Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – March 06, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – MIH – Events} Ramakrishna Math and Ramakrishna Mission
- Context (PIB): Recently the Prime Minister, went to a hospital in Kolkata to enquire about health of the President of Ramakrishna Math and Ramakrishna Mission.
Ramakrishna Math and Ramakrishna Mission
- The Ramakrishna Movement is a Hindu spiritual movement inspired by the teachings of Sri Ramakrishna (1836–1886), a mystic saint from Bengal, India.
- The Ramakrishna Math and Ramakrishna Mission are twin organizations of the Ramakrishna Movement or the Vedanta Movement.
- The Headquarters of both Ramakrishna Math and Mission is situated in Belur Math on the bank of river Ganga in West Bengal.
- Ramakrishna Math is an Order of sannyasins.
- Ramakrishna Mission is a registered society engaged in the service of mankind, founded by Swami Vivekananda (1863-1902).
- The organisation mainly propagates the Hindu philosophy of Vedanta (Advaita Vedanta) and four yogic ideals – Jnana, Bhakti, Karma, and Raja yoga.
{GS2 – Governance – Laws} Maratha Quota Law
- Context (TH I IE I IE): Maharashtra recently passed the Maharashtra State Reservation for Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Bill 2024.
- It sets aside 10% reservation for the Maratha community in jobs and education under socially and educationally backward categories.
- This is the third time in the last decade that the State has introduced legislation for a Maratha quota.
- The Bill was drafted based on a report by the Maharashtra State Backward Class Commission.
- This report identified the Marathas as socially and educationally backward, justifying the need for reservation.
Provisions of the Bill
- It ensures that the principle of creamy layer is applicable, thereby targeting the most marginalised within the community.
- The Bill does not disturb the existing OBC quota and is distinct from the earlier notification on the issuance of Kunbi caste certificates to eligible Marathas for inclusion within the OBC category.
- Non-Kunbi Marathas will continue to be covered under the new law, making the Maratha community eligible for reservations under two separate categories for the first time.
- Maharashtra currently has a reservation of 62%, including various categories such as SC, ST, OBC, Vimukt Jati, Nomadic Tribes, EWS and others.
- With the addition of 10% reservation for the Marathas, the total reservation in the state will now reach 72%.

History of Maratha Reservation
- Narayan Rane Committee: In 2014, a Narayan Rane-led committee recommended a 16% reservation for Marathas ahead of elections.
- 2014: The Maharashtra government announced a 16% reservation for Marathas under a new category called the Educationally and Socially Backward Class (ESBC).
- Bombay High Court’s Ruling: The Bombay HC, while acknowledging the need for Maratha reservations, stated that the 16% quota was not justifiable and suggested that a quota of 12% in education and 13% in jobs would be more appropriate.
- Gaikwad Commission: In 2018, the Gaikwad Commission’s findings recommended granting 16% reservation.
- 2018 Maharashtra Law: The Maharashtra Legislature passed a bill proposing 16% reservation for Marathas under the Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBC) Act, 2018.
- Supreme Court Intervention: Implementing the quota faced challenges and was subject to scrutiny in the courts. Petitioners argued against the reservation, claiming it violated the SC’s 50% cap on reservations established in the Indra Sawhney case (1992).
- The Maharashtra government, defending the quota, cited the community’s backwardness as justification.
- 2021 Supreme Court Verdict: The SC struck down the Maharashtra law granting reservations to the Maratha community in admissions and government jobs, stating
- It exceeded the 50% cap on reservations.
- The reservation law did not meet the criteria to break this limit.
- The Maratha community was not a socially and educationally backward class to the extent that it warranted surpassing the cap.
- Marathas are a “dominant forward class and are in the mainstream of national life.”
- The President (that is, the GoI) alone was empowered to identify SEBCs and include them in the Central List for claiming reservation benefits.
- States could only suggest to the President or the relevant statutory commissions that the list be included, excluded, or modified.
- Maharashtra State Backward Class Commission:
- The Commission was established in December 2023 to reassess the Maratha reservation issue.
- The Commission cites extreme poverty, agricultural income decline, and land-holding partitions as reasons for the Maratha community’s plight.
