Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI)
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE | PIB | TH): India has successfully hosted the annual Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Summit for 2023 at the Bharat Mandapam in New Delhi.
|
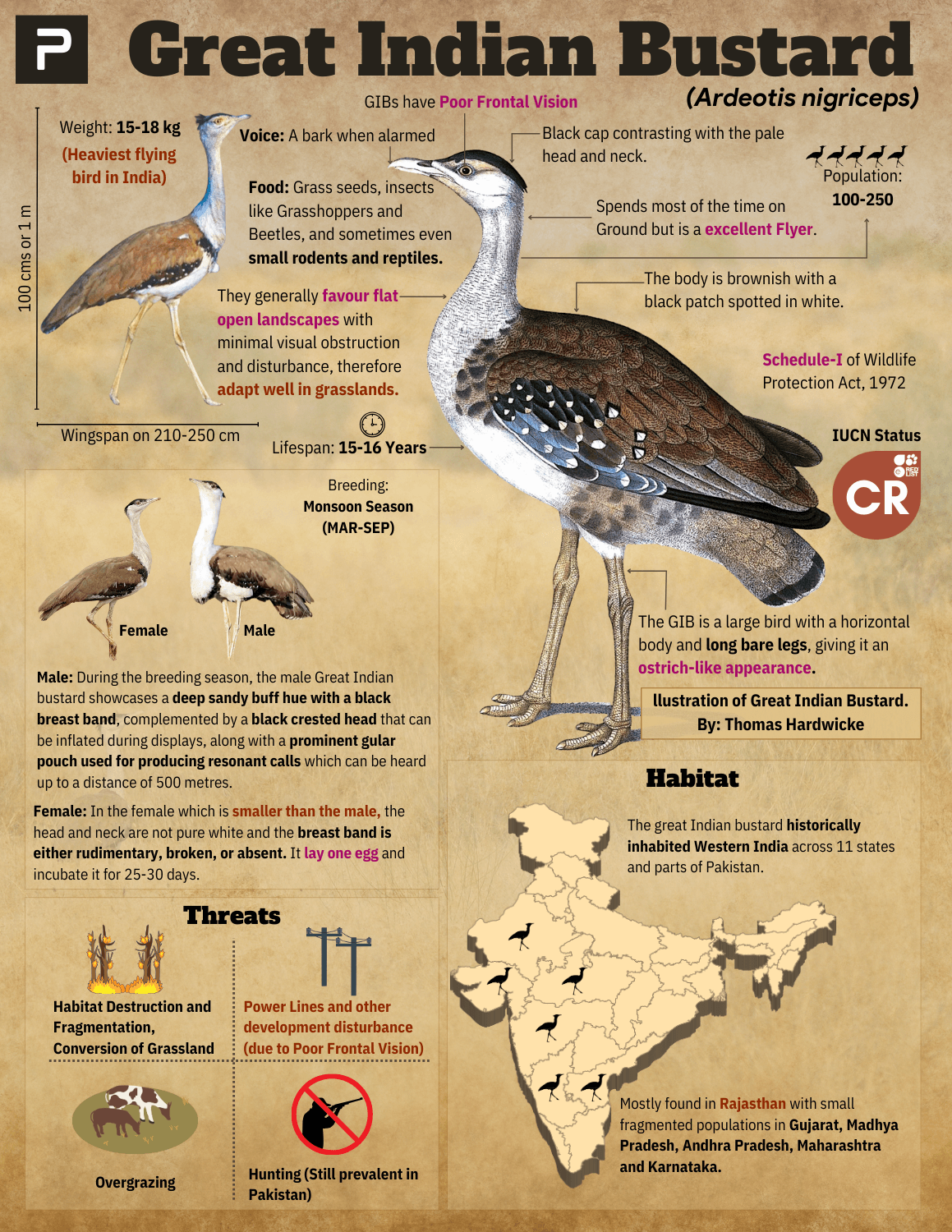
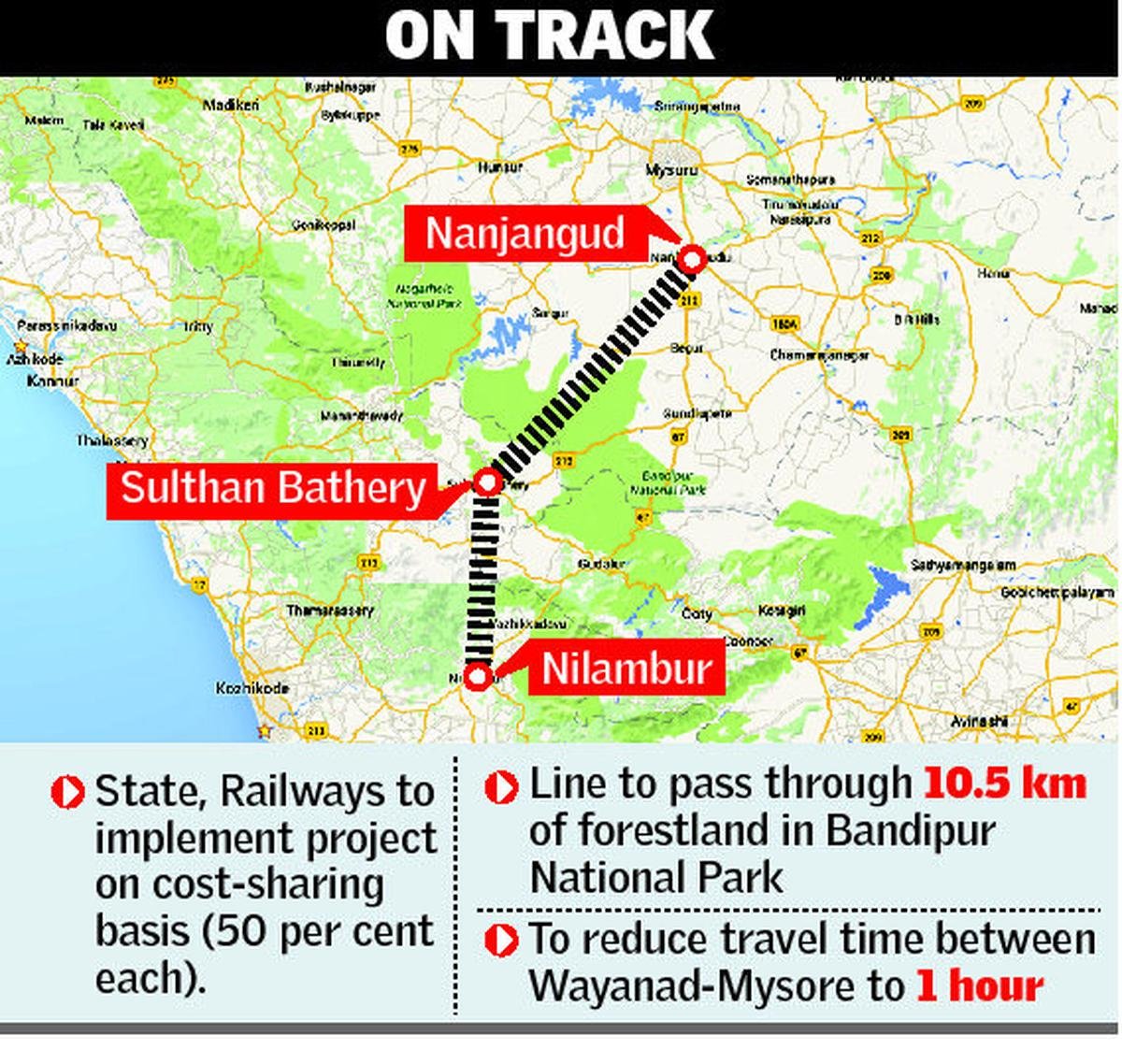
Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI)
- GPAI is a multi-stakeholder initiative bridging the gap between AI theory and practice through research and applied activities on AI priorities.
- It will bring experts from industry, civil society, governments, and academia to promote the responsible evolution of AI.
- It is built around a shared commitment to the OECD Recommendation on AI.
- Initially, it will work on four themes:
- Responsible AI
- Data Governance
- Future of Work
- Innovation and Commercialisation
- Its founding members are Australia, Canada, the European Union, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Mexico, New Zealand, Singapore, Slovenia, the UK and the US.
- Launched in 2020 with 15 members, GPAI’s membership now includes 28 countries and the EU.
- India became the Council Chair of the GPAI in November 2022 after France.
|
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
|
New Delhi Declaration
- In the 2023 summit. GPAI unanimously adopted the New Delhi Declaration, emphasising:
- Risk mitigation in AI development
- Equitable resource access for AI innovation
- The declaration acknowledges AI’s rapid advancement and recognises its potential for economic growth, innovation, job creation, and societal benefits.
- The declaration also flagged concerns about AI systems, including misinformation and bias, unemployment, intellectual property and personal data protection, threats to human rights and democratic values, deepfakes, cybersecurity, and cyber-terrorism.
- It also agreed to support AI innovation in agriculture as a new “thematic priority”.
- It said that GPAI will aim for diverse membership, prioritising low and middle-income countries.
