
Classification of Mountains on the basis of Location, Origin
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Rs. 393
in stock
3 new from Rs. 393
1 used from Rs. 290
as of April 26, 2024 8:52 AM
Amazon.in
Last updated on April 26, 2024 8:52 AM
Classification of mountains on the basis of location
- Continental mountains
- Oceanic mountains
Continental mountains
- Coastal mountains
- Inland mountains
Coastal mountains
- the Rockies,
- the Appalachians,
- the Alpine mountain chains,
- the Western Ghats and
- the Eastern Ghats (India);
Inland mountains
- the Vosges and the Black Forest (Europe),
- the Kunlun, Tienshan, Altai mountains of Asia,
- the Urals of Russia, the Aravallis,
- the Himalayas, the Satpura, and the Maikal of India.
Oceanic mountains
- Oceanic mountains are found on continental shelves and ocean floors.
- If the height of the mountains is considered from the ocean floor, Mauna Kea (9140 m), would be the highest mountain. It is a dormant volcanic mountain in the Hawaii hotspot volcanic chain.
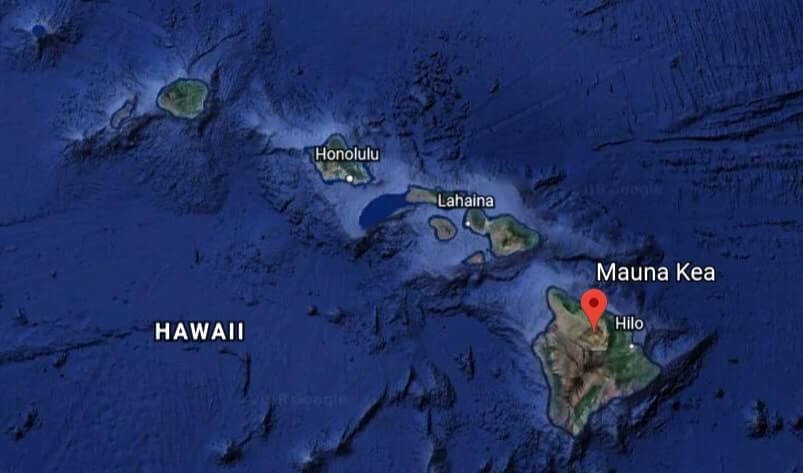
Mauna Kea, a dormant volcano in the island of Hawaii
Classification of mountains on the basis of the period of origin
- A total of nine orogenic or mountain building movements have taken place so far.
- Some of them occurred in Pre-Cambrian times between 600-3,500 million years ago.
- The three more recent orogenies are the Caledonian, Hercynian and Alpine.
Precambrian mountains
- They belong to the Pre-Cambrian period, a period that extended for more than 4 billion years.
- The rocks have been subjected to upheaval, denudation and metamorphosis.
- So, the remnants appear as residual mountains.
- Some of the examples are Laurentian mountains, Algoman mountains etc.
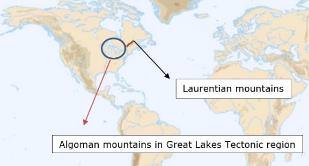
Caledonian mountains
- They originated due to the great mountain-building movements and associated tectonic movements of the late Silurian and early Devonian periods (approximately 430 million years and 380 million years ago).
- Examples are the Appalachians, Aravallis, Mahadeo etc.
Hercynian mountains
- These mountains originated during the upper Carboniferous to Permian Period in Europe (approximately 340 million years and 225 million years ago).
- Some examples are the mountains of Vosges and the Black Forest, Altai, Tien Shan mountains of Asia, Ural Mountains etc.
Alpine mountain system
- Has its origin in the Tertiary Period (65 million years to 7 million years ago).
Examples are
- the Rockies of North America, the Alpine mountains of Europe,
- the Atlas Mountains of north-western Africa,
- the Himalayas of the Indian subcontinent
- the mountains radiating from Pamir knot like Pontic, Taurus, Elburz, Zagros and Kunlun etc.
- Being the most recently formed, these ranges, such as the Alps, Himalayas, Andes and Rockies are the loftiest with rugged terrain.
Classification of mountains on the basis of mode of origin
- Original or Tectonic mountains
- Circum-erosional or Relict or Residual mountains
Original or Tectonic mountains
- Original or Tectonic mountains are the product of tectonic forces.
- The tectonic mountains may be categorized into
- fold mountains (the Himalayas, the Rockies, the Andes),
- block mountains (Vosges mountains in France, the Black Forest in Germany, Vindhya and Satpura in India) and
- volcanic mountains (Cascade Range in the USA, Mount Kenya, Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Fujiyama).
Volcanic mountains
- Volcanic mountains are formed due to volcanic activity.
- Mount Aconcagua, Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Mauna Kea and Mount Fujiyama are examples of such mountains.
- These are, in fact, volcanoes which are built up from material ejected from fissures in the earth’s crust.
- The materials include molten lava, volcanic bombs, cinders, ashes, dust and liquid mud.
- They fall around the vent in successive layers, building up a characteristic volcanic cone.
- Volcanic mountains are often called mountains of accumulation.
- They are common in the Circum-Pacific belt.

Circum-erosional or Relict or Residual mountains
- Circum-erosional or Relict or Residual mountains (Aravallis in India, Urals in Russia) are the remnants of old fold mountains derived as a result of denudation (strip of covering).
- Residual mountains may also evolve from plateaus which have been dissected by rivers into hills and valleys.
- Examples of dissected plateaux, where the down-cutting streams have eroded the uplands into mountains of denudation, are the Highlands of Scotland, Scandinavia and the Deccan Plateau.
Rs. 393
in stock
3 new from Rs. 393
1 used from Rs. 290
as of April 26, 2024 8:52 AM
Amazon.in
Last updated on April 26, 2024 8:52 AM













thank you for such great posts.. It has become easy to understand geography. Now I have started studying geography through your posts only.