- It highlights that 94% of farmer suicides in the state are from the Maratha community.
- The Commission notes inadequate representation in public services, attributing it to the community’s backwardness.
- It notes that the population of Marathas in the state is 28%, while 84 % of them are not advanced.
- Such a large backward community cannot be added to the OBC bracket.
- It recommends separate reservations to increase Maratha’s representation in government jobs and developed sectors.
- The Commission highlighted “exceptional circumstances and extraordinary situations”, justifying reservations to the Maratha community above the 50% ceiling set by the SC.
Marathas
|
Arguments in Favour of the Reservation
Socio-Economic Backwardness:
- The empirical data underscores the socio-economic challenges faced by the community, justifying the need for a reservation to uplift them from poverty and marginalisation.
- The high percentage of farmer suicides highlights the economic distress and the urgent need for targeted interventions to uplift the community.
Representation
- Marathas have historically been excluded from mainstream opportunities due to their backwardness.
- Reservation in government jobs and education can enhance their representation and participation in various sectors.
Arguments Against Maratha Reservation
Legal Viability
- Given the history of previous Maratha reservation attempts facing legal challenges and eventual setbacks in higher courts, doubts persist about the new Bill’s ability to withstand judicial scrutiny.
- SC’s previous ruling struck down Maratha reservations due to insufficient empirical data justifying quota extension beyond the 50% ceiling.
The Kunbi Certificate Controversy
- A draft notification proposing recognition of “sage soyare” (extended relatives of Marathas with Kunbi lineage) as Kunbi, eligible for OBC reservation, stirred controversy.
- Opposition parties have raised questions about the viability of the new reservation and its potential impact on existing OBC reservations.
Dissent within the Maratha Community
- Some activists and leaders within the Maratha community expressed dissatisfaction with the separate reservation, preferring inclusion within the OBC category.
Need for a Comprehensive Approach
- While reservation may address immediate concerns, it may not effectively address the root causes of Maratha’s backwardness.
- A holistic approach addressing issues like education, skill development, and infrastructure is essential for sustainable development.
{GS2 – Social Sector – Education} Holistic Progress Card
- Context (IE I TH): The National Council for Educational and Research Training (NCERT) has introduced a new Holistic Progress Card (HPC).
- HPC includes feedback from parents, peers and self-assessment by students to monitor their holistic development regularly.
- It will measure, apart from academic performance, a child’s progress in interpersonal relationships, self-reflection, creativity, and emotional application in classrooms.
- Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development (PARAKH), a standard-setting body under the NCERT, has devised the Holistic Progress Card (HPC).

Objective
- The HPC, aligning with National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE) guidelines, aims for a learner-centred evaluation.
- Traditionally, schools focused on year-end exams, with teachers solely responsible for assessment
- Under the HPC model, the students will be regularly assessed through class activities where they are not just passive learners but active agents.
Key features of the Holistic Progress Card (HPC)
Classes involved
- The HPC is created for the
- Foundational stage (Classes 1 and 2),
- Preparatory stage (Classes 3 to 5), and
- Middle stage (Classes 6 to 8).
- Efforts are currently underway to develop a similar framework for the secondary stage.
Parameters of evaluation
- At every stage, besides academics, students are evaluated on self-awareness, relationships, problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and creativity.
- After each activity, students reflect on their progress by circling statements like “I learned something new,” “I expressed creativity,” or “I helped others.”
- The activities will prompt students to apply diverse skills and competencies that will demonstrate whether they have been able to grasp concepts.
- The difficulty level they experience while performing a task will also be assessed.
Method of evaluation
Self-assessment
- Self-assessment is included in the HPC for all students from Class 1 to Class 8.
- In middle school (Classes 6 to 8), students are prompted to set academic and personal goals with specific timelines at the start of the year.
- The middle stage HPC also involves an “ambition card” where students list their goals for the year and areas for improvement, as well as the skills and habits needed to achieve them.
- “Student’s self-reflection” is part of the HPC for all students from Class 1 to Class 8.
Parental involvement
- The HPC will connect home and school by involving parents in their child’s learning.
