GPS Based Toll Collection
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
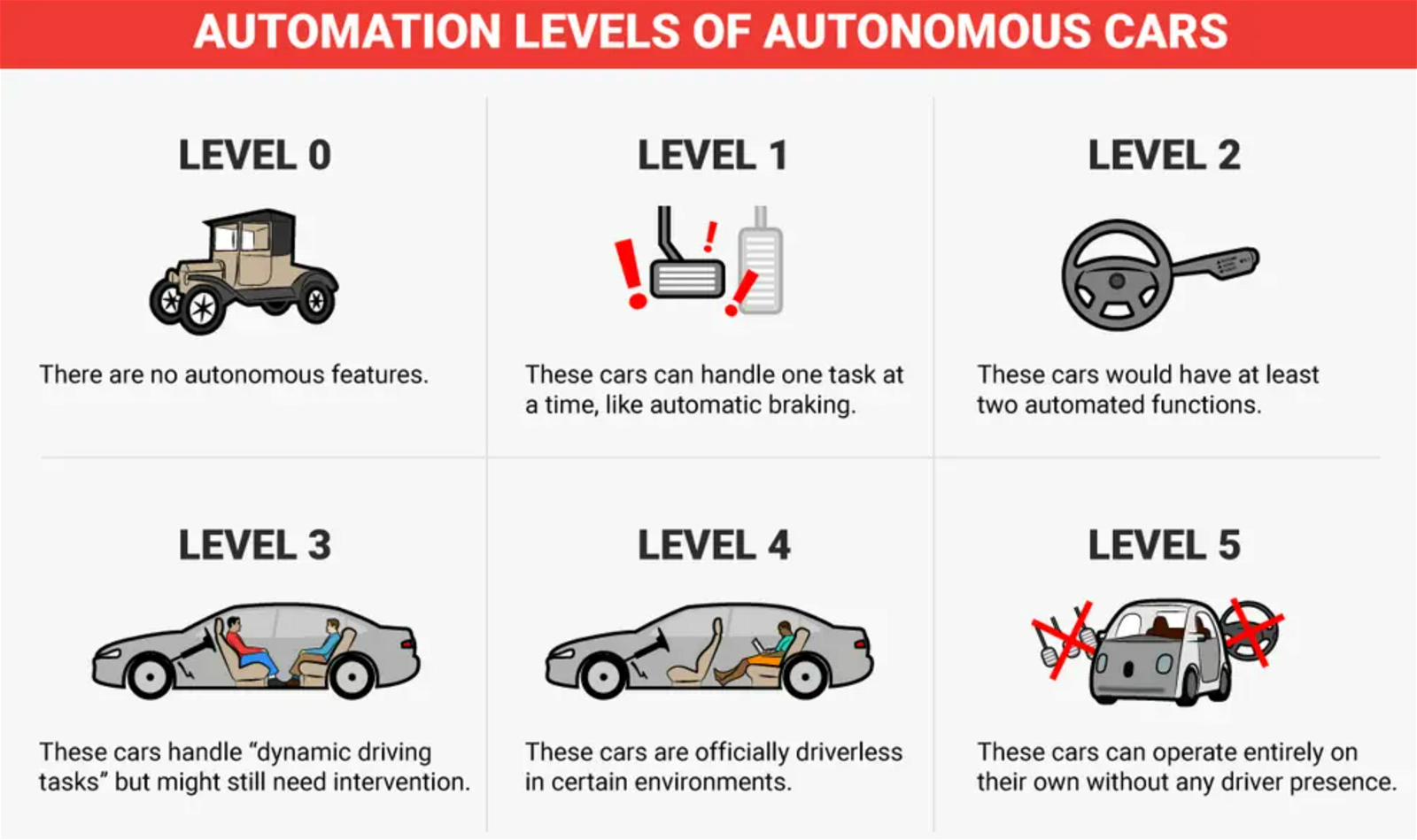
- Context (Swarajya): NHAI is set to launch GPS-based toll collection on various routes throughout the country. It is set to replace the current FASTag system.
How does a GPS-based tolling system operate?
- GPS Tracker: Vehicles get a tracking device for movement monitoring.
- Geofencing: Highways will be geo-fenced, creating virtual boundaries.
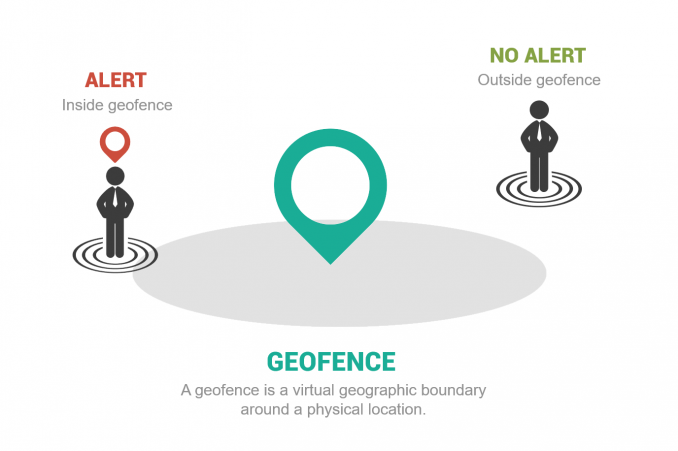
- To set up a geo-fencing service, an administrator employs GPS– or RFID-enabled software to establish a virtual boundary around a specified location.
- Software detects mobile devices entering or leaving areas.
- Tolls are charged based on distance at highway exits.
- No toll plaza stops are required, thanks to sensor-based technology.
- Users must register vehicles and link them to bank accounts for toll payments.
- Concerns: Privacy issues as the system tracks the precise location of vehicles.
- Alternative approach: Automatic number plate recognition cameras for tracking vehicle entry and exit, eliminating the need for GPS devices and allowing toll collection on the go.
- Countries: it has already been implemented in several countries including Germany and Singapore.
What is Geofencing?
- Geofencing is the usage of a virtual geographic boundary around a physical location, which allows users to detect when someone enters or leaves a location.
- Geo-fencing services are also used by enterprises to automate attendance, timecards, monitor employees in the field, and keep track of company property.
- Geo-fencing work on Jaipur-Delhi-Agra e-highway is being implemented by various geospatial tech companies in association with National Highways on pilot basis.





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)