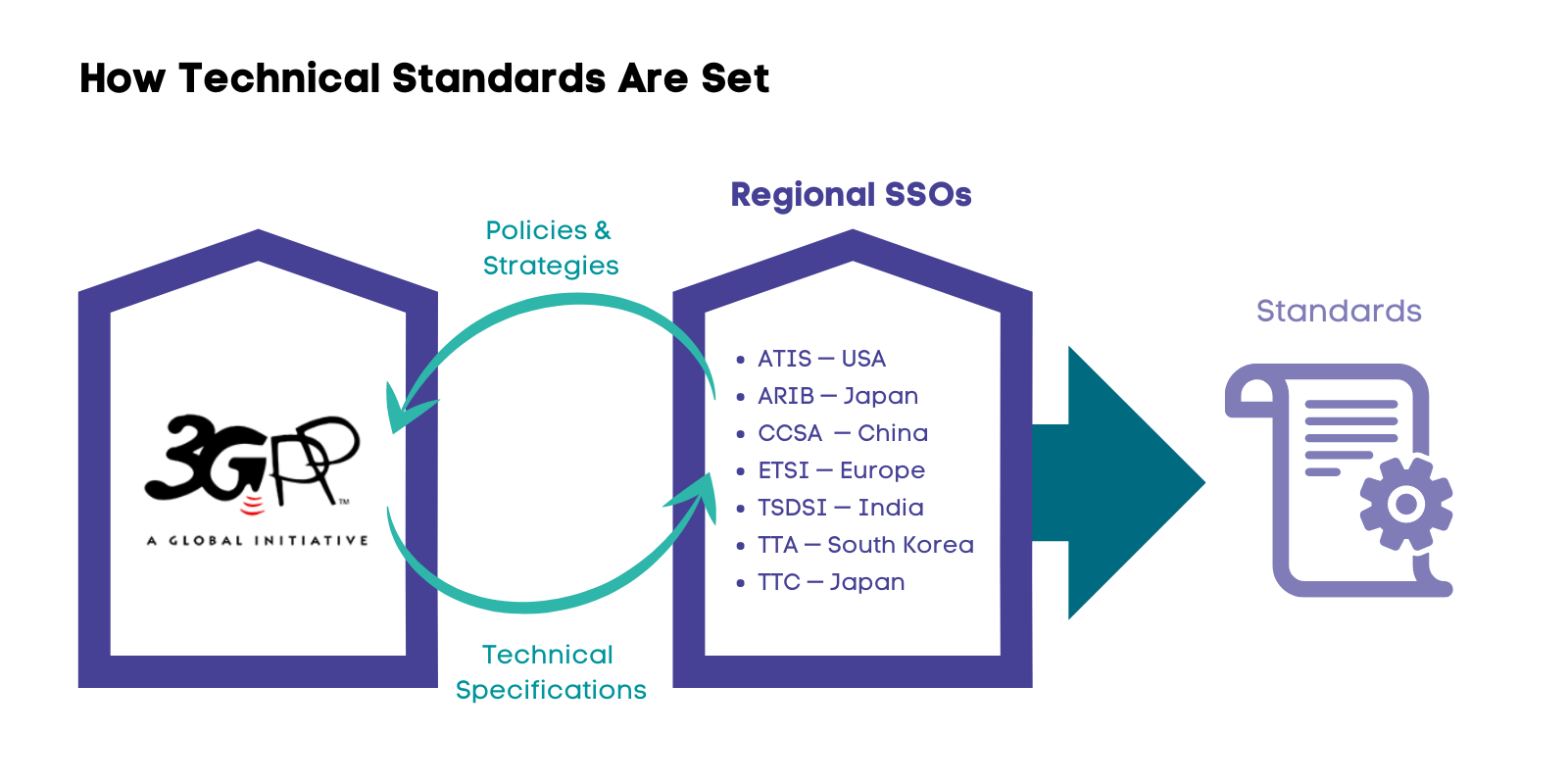
{GS3 – S&T – IPR} Standard Essential Patents
- Context (TH): The Telecom manufacturing sector in India is facing significant obstacles due to certain technology companies asserting their ‘standard essential patents‘ (SEPs).
- Until now, the judiciary has been responsible for regulating SEPs, but as an institution, it has largely failed to address these issues effectively.
About SEPs
- These are patents that cover technologies that are adopted by the industry as “standards”.
- In the telecom industry, CDMA and GSM are SEPs, alongside LTE, all serving as industry standards.
- Such technological standards are essential to ensure the interoperability of different brands of cellular phones manufactured by different companies.
- For instance, once GSM became a standard, manufacturers had to ensure handset compatibility; failure to do so would lead to diminished demand for their phones.
What is standard in a SEP?
- The meaning of standard in this context is a “technical standard” or, more specifically, an “industry standard”.
- They are standards in technology requirements that need to be met to provide so that a product or process functions in a specific manner.
Essentiality of a Particular Standard
- A patent earns this title when it becomes impossible to produce a product that meets the industry standards set by standard-setting organisations (SSOs) without stepping on the toes of that patent.
Credits: https://www.inquartik.com/blog/basic-standard-essential-patents-the-basics/
SEP and Royalty Issues
- The process of setting standards in the technology sector is largely privatised and dominated by SSOs, mainly run by private technology companies.
- The companies that own the SEPs gain enormously because every manufacturer of cellular phones has to license the technological standards in question in order to survive in the market.
- The lack of alternatives also means that owners of SEPs can demand extortionary royalties or licensing terms from manufacturers that block competition. This is called the “patent holdup” problem.