- Parents will provide feedback on homework completion, classroom engagement, and the child’s ability to balance screen time with extracurricular activities at home.
Peer evaluation
- The new assessment method also values peer evaluation.
- After each classroom activity, students must indicate whether their classmates effectively participated in learning and engagement.
Teacher’s Role
- Teachers will register the strengths of a student, such as their ability to “collaborate”, “follow instructions”, “show “creativity” or “empathy”, etc.
- Weaknesses like “lack of attention”, “peer pressure”, and “lack of preparation” will help teachers identify areas where students need help.
Digitisation
- The NCERT has plans to digitise the records of schoolchildren on a dedicated platform.
- States are advised to establish a central digital repository of data called the Vidya Samiksha Kendra to track student enrolment and progress in their learning levels, among other details.
- The states, as directed by the NCERT, will have to upload the student HPC online.
Secondary Stage HPC
- NCERT is currently preparing the HPC with inputs from SCERTs and the state and central boards.
- The secondary stage HPC will be exceptional as it will include Board exams as well.
- After consultation with the Boards and SCERT, the secondary stage HPC will be out.
Why was the progress card changed?
- According to the NEP 2020, the HPC is a means to build on the self-awareness and self-esteem of students by communicating their strengths and areas of improvement.
- Instead of testing rote memorisation skills, the HPC focuses on evaluating higher-order skills, such as analysis, critical thinking, and conceptual clarity of students.
- Based on NEP’s recommendation, the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF-SE) was rolled out in 2023.
- The assessment of a student’s progress should be analysed through a systematic collection of evidence.
- NCF-SE also suggests peer and self-assessment to help students monitor their learning.
- Classroom assessment through activities like projects, debates, presentations, experiments, investigations, role plays, etc., for a deeper understanding of a student’s “core competencies”.
Implementation of NCERT Directive
- NCERT wrote to the states and UTs to start implementation of the HPC in schools.
- The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) released its own “implementation manual” for the HPC model of assessment for the foundational stage up to Class 2.
- The Board adopted the HPC with specific tweaks that categorise students aged 3 to 6 into a ‘beginner’, ‘progressing’, or ‘proficient’ category.
- Unlike the NCERT HPC, which is pretty detailed, the CBSE model encourages teachers to mark a student’s level of attainment using neutral icons such as flowers, trees, smileys, etc.
- Progress reports are prepared mainly by teachers in consultation with parents and student inputs.
Significance of HPC
- The HPC goes beyond numerical grades, focusing on descriptive and analytical evaluations.
- It encompasses academic achievements as well as the development of critical skills in a child.
- It promotes a shift from summative to formative assessment, fostering competency-based evaluation and holistic growth.
- It seeks to provide teachers and parents with insights to support each student in learning.
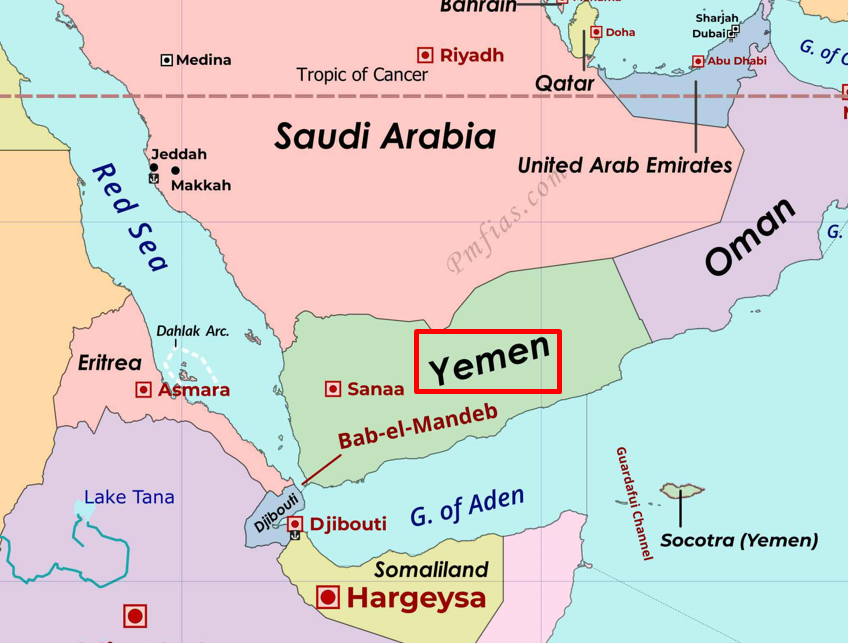
{GS3 – Envi – Degrdation} Sinking of Rubymar in Red Sea
- Context (DTE): The US military has issued a warning about environmental risks in the Red Sea after the Rubymar, a UK-owned bulk carrier, sank on March 2.
