
Plate Tectonics vs. Continental Drift and See Floor Spreading
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
Last updated on April 19, 2024 7:28 PM
Plate Tectonics
- It was from the continental drift theory, convection current theory and the theory of seafloor spreading, the theory of Plate Tectonics was formulated.
- In 1967, McKenzie and Parker suggested the theory of plate tectonics. Morgan later outlined the theory in 1968.
- According to the theory of plate tectonics, the earth’s lithosphere is broken into distinct plates which are floating on a ductile layer called asthenosphere (upper part of the mantle).
- Plates move horizontally over the asthenosphere as rigid units.
- The lithosphere includes the crust and top mantle with its thickness range varying between 5-100 km in oceanic parts and about 200 km in the continental areas.
- The oceanic plates contain mainly the Simatic crust and are relatively thinner, while the continental plates contain Sialic material and are relatively thicker.
- Lithospheric plates (tectonic plates) vary from minor plates to major plates, continental plates (Arabian plate) to oceanic plates (Pacific plate), sometimes a combination of both continental and oceanic plates (Indo-Australian plate).
- The movement of these crustal plates (due to convection currents in the mantle) causes the formation of various landforms and is the principal cause of all earth movements.
Force for plate movement
- Convection currents in the mantle that are generated due to thermal gradients.
Rates of Plate Movement
