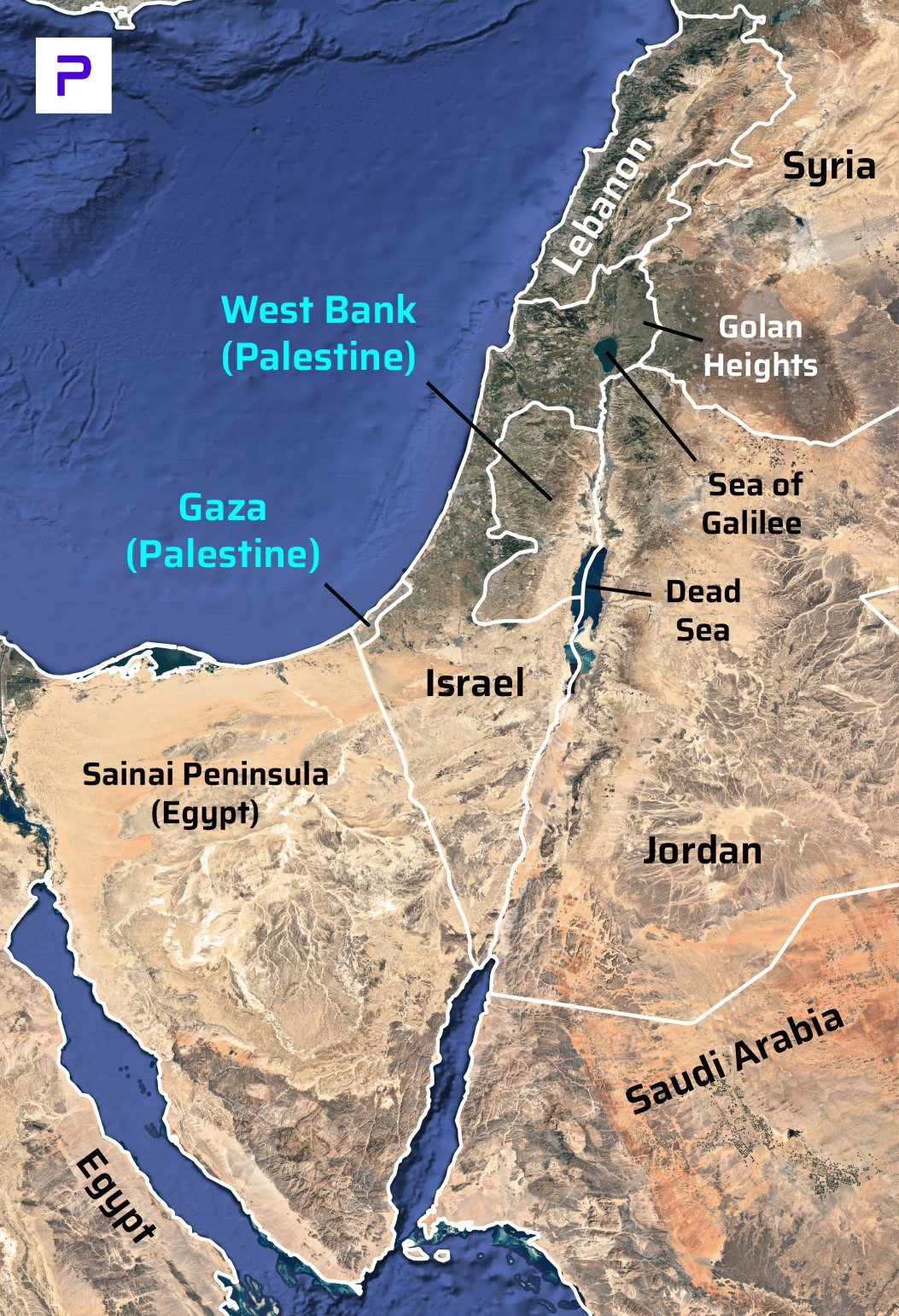
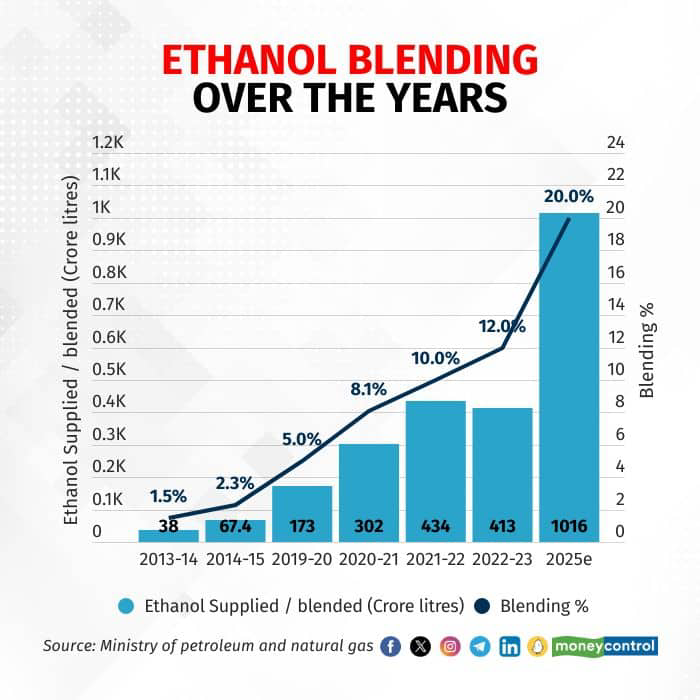
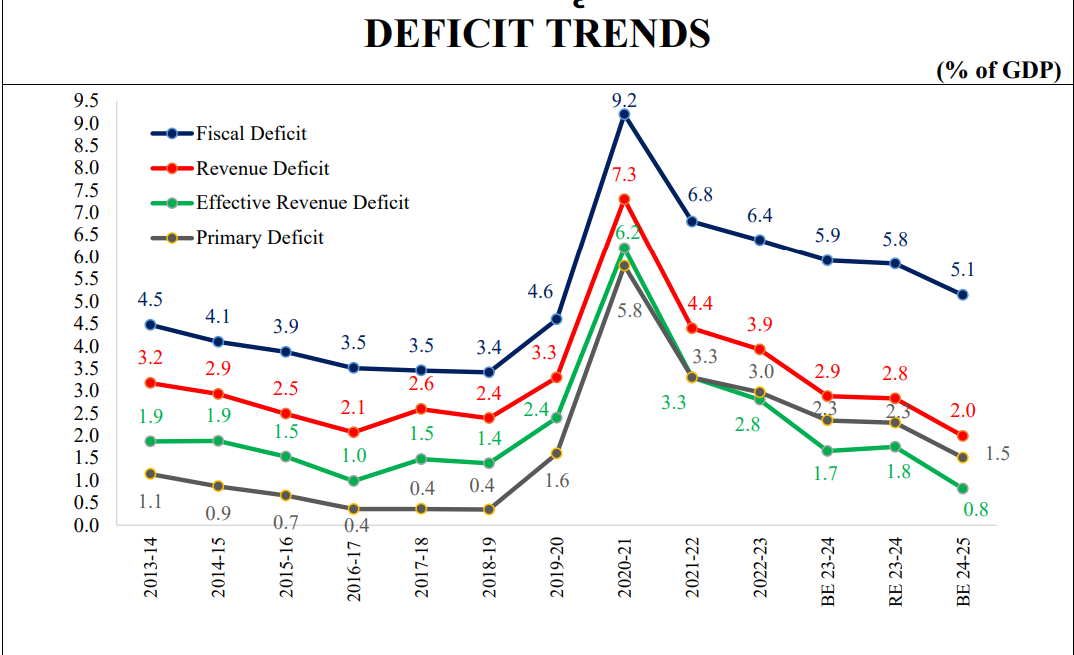
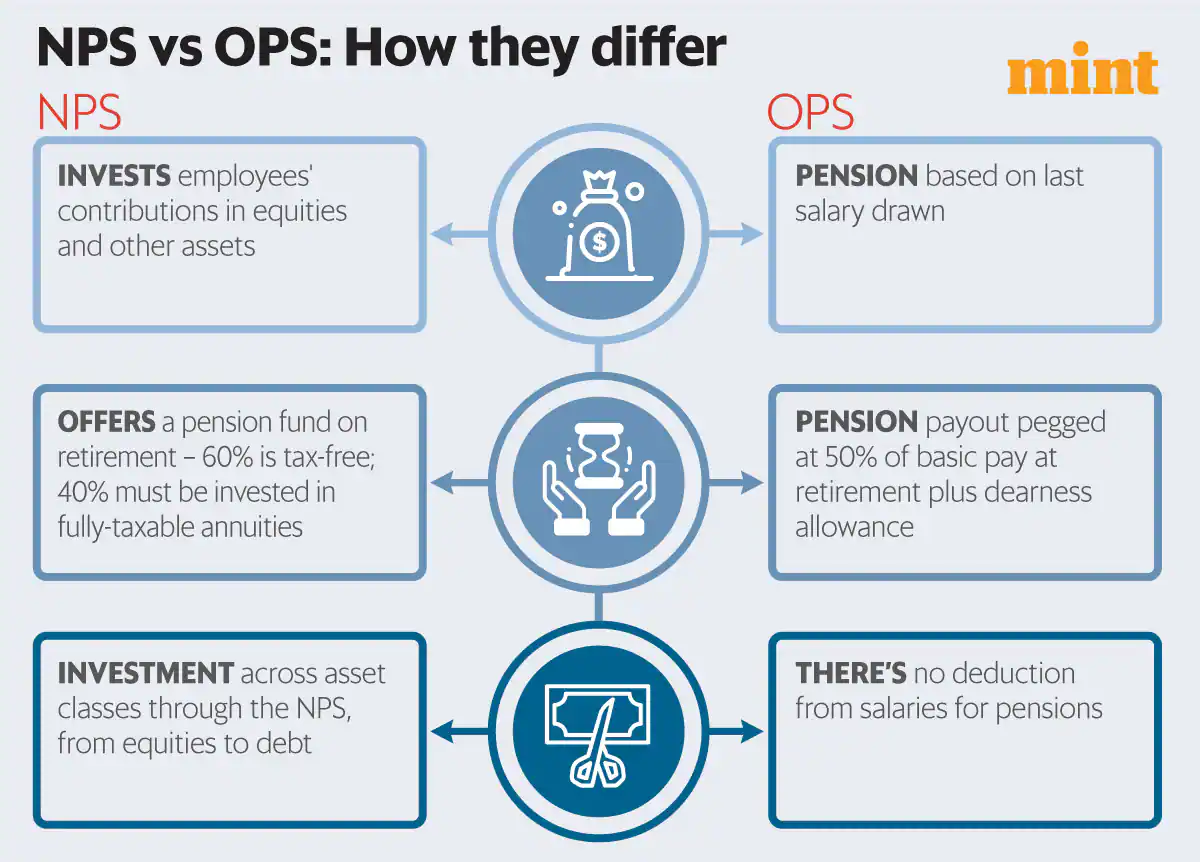
Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
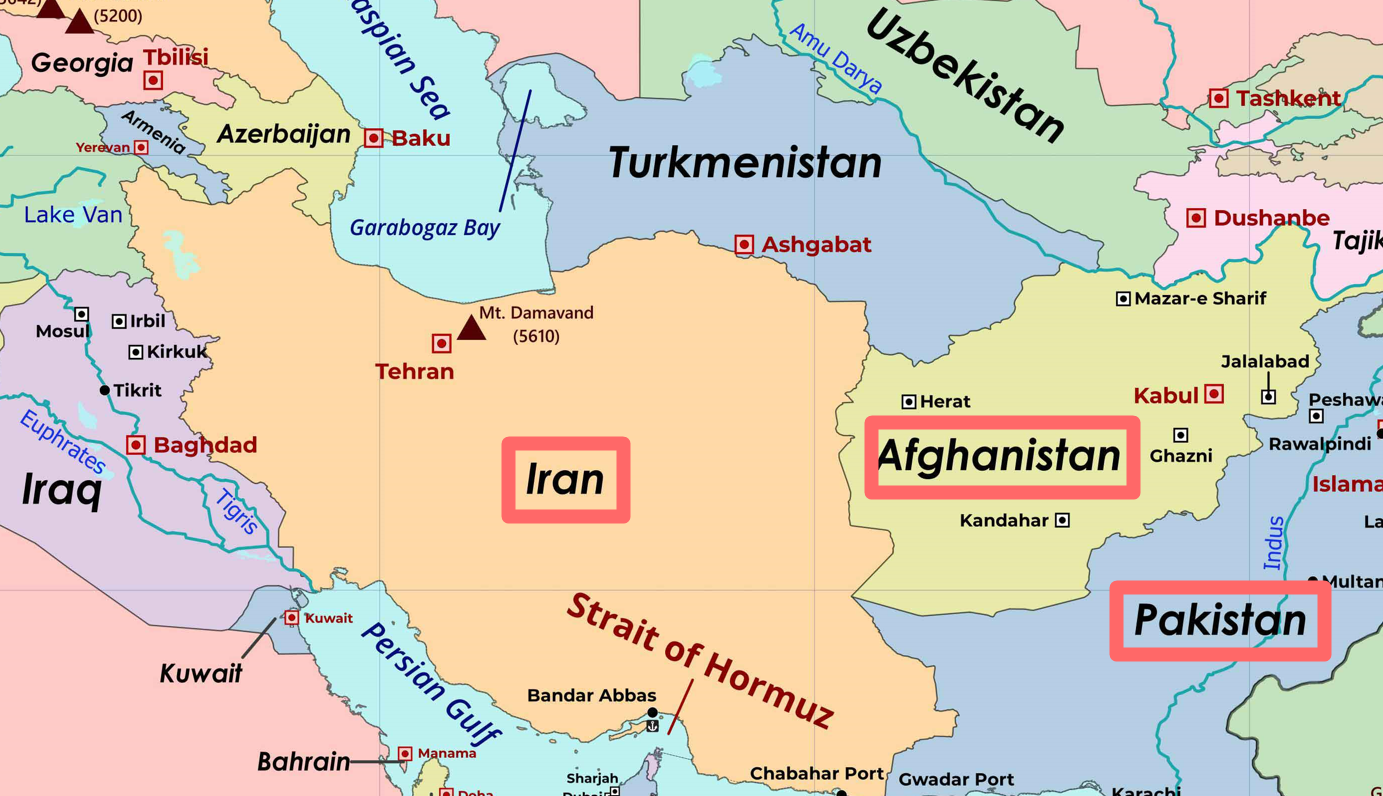
- OPEC is a permanent, intergovernmental organization established at the Baghdad Conference in 1960.
- Founding members: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Member countries: Algeria, Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Venezuela. Gabon rejoined OPEC in 2016.
- Secretariat: Vienna, Austria.
- Objective: To secure fair and stable prices for petroleum producers; an efficient, economic, and regular supply of petroleum to consuming nations; and a fair return on capital to those investing in the industry.
- It operates on the principle of unanimity, and one member, one vote.
- Significance: 80% of the world’s proven crude oil reserves are located in OPEC Member Countries.
- India sources about 70% of crude oil, 60% of its Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), and 30% of its liquefied natural gas (LNG), and 45% of petroleum products demand from OPEC.
- OPEC Publication: World Oil Outlook
OPEC+
|




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)