- The vessel was carrying around 21,000 metric tons of ammonium phosphate sulfate fertilizer.
- The attacks were carried out in support of Palestinians in Gaza who were under attack by Israel in retaliation for the October 7, 2023, attacks by Hamas (the group controlling the Gaza Strip).
Rich Biodiversity in the Red Sea

- UNESCO Natural Heritage Sites in Red Sea: Socotra Archipelago, Dungonab Bay and Senganeeb Atoll.
- Other distinctive features of the region: Farsan and Dahlak Archipelagos (southern Red Sea) and the flourishing coral reefs (northern and central parts of the Red Sea).
- 14.7% of the Red Sea fishes are of endemic species.
- 90% of the Red Sea dotty backs and triple fins and 50% of the Red Sea butterfly fishes are endemic species.
- Potential climate refuge for coral reefs because of the relatively higher resilience of its corals compared to other parts of the world.
- In addition, the region also supports extensive seagrass beds and mangroves.
- The biological productivity in the Gulf of Aden is amongst the highest in the world.
{GS3 – S&T – AI} AI & Carbon Emissions
- Context (TH): Training GPT-3, produced 502 metric tonnes of carbon. This is like driving 112 petrol cars for a year. GPT-3 also releases 8.4 tonnes of carbon dioxide each year during inference.
- AI emissions arise from the infrastructure, like data centres, needed to support these systems.
- Since the early 2010s, the energy needs of large language models, like ChatGPT, have surged by 300,000 times.
- As they become more common and complex, they are likely to keep increasing energy demands. This trend could make AI a major source of CO₂ emissions.
- However, two technologies, spiking neural networks and lifelong learning, show potential to reduce carbon footprints.
How are SNNs different from ANNs?
- The key difference is how neurons transmit information. ANNs use continuous activity, while SNNs use intermittent spikes.
- Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are a more energy-efficient option than Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs).
ANNs
- The lifetime of an AI involves two stages: training and inference.
- Training: A dataset is used to build and improve the system.
- Inference: The trained system makes predictions on new data.
- Example: Training uses a dataset to improve the system, like teaching a self-driving car with diverse driving scenarios. After training, the AI predicts effective manoeuvres for the car using ANNs.
- ANNs have many elements called parameters, over 100 billion in total, adjusted during training.
- Large parameter numbers enhance AI capabilities but make training and inference resource intensive.
- Further, ANNs process data using decimal numbers, demanding precision and significant computing power. As ANNs grow and become more complex, they become more energy intensive.
SNNs
- It is inspired by the working of Neurons in the human brain.
- In the human brain, neurons use intermittent electrical signals called spikes to communicate.
- These spikes don’t contain information; their timing is what matters.
- Spikes have a binary nature, often represented as 0 or 1, showing that neurons are active when spiking and inactive otherwise.
- Similarly, SNNs use spikes only when processing information, making them up to 280 times more energy efficient than ANNs.
Lifelong learning
- L2 is another method to save energy in ANNs over time.
- When ANNs learn new tasks one after another, they often forget what they learned before, needing fresh training.
- Whereas L2, a group of algorithms, lets AI models learn various tasks without forgetting old knowledge. This cuts down on frequent retraining and lowers energy use.
Large language models (LLMs)
|
{GS3 – S&T – Space} MethaneSAT
- Context (IE): Global Methane Emission Monitoring Satellite MethaneSAT was Successfully launched by SpaceX Falcon9 rocket from California.
- Though it is not the first spacecraft to identify and quantify methane emissions, it will provide more details and have a much wider field of view than any of its predecessors.