- The Arctic Ridge has the slowest rate (less than 2.5 cm/year), and the East Pacific Rise in the South Pacific (about 3,400 km west of Chile), has the fastest rate (more than 15 cm/year).
Major tectonic plates
- Antarctica and the surrounding oceanic plate
- North American plate
- South American plate
- Pacific plate
- India-Australia-New Zealand plate
- Africa with the eastern Atlantic floor plate
- Eurasia and the adjacent oceanic plate
Minor tectonic plates
- Cocos plate: Between Central America and Pacific plate
- Nazca plate: Between South America and Pacific plate
- Arabian plate: Mostly the Saudi Arabian landmass
- Philippine plate: Between the Asiatic and Pacific plate
- Caroline plate: Between the Philippine and Indian plate (North of New Guinea)
- Fuji plate: North-east of Australia
- Turkish plate
- Aegean plate (Mediterranean region)
- Caribbean plate
- Juan de Fuca plate (between Pacific and North American plates)
- Iranian plate.
- There are many more minor plates other than the ones mentioned above.
- Most of these minor plates were formed due to stress created by converging major plates.
- Example: the Mediterranean Sea is divided into numerous minor plates due to the compressive force exerted by Eurasian and African plates.
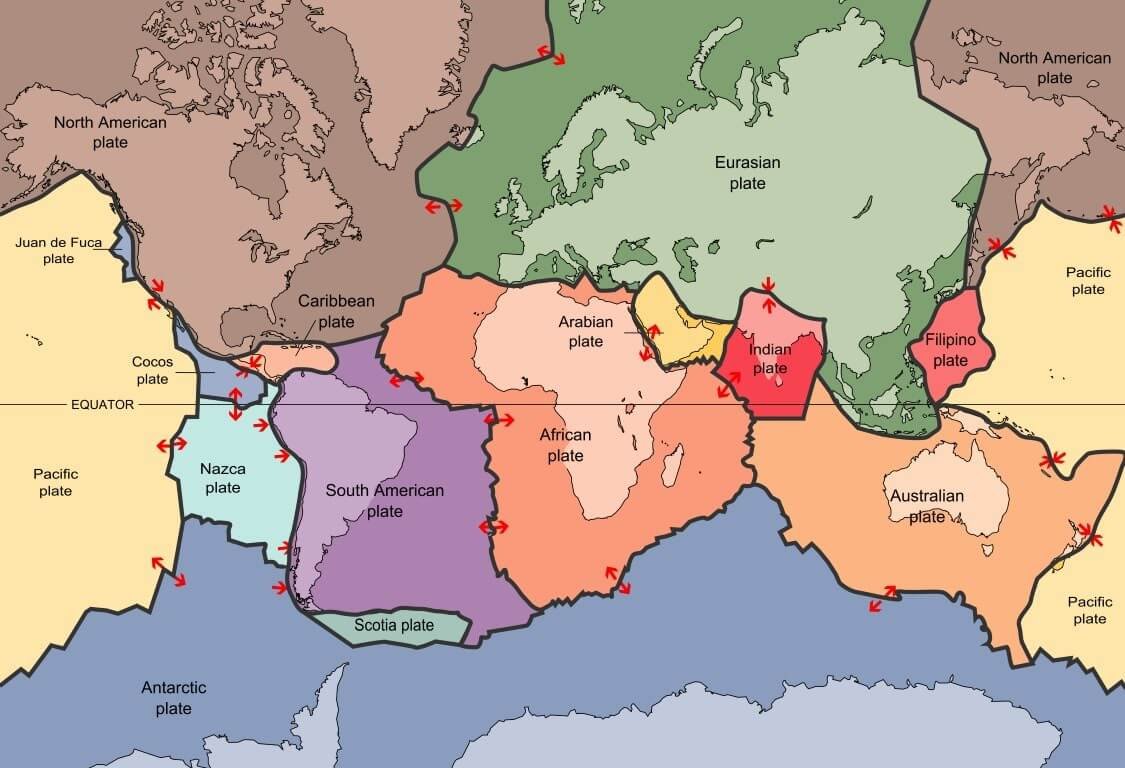
Plate Boundaries
The figure below shows the changes in landform with time due to the interaction of various plates.
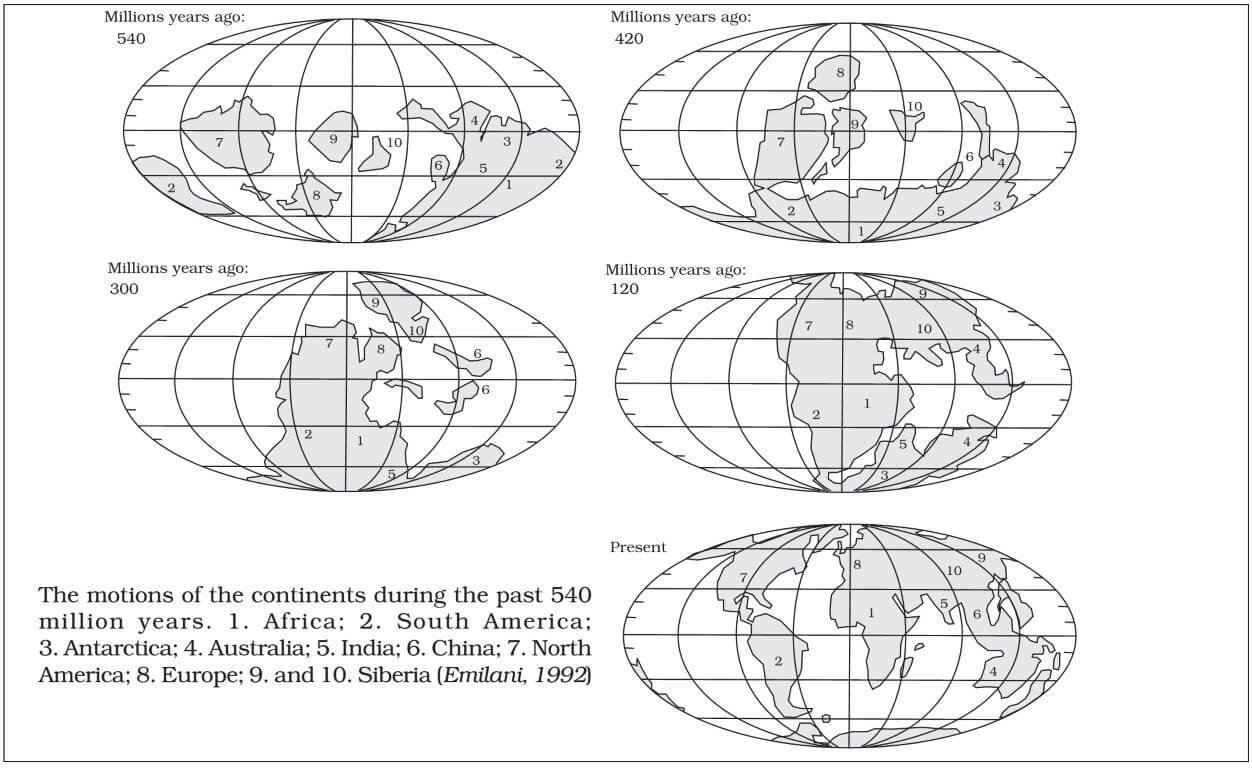
The position of the continents through geologic past
Watch the video for quick and better understanding
Evidence in Support of Plate Tectonics
- Evidence for both See Floor Spreading and Plate tectonics are complimentary (almost same evidences).