- In the same manner, any SSO may avoid adopting a standard if the SEP owner is reluctant to license the patent in advance, as the SSO’s level of adoption is a determining factor of the SEP value.
- In theory, the SSOs are supposed to prevent such a scenario by requiring the owners of SEPs to license their technologies at a fair, reasonable and non-discriminatory (FRAND) rate.
FRAND OR (F)RAND OR F/RAND
- FRAND is the acronym for fair, reasonable and non-discriminatory.
- These terms are required by SSOs to ensure fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory licensing of patents by SSO members to other members and sometimes non-members.
- The FRAND terms ensure a balance between the standard’s use by all industry manufacturers and the fair benefits reaped by the SEP owner.
Frand in India
- The position of the F/RAND litigation in India is relatively new as compared to the European Union and the United States.
- At present, the Competition Commission of India (which has just begun deciding cases on topics like calculating FRAND loyalty) and the Courts are overrunning each other.
Opposite Stands of CCI and Judiciary on Frand Issues
- CCI prefers using the minor patent-practising component to calculate FRAND royalty, while the Delhi High Court uses the downstream product as the basis.
|
Judicial lethargy and Judicial Activism
Lack of Investigation into Abusive Licensing Practices
- Due to judicial lethargy and delays, the GOI has not yet investigated potentially abusive licensing practices of technology companies owning SEPs.
Protracted Litigation
- Litigation surrounding competition law issues has been mired in delays and remained pending for an extended period, resulting in a lack of resolution.
- For instance, a case involving Ericsson challenging the Competition Commission of India’s power lasted for seven years before a judgment was delivered.
Impact on Manufacturers and Unprecedented Interim Orders
- The prolonged litigation and uncertainty have adversely affected manufacturers, particularly Indian companies.
- During the pendency of trials, The Delhi HC has issued unprecedented “deposit” orders, Manufacturers have been required to deposit substantial sums of money with the court.
- This has strained their financial resources and affected their ability to operate effectively.
- These orders lack legal basis and are unfair to defendants, depriving them of working capital for the duration of the trial.
Impact on the Investment and Manufacturing Sector
- Judicial lethargy and activism have negative implications for the GOI’s efforts to attract investment in the manufacturing sector.
- Delays and uncertainties in legal proceedings deter potential investors and undermine the effectiveness of government initiatives like the “production-linked incentives” scheme.
Questioning the Policies of Government
- The situation raises questions about the rationale behind GOI’s policies that incentivise manufacturing while overlooking issues related to abusive licensing practices by SEP owners.
- This inconsistency may hinder efforts to promote economic growth and job creation in the country.
{Prelims – In News} India’s First Newspaper
- Context (IE): The Bengal Gazette became the first newspaper ever published in India in 1780.
- Ireland-born James Augustus Hicky served as its founder-editor. He became renowned as “Jewel in the Crown of the British Empire”.
- He started printing from jail, where he was sentenced due to his inability to pay his debt.
- Seeing the success and demand for printing, he started the Bengal Gazette.
- It published opinions, general events and local issues, suggesting Britishers invest more in infrastructure and sanitation.
- It initially avoided political news to save itself from any trouble.
- Though many nullify its role, Hicky’s paper shed light on government corruption and civic issues and, at times, criticised the British East India Company.
- Hickey criticised Hastings’ expansion policy in the subcontinent during the 1780s, describing Hastings as being Robert Clive’s “miserable successor”.
- He even called Warren Hastings “Wild, Pusillanimous, disgraceful, and wicked” and “Despotic.”
- He was alleged to have even called troops to mutiny.
- It was sued for libel around two years into its publication, leading to its closure.
- He played a great role in advancing the growth of journalism in India. Many of Hicky’s associates went on to launch their own newspapers.
{Prelims – In News} Sea Lions
- Context (BBC): A record number of sea lions gather in San Francisco.
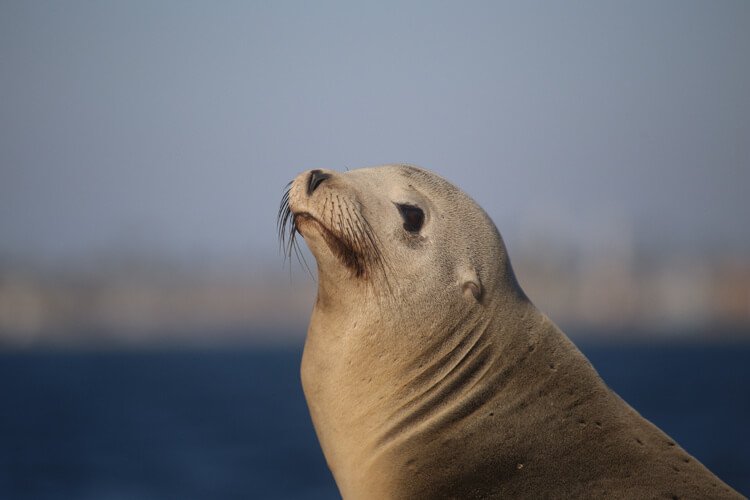

- Family: Otariidae. They live both on land and sea. Diet: Carnivorous.
- Physical properties: Streamlined body with brown or tan coat, large head, and long, flexible neck.
- Sea lion got its name because most males have manes. They roar to defend the females in their groups.
- They have external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly.
- Habitat: Western coast and islands of North America, from southeast Alaska to central Mexico, on rocky shorelines, islands, and sandy beaches.
- The average life is 20-30 years. They can be as heavy as 1200 pounds.
- There are five species of sea lion: California, northern, southern, Australian, and New Zealand.







![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)