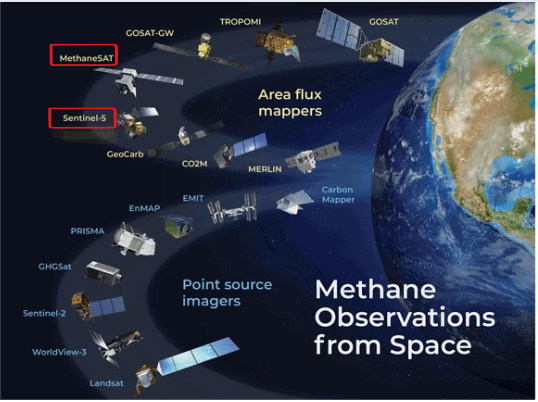
Need to track and measure methane emissions
- Methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, is the second-largest contributor to global warming, following carbon dioxide.
- It is responsible for 30% of global heating since the Industrial Revolution.
- Methane is 80 times more potent in warming than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period (UNEP).
- The gas also helps create ground-level ozone, a colourless and irritating gas.
- Exposure to ground-level ozone might cause one million premature deaths annually.
- Fossil fuel operations account for about 40 per cent of all human-caused methane emissions.
What is MethaneSAT?
- It is a satellite project led by the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), a US nonprofit organisation.
- EDF collaborated with Harvard University, the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, and the New Zealand Space Agency for its development.
- The satellite will orbit the Earth 15 times daily, focusing on monitoring the oil and gas sector.
- Aim: To collect data revealing methane emissions’ sources, intensity, and changes over time.
- Google (Mission partner): The data collected by MethaneSAT will undergo analysis using cloud computing and AI technology provided by Google.
- The findings will be shared with the public through Google’s Earth Engine platform.This will allow stakeholders and regulators to take action to reduce methane emissions.
Significance of MethaneSAT
-
Limitations in earlier satellites
- Some provided high-resolution data but only for specific sites, while others covered larger areas but missed smaller sources, which contributed to most emissions.
- An IEA report suggests global methane emissions are 70% higher than reported by governments due to these limitations. MethaneSAT is expected to fix the issue.
- Advantages in MethaneSAT
- It can detect changes in methane concentrations as low as three parts per billion.
- This capability enables it to identify smaller emission sources compared to previous satellites.
- Additionally, MethaneSAT has a wide-camera view of about 200 km by 200 km, allowing it to spot larger emitters known as super emitters.
Steps taken to reduce Methane Pollution
- Over 150 countries signed the Global Methane Pledge in 2021. The pledge aims to cut collective methane emissions by at least 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- At the latest COP, more than 50 companies committed to virtually eliminating methane emissions and routine flaring.
|
{Prelims – In News} Gevra Coal Mine
- Context (PIB): Coal India subsidiary South Eastern Coalfield Limited’s Gevra mine, received environmental clearance to increase its production capacity (52.5 million tons to 70 million tons per year), making it the largest coal mine in Asia.
About Gevra mine
- It is located in Korba, Chhattisgarh.
- It is an open cast mine spread over an area of 27 square kilometer.
- It is the largest coal mine in India and fourth largest in the world.
Open Cast Mining
|
{Prelims – In News} Google Play Billing System
- The apps belonged to major Indian digital companies like Matrimony, Info Edge, Shaadi.com, and Kuku FM. Google took this action due to non-compliance with its app billing policy.
Background
- Google announced the mandatory integration of its Play billing system globally in October 2020.
- Under the Google Play Billing System, developers must pay a service fee of 15-30% per transaction.
- In India, developers requested relief from Google’s policies, prompting the CCI to instruct Google to allow alternative payment options.
- Other payment processors like Paytm, UPI, and Razorpay charge only 1-5% commission for the same service.
- Additionally, these transactions have better features, such as faster settlement periods.
- In response, Google introduced a user-choice billing system that allows alternatives but includes a commission on in-app purchases.
- The user-choice billing system, too, attracts a commission of 11-26%.
- Way forward: India needs an App Store/Play Store that is a part of digital public infrastructure, like UPI and ONDC.
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)