Paleomagnetism
- Paleomagnetic rocks are the most important evidence. The orientation of iron grains on older rocks shows an orientation which points to the existence of the South Pole, once upon a time, somewhere between present-day Africa and Antarctica (polar wandering).
Older rocks form the continents while younger rocks are present on the ocean floor
- On continents, rocks of up to 3.5 billion years old can be found while the oldest rock found on the ocean floor is not more than 75 million years old (western part of Pacific floor).
- As we move, towards ridges, still younger rocks appear. This points to an effective spread of seafloor (See floor spreading is almost similar to plate tectonics except that it examines the interaction between oceanic plates only) along oceanic ridges which are also the plate margins.
Gravitational anomalies
- In trenches, where subduction has taken place (convergent edge), the value of gravitational constant ‘g’ is less. This indicates a loss of material.
- For instance, gravity measurements around the Indonesian islands have indicated that large gravity anomalies are associated with the oceanic trench bordering Indonesia.
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
- The fact that all plate boundary regions are areas of earthquake and volcanic disturbances goes to prove the theory of plate tectonics.
The significance of Plate Tectonics
- Almost all major landforms formed are due to plate tectonics.
- New minerals are thrown up from the core with the magmatic eruptions.
- Economically valuable minerals like copper and uranium are found near the plate boundaries.
- From present knowledge of crustal plate movement, the shape of landmasses in future can be predicted.
- For instance, if the present trends continue, North and South America will separate. A piece of land will separate from the east coast of Africa. Australia will move closer to Asia.
Comparison: Continental Drift – See Floor Spreading – Plate Tectonics
Continental Drift |
See Floor Spreading |
Plate Tectonics |
|
|
Explained by |
Put forward by Alfred Wegener in 1920s | Arthur Holmes explained Convectional Current Theory in the 1930s.
Based on convection current theory, Harry Hess explained See Floor Spreading in the 1940s |
In 1967, McKenzie and Parker suggested the theory of plate tectonics. Morgan later outlined the theory in 1968 |
|
Theory |
Explains the Movement of Continents only | Explains the Movement of Oceanic Plates only | Explains the Movement of Lithospheric plates that include both continents and oceans. |
|
Forces for movement |
Buoyancy, gravity, pole-fleeing force, tidal currents, tides, | Convection currents in the mantle drag crustal plates | Convection currents in the mantle drag crustal plates |
|
Evidence |
Apparent affinity of physical features, botanical evidence, fossil evidence, Tillite deposits, placer deposits, rocks of same age across different continents etc. | Ocean bottom relief, Paleomagnetic rocks, distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes etc. | Ocean bottom relief, Paleomagnetic rocks, distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes, gravitational anomalies at trenches, etc. |
|
Drawbacks |
Too general with silly and sometimes illogical evidence. | Doesn’t explain the movement of continental plates |
——————— |
|
Acceptance |
Discarded | Not complete | Most widely accepted |
|
Usefulness |
Helped in the evolution of convection current theory and seafloor spreading theory | Helped in the evolution of plate tectonics theory | Helped us understand various geographical features. |
Last updated on April 19, 2024 7:28 PM













GREAT WORK SIR……THANKS
Nice sir … thankyou
Nice lecture and can be important for theirs lucrative future and will be beneficial for us the achieving the lucrative goal
amazing. god bless u sir.
It’s really helpful… thanks
Thank you so much, sir! The post was really helpful, especially the difference part.