Russian Presidential Elections
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE I IESS): Russian President Vladimir Putin, 71, won the recent Presidential elections by securing 87.97 per cent of the votes.
- With a six-year term set to follow, he will become Russia’s or Soviet’s longest-serving leader since Joseph Stalin in more than 200 years.
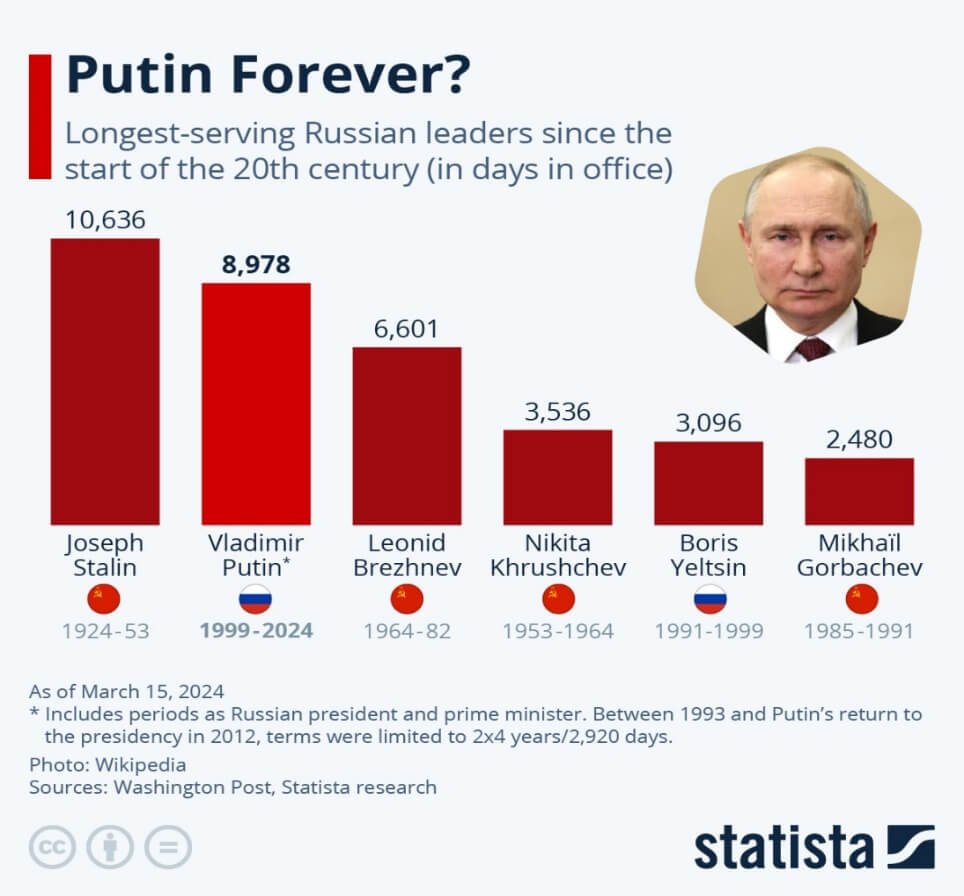
- Prior to the 2020 referendum, the Russian Constitution barred more than two consecutive presidential terms.
- According to the referendum, the current President of Russia can stay in power for two more six-year terms (until 2036) after his term expires in 2024.
- Putin has held continuous positions as president or prime minister since 1999:
- Prime minister from 1999 to 2000 and from 2008 to 2012,
- President from 2000 to 2008 and from 2012 till now.
Presidential Eligibility
- Term Limits: The 2020 amendments established a strict limit of two presidential terms in total but also specified that terms served before the amendment would not count towards this limit.
- This adjustment effectively allows for the possibility of President Putin serving until 2036 if he continues to be re-elected.
- Age Requirement: Candidates must be at least 35 years old.
- Residency Requirement: Candidates are required to have been residents of Russia for at least 25 years.
- Citizenship and Residence Permit: Candidates cannot hold foreign citizenship or a residence permit in a foreign country at the time of the election or at any time before.
- After the 2020 amendments, the limit was increased from 10 years to 25 years, and a clause related to not having foreign citizenship or a foreign residence permit was introduced.
Election
- The presidential election is mainly regulated by the Presidential Election Law (PEL) and the Basic Guarantees of Electoral Rights (BGL).
- The Federation Council calls the presidential elections.
- If it does not call a presidential election that is due, the Central Election Commission will call it.
- Election Day is the second Sunday of the month, and the presidential electoral constituency is the territory of the Russian Federation as a whole.
- The president is elected by direct popular vote in a two-round majoritarian contest:
- If no candidate receives over 50% of the vote in the first round, the two candidates with the most votes advance to a run-off.
- The second (run-off) round is held exactly three weeks after the first. The second round shall appoint with the written consent of the candidate to participate in the second round.
Nomination of candidates
- Candidates can be nominated by a political party or run as independents.
- Each faction in the State Duma, the lower house of the Russian parliament, has the right to nominate a candidate for the presidential elections.
- A political party can only nominate one candidate. Also, the same candidate can only be nominated by one political party.
- Political parties may not nominate candidates at the congress but may decide to support a candidate nominated by another party or an independent candidate.
Vacancy or disability
- Vacancies in the office of president may arise under several possible circumstances: death, resignation and removal from office.
- In all cases when the president is unable to perform their duties, their powers are temporarily transferred to the prime minister until the new president takes office.
Powers and duties
Guarantor of the Constitution
- The President is the guarantor of the Constitution and the entire system of constitutional law.
- He ensures that the constitutions, laws and regulations of the constituent territories are in full compliance with the country’s constitution and federal laws.
Nominations
- The President nominates candidates for official state positions, who must ultimately be appointed based on parliamentary vote.
- The President submits nominations to the Federation Council, for appointment as the judges of the Constitutional Court, the SC, the Supreme Arbitration Court, and the prosecutor general of Russia.
- The President submits nominations to the State Duma, for appointment as the chairperson of the Central Bank.
Legislation
- Under the procedure stipulated by the Constitution, the president exercises their right to submit draft legislation, as well as the right to sign bills into law or to veto them.
- The president has the right to suspend laws and regulations issued by executive bodies of Russia’s constituent territories if such rules and regulations contravene-
- The Constitution, federal laws or international obligations of the Russian Federation, or
- Violate human and civil rights and liberties.
Why do Russian elections Matter?
- The Russian elections are often described by Western governments as being undemocratic, with Putin’s regime accused of repressing opposition voices.
- Since Putin first became Prime Minister in 1999, several of his opponents have been barred from contesting polls.




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)