How does the New Delhi Declaration contrast with the Bletchley Declaration?
- The world’s first AI Safety Summit was held at Bletchley Park in the UK in 2023.
- At the summit, the Bletchley Park Declaration was signed to minimise risks from ‘frontier AI’.
- Thus, the centre of the Bletchley Declaration was security and safety risks related to AI.
- In contrast, the New Delhi Declaration found a middle path between promoting and regulating AI.
- It addresses AI risks but strongly supports innovation in various sectors like agriculture and healthcare.
Frontier AI
|
Change in India’s Position in AI Regulation
- India shifted from its view of no AI legal intervention to actively formulating regulations based on a “risk-based, user-harm” approach.
- Though the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) acknowledged AI’s ethical and associated risks, it did not consider any law to regulate the AI sector.
- However, after deepfakes of popular personalities gained traction (e.g., actress Rashmika Mandana’s video), MeitY is considering concrete legislative steps to address AI-based misinformation.
- At the GPAI Summit, PM flagged AI’s dual potential as a development as well as a destructive tool.
- He called for a global framework to provide guardrails and ensure its responsible use.
How does the New Delhi Declaration Favour India’s Aspiration for Sovereign AI?
- The declaration supports India’s intention, as Lead Chair for 2024, to endorse efforts to foster collaborative AI for global partnership among GPAI members.
- This is a significant win for India, which has advocated a collaborative approach to building AI systems to push its Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) model worldwide.
- Besides, access to member nations’ computing capabilities will also boost India’s plans to build a sovereign AI system.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
India’s DPI Approach